Abstract
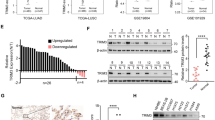
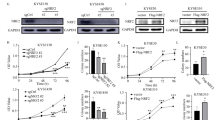
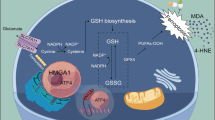
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a prevalent malignancy of the digestive system. Hypoxia is a crucial player in tumor ferroptosis resistance. However, the molecular mechanism of hypoxia-mediated ferroptosis resistance in ESCC remains unclear. Here, USP2 expression was decreased in ESCC cell lines subjected to hypoxia treatment and was lowly expressed in clinical ESCC specimens. Ubiquitin-specific protease 2 (USP2) depletion facilitated cell growth, which was blocked in USP2-overexpressing cells. Moreover, USP2 silencing enhanced the iron ion concentration and lipid peroxidation accumulation as well as suppressed ferroptosis, while upregulating USP2 promoted ferroptotic cell death in ESCC cells. Furthermore, knockout of USP2 in ESCC models discloses the essential role of USP2 in promoting ESCC tumorigenesis and inhibiting ferroptosis. In contrast, overexpression of USP2 contributes to antitumor effect and ferroptosis events in vivo. Specifically, USP2 stably bound to and suppressed the degradation of nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4) by eliminating the Lys48-linked chain, which in turn triggered ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in ESCC cells. Our findings suggest that USP2 plays a crucial role in iron metabolism and ferroptosis and that the USP2/NCOA4 axis is a promising therapeutic target for the management of ESCC.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.
Abnet CC, Arnold M, Wei WQ. Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:360–73.
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2241–52.
Zhu H, Ma X, Ye T, Wang H, Wang Z, Liu Q, et al. Esophageal cancer in China: practice and research in the new era. Int J Cancer. 2023;152:1741–51.
Jing X, Yang F, Shao C, Wei K, Xie M, Shen H, et al. Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:157.
Wicks EE, Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factors: cancer progression and clinical translation. J Clin Invest. 2022;132:e159839.
Ivan M, Fishel ML, Tudoran OM, Pollok KE, Wu X, Smith PJ. Hypoxia signaling: challenges and opportunities for cancer therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;85:185–95.
Lin Z, Song J, Gao Y, Huang S, Dou R, Zhong P, et al. Hypoxia-induced HIF-1α/lncRNA-PMAN inhibits ferroptosis by promoting the cytoplasmic translocation of ELAVL1 in peritoneal dissemination from gastric cancer. Redox Biol. 2022;52:102312.
Xiong J, Nie M, Fu C, Chai X, Zhang Y, He L, et al. Hypoxia enhances HIF1α transcription activity by upregulating KDM4A and mediating H3K9me3, thus inducing ferroptosis resistance in cervical cancer cells. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:1608806.
Fan Z, Yang G, Zhang W, Liu Q, Liu G, Liu P, et al. Hypoxia blocks ferroptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via suppression of METTL14 triggered YTHDF2-dependent silencing of SLC7A11. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:10197–212.
Lei G, Zhuang L, Gan B. Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22:381–96.
Mou Y, Wang J, Wu J, He D, Zhang C, Duan C, et al. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: opportunities and challenges in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:34.
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18:280–96.
Liang C, Zhang X, Yang M, Dong X. Recent progress in ferroptosis inducers for cancer therapy. Adv Mater. 2019;31:e1904197.
Tang D, Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31:107–25.
Ajoolabady A, Aslkhodapasandhokmabad H, Libby P, Tuomilehto J, Lip GYH, Penninger JM, et al. Ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in the management of metabolic diseases. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2021;32:444–62.
Friedmann Angeli JP, Krysko DV, Conrad M. Ferroptosis at the crossroads of cancer-acquired drug resistance and immune evasion. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019;19:405–14.
Rodriguez R, Schreiber SL, Conrad M. Persister cancer cells: Iron addiction and vulnerability to ferroptosis. Mol Cell. 2022;82:728–40.
Tu Y, Xu L, Xu J, Bao Z, Tian W, Ye Y, et al. Loss of deubiquitylase USP2 triggers development of glioblastoma via TGF-β signaling,. Oncogene. 2022;41:2597–608.
Zhu L, Chen Z, Guo T, Chen W, Zhao L, Guo L, et al. USP2 Inhibits Lung Cancer Pathogenesis by Reducing ARID2 Protein Degradation via Ubiquitination. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:1525216.
Xiao W, Wang J, Wang X, Cai S, Guo Y, Ye L, et al. Therapeutic targeting of the USP2-E2F4 axis inhibits autophagic machinery essential for zinc homeostasis in cancer progression. Autophagy. 2022;18:2615–35.
Gao M, Monian P, Pan Q, Zhang W, Xiang J, Jiang X. Ferroptosis is an autophagic cell death process. Cell Res. 2016;26:1021–32.
Zhou B, Liu J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Kroemer G, Tang D. Ferroptosis is a type of autophagy-dependent cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;66:89–100.
Mennerich D, Kubaichuk K, Kietzmann T. DUBs, hypoxia, and cancer. Trends Cancer. 2019;5:632–53.
Yang H, Hu Y, Weng