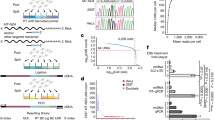
Abstract
Background
We aim to report two unrelated patients with pulmonary surfactant dysfunction (PSD) that carried two novel NKX2-1 frameshift variants, and evaluated the impact of these variants in vitro.
Methods
We enrolled children with PSD and NKX2-1 variants, and collected their clinical information and follow-up data. We constructed wild-type (WT) and variant NKX2-1 plasmids and transfected them into A549 and HEK293T cells. The functional characterization of variants was then evaluated by qRT-PCR, western blot, immunofluorescence, electrophoretic mobility shift assay, and dual-luciferase reporter assay.
Results
Two novel heterozygous frameshift variants of NKX2-1, i.e., c.705delC (Gly236Alafs*29) and c.313_316 dup (Asn106Lysfs*304), were identified in children from two unrelated families. We discerned attenuated mRNA and protein expression in the Asn106Lysfs*304 variant, and reduced DNA -binding as well as transcriptional activation capabilities in both variants. While the Asn106Lysfs*304 variant lost its synergistic interactions with PAX8 and TAZ, the Gly236Alafs*29 variant partially retained its residual transcriptional activation capabilities and synergistic interactions with PAX8 and TAZ.
Conclusions
We reported on two children with two novel NKX2-1 frameshift variants. In vitro experiments revealed that the two frameshift variants have common and different mechanisms based on the loss or conservation of domains, which partially explained the phenotypical heterogeneity.
Impact
-
Pulmonary surfactant dysfunction is a rare heterogeneous disease that exhibits a great burden on children’s quality of life.
-
We reported two novel NKX2-1 frameshift variants carried by two children with different clinical phenotypes, thus broadening our knowledge base of gene variations and phenotypes in NKX2-1.
-
We performed an in vitro study and uncovered different pathogenic mechanisms underlying the actions of two novel variants, and thereby partially explained the mechanisms of phenotypical heterogeneity caused by NKX2-1 variants.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 14 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $18.50 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bush, A. et al. European protocols for the diagnosis and initial treatment of interstitial lung disease in children. Thorax 70, 1078–1084 (2015).
Kurland, G. et al. An official American thoracic society clinical practice guideline: Classification, evaluation, and management of childhood interstitial lung disease in infancy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 188, 376–394 (2013).
Yonker, L. M. & Kinane, T. B. Pediatric interstitial lung disease: thyroid transcription Factor-1 mutations and their phenotype potpourri. Chest 144, 728–730 (2013).
Nogee, L. M., de Mello, D. E., Dehner, L. P. & Colten, H. R. Brief report: deficiency of pulmonary surfactant protein B in congenital alveolar proteinosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 328, 406–410 (1993).
Trueba, S. S. et al. Pax8, Titf1, and Foxe1 gene expression patterns during human development: new insights into human thyroid development and thyroid dysgenesis-associated malformations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90, 455–462 (2005).
Guazzi, S. et al. Thyroid Nuclear Factor 1 (Ttf-1) Contains a Homeodomain and Displays a Novel DNA Binding Specificity. Embo J. 9, 3631–3639 (1990).
Kolla, V. et al. Thyroid Transcription Factor in Differentiating Type Ii Cells: Regulation, Isoforms, and Target Genes. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 36, 213–225 (2007).
Toonen, R. F., Gowan, S. & Bingle, C. D. The Lung Enriched Transcription Factor Ttf-1 and the Ubiquitously Expressed Proteins Sp1 and Sp3 Interact with Elements Located in the Minimal Promoter of the Rat Clara Cell Secretory Protein Gene. Biochem J. 316, 467–473 (1996).
Guha, A. et al. Neuroepithelial Body Microenvironment Is a Niche for a Distinct Subset of Clara-Like Precursors in the Developing Airways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 12592–12597 (2012).
Silberschmidt, D. et al. In vivo role of different domains and of phosphorylation in the transcription Factor Nkx2-1. BMC Dev. Biol. 11, 9 (2011).
Park, K. S. et al. Taz Interacts with Ttf-1 and Regulates Expression of Surfactant Protein-C. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 17384–17390 (2004).
Martis, P. C. et al. C/Ebpalpha is required for lung maturation at birth. Development 133, 1155–1164 (2006).
Maeda, Y. et al. Parp-2 Interacts with Ttf-1 and regulates expression of surfactant Protein-B. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 9600–9606 (2006).
Lin, S., Perl, A. K. & Shannon, J. M. Erm/Thyroid Transcription Factor 1 Interactions Modulate Surfactant Protein C Transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 16716–16726 (2006).
Guillot, L. et al. Nkx2-1 mutations leading to surfactant protein promoter dysregulation cause interstitial lung disease in “Brain-Lung-Thyroid Syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 31, E1146–E1162 (2010).
Carré, A. et al. Five New Ttf1/Nkx2.1 mutations in brain-lung-thyroid syndrome: Rescue by Pax8 Synergism in One Case. Hum. Mol. Genet 18, 2266–2276 (2009).
Nettore, I. C. et al. Identification and functional characterization of a novel mutation in the Nkx2-1 Gene: comparison with the data in the literature. Thyroid 23, 675–682 (2013).
Hamvas, A. et al. Heterogeneous pulmonary phenotypes associated with mutations in the thyroid transcription factor Gene Nkx2-1. Chest 144, 794–804 (2013).
