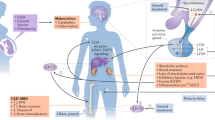
Abstract
Background
The effect of recombinant human GH (rhGH) in Chinese children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is unclear.
Methods
This was a 52-week, multicenter, randomized, open-label, negative-controlled phase 3 study. Prepubertal subjects were randomized 1:1 to either daily subcutaneous injections of rhGH 0.05 mg/kg/day or no treatment for 52 weeks.
Results
A total of 68 subjects with a mean age of 7.8 ± 3.27 years were enrolled. At week 52, the height standard deviation score (HT-SDS) in the treated group increased by 0.75 ± 0.58, which was significantly higher compared with 0.17 ± 0.47 in the untreated group (least squares mean 0.58, 95% confidence interval, 0.32–0.84; P < 0.001). At week 52, significant improvements were observed in other growth parameters (height velocity [P < 0.001]), insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) SDS [P < 0.001], IFG-1/insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 molar ratio [P < 0.001], and height [P < 0.001]) compared with the untreated control. Seven patients reported treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) and most TRAEs were mild in severity. Most subjects recovered without further intervention.
Conclusions
Daily rhGH for 52 weeks in children with CKD-induced growth retardation significantly improved HT-SDS and other growth parameters without compromising safety.
Impact
-
The efficacy and safety of growth hormone (GH) therapy in Chinese children with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are unclear.
-
This study found that giving short stature Chinese children with CKD daily recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) for 52 weeks improved growth parameters without compromising safety.
-
This study’s information can give physicians the confidence to treat these patients in their clinical practice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 14 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $18.50 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due individual privacy of clinical trial participants should be protected but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Janjua, H. S. & Mahan, J. D. Growth in chronic kidney disease. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 18, 324–331 (2011).
Mahan, J. D. et al. Assessment and treatment of short stature in pediatric patients with chronic kidney disease: a consensus statement. Pediatr. Nephrol. 21, 917–930 (2006).
Tonshoff, B., Kiepe, D. & Ciarmatori, S. Growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor system in children with chronic renal failure. Pediatr. Nephrol. 20, 279–289 (2005).
Roelfsema, V. & Clark, R. G. The growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor axis: its manipulation for the benefit of growth disorders in renal failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 12, 1297–306. (2001).
Drube, J. et al. Clinical practice recommendations for growth hormone treatment in children with chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 15, 577–89. (2019).
Fine, R. N., Attie, K. M., Kuntze, J., Brown, D. F. & Kohaut, E. C. Recombinant human growth hormone in infants and young children with chronic renal insufficiency. Genentech Collaborative Study Group. Pediatr. Nephrol. 9, 451–457 (1995).
Fine, R. N., Kohaut, E., Brown, D., Kuntze, J. & Attie, K. M. Long-term treatment of growth retarded children with chronic renal insufficiency, with recombinant human growth hormone. Kidney Int. 49, 781–785 (1996).
Fine, R. N., Kohaut, E. C., Brown, D. & Perlman, A. J. Growth after recombinant human growth hormone treatment in children with chronic renal failure: report of a multicenter randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Genentech Cooperative Study Group. J. Pediatr. 124, 374–382 (1994).
Pozzo, A. M. & Kemp, S. F. Growth and growth hormone treatment in children with chronic diseases. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 41, 747–759 (2012).
Group, K. W. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in Children with CKD: 2008 update. Executive summary. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 53, S11–S104 (2009).
Li, H., Ji, C. Y., Zong, X. N. & Zhang, Y. Q. [Height and weight standardized growth charts for Chinese children and adolescents aged 0 to 18 years]. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi 47, 487–492 (2009).
Hodson, E. M., Willis, N. S. & Craig, J. C. Growth hormone for children with chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, CD003264 (2012).
Hertel, N. T. et al. Recombinant human growth hormone treatment, using two dose regimens in children with chronic renal failure-a report on linear growth and adverse effects. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 15, 577–588 (2002).
Kuizon, B. D. & Salusky, I. B. Growth retardation in children with chronic renal failure. J. Bone Min. Res 14, 1680–1690 (1999).
Kitagawa, T. et al. GH treatment of children with chronic renal insufficiency: a Japanese clinical trial. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 6, 73–80 (1997).
Haffner, D. et al. Effect of growth hormone treatment on the adult height of children with chronic renal failure. German Study Group for Growth Hormone Treatment in Chronic Renal Failure. N. Engl. J. Med 343, 923–930 (2000).
Hokken-Koelega, A. et al. Long-term effects of growth hormone treatment on growth and puberty in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. Pediatr. Nephrol. 14, 701–706 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the patients who participated in this study and their families and all personnel at each study site who cared for the patients and coordinated with the sponsor to make this trial possible. We thank Feihong Luo and Ruoqian Cheng of Children’s Hospital of Fudan University for Tanner stage assessment, and Ping Yin of Huazhong University of Science and Technology for assisting the statistical work. We thank Mengmeng Chen of GeneScience Pharmaceuticals for editorial assistance; Lawrence Law of Parexel for medical writing support.
Funding
This research was funded by GeneScience Pharmaceuticals. The funder was involved in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis; review of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors meet all four of the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors’ (ICMJE) criteria for authorship: • Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; • Drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content; • Final approval of the version to be published; • Agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. X.T., Q.C. drafted the initial manuscript, carried out the initial analyses and and revised the manuscript. H.X., X.L., W.H., C.C., Y.W., J.M., X.N., C.L., Y.L., J.Z., M.W. revised the manuscript for important intellectual content. Z.Y., J.C., X.F., F.Z., P.W., L.S., K.X., Z.C., J.T., X.W., Z.L., J.W., J.H., G.C., Y.Z., H.Y. offered administrative, technical, or material support. A.Z., M.W. obtained the study funding. Q.S. and H.X. conceptualized and designed the study, had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained prior to the patient entering the study. The investigators explained the nature, purpose, and risks of the study to each patient/guardian. Each patient/guardian was informed that he/she could withdraw from the study at any time and for any reason. Each patient/guardian was given sufficient time to consider the implications of the study before deciding whether to participate. Patients/guardians who chose to participate signed an informed consent document.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Chen, Q., Chen, J. et al. Growth hormone treatment in pre-pubertal short Chinese children with chronic kidney disease prior to transplantation. Pediatr Res 94, 268–274 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-022-02429-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-022-02429-6