Moya, C. M. et al. Taz/Wwtr1 Mediates the Pulmonary Effects of Nkx2-1 Mutations in Brain-Lung-Thyroid Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 103, 839–852 (2018).
Hong, D. et al. A Novel Surfactant Protein C mutation resulting in aberrant protein processing and altered subcellular localization causes infantile interstitial lung disease. Pediatr. Res 81, 891–897 (2017).
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. & Coulson, A. R. DNA sequencing with Chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Ghaffari, M., Zeng, X., Whitsett, J. A. & Yan, C. Nuclear localization domain of thyroid transcription Factor-1 in respiratory epithelial cells. Biochem J. 328, 757–761 (1997).
Gras, D. et al. Benign Hereditary Chorea: Phenotype, Prognosis, Therapeutic Outcome and Long Term Follow-up in a Large Series with New Mutations in the Titf1/Nkx2-1 Gene. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 83, 956–962 (2012).
Thorwarth, A. et al. Comprehensive genotyping and clinical characterisation reveal 27 Novel Nkx2-1 mutations and expand the phenotypic spectrum. J. Med Genet. 51, 375–387 (2014).
Glik, A., Vuillaume, I., Devos, D. & Inzelberg, R. Psychosis, short stature in Benign hereditary chorea: A Novel thyroid transcription Factor-1 Mutation. Mov. disord. 23, 1744–1747 (2008).
Wright, J. R. Immunomodulatory Functions of Surfactant. Physiol. Rev. 77, 931–962 (1997).
Li, G. et al. Surfactant Protein-a–Deficient mice display an exaggerated early inflammatory response to a beta-resistant strain of influenza a virus. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 26, 277–282 (2002).
LeVine, A. M. et al. Surfactant Protein-a-Deficient Mice Are Susceptible to Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 19, 700–708 (1998).
LeVine, A. M. et al. Surfactant Protein a-Deficient Mice Are Susceptible to Group B Streptococcal Infection. J. Immunol. 158, 4336–4340 (1997).
Shinohara, H. et al. A novel mutation in Nkx2-1 shows dominant-negative effects only in the presence of Pax8. Thyroid 28, 1071–1073 (2018).
Di Palma, T. et al. Taz Is a Coactivator for Pax8 and Ttf-1, Two Transcription Factors Involved in Thyroid Differentiation. Exp. Cell Res. 315, 162–175 (2009).
Di Palma, T. et al. The paired domain-containing factor Pax8 and the Homeodomain-containing factor Ttf-1 directly interact and synergistically activate transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 3395–3402 (2003).
Nattes, E. et al. Heterogeneity of lung disease associated with Nk2 homeobox 1 mutations. Respir. Med. 129, 16–23 (2017).
Wambach, J. A. et al. Genotype-phenotype correlations for infants and children with Abca3 deficiency. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 189, 1538–1543 (2014).
Hong, D. et al. Clinical and Genetic Spectrum of Interstitial Lung Disease in Chinese Children Associated with Surfactant Protein C Mutations. Ital. J. Pediatr. 45, 117 (2019).
Safi, K. H. et al. Interstitial lung disease of infancy caused by a new Nkx2-1 mutation. Clin. Case Rep. 5, 739–743 (2017).
Konishi, T. et al. Benign hereditary chorea: dopaminergic brain imaging in patients with a Novel Intronic Nkx2.1 Gene Mutation. J. Neurol. 260, 207–213 (2013).
Riordan, J. D. & Nadeau, J. H. From peas to disease: modifier genes, network resilience, and the genetics of health. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 101, 177–191 (2017).
Morris, C., Cluet, D. & Ricci, E. P. Ribosome dynamics and mRNA turnover, a complex relationship under constant cellular scrutiny. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 12, e1658 (2021).
Muñoz, O., Lore, M. & Jagannathan, S. The Long and Short of Ejc-Independent Nonsense-Mediated Rna Decay. Biochem Soc. Trans. 51, 1121–1129 (2023).
Müller, M. B. D., Kasturi, P., Jayaraj, G. G. & Hartl, F. U. Mechanisms of readthrough mitigation reveal principles of Gcn1-mediated translational quality control. Cell 186, 3227–3244.e3220 (2023).
De Felice, M., Damante, G., Zannini, M., Francis-Lang, H., & Di Lauro, R. Redundant Domains contribute to the transcriptional activity of the thyroid transcription Factor 1. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 26649–26656 (1995).
Delestrain, C. et al. Deciphering an isolated lung phenotype of Nkx2-1 Frameshift pathogenic variant. Front Pediatr. 10, 978598 (2022).
Flamein, F. et al. Molecular and cellular characteristics of Abca3 mutations associated with diffuse parenchymal lung diseases in children. Hum. Mol. Genet. 21, 765–775 (2012).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the patients and their families involved in this study.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82171707) and the Key Projects of the Natural Science Foundation from Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology (No. 2022D012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
(I) Substantial contributions to conception and design: H.W., L.Q.; (II) Acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data: H.W., G.J., D.D., D.H., W.Z., L.Q.; (III) Drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content: H.W., L.Q.; (IV) Final approval of the version to be published: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the ethics committees of Children’s Hospital of Fudan University. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s guardian.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Jiang, G., Dai, D. et al. Functional characterization of two novel NKX2-1 frameshift variants that cause pulmonary surfactant dysfunction. Pediatr Res 95, 744–751 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-023-02882-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-023-02882-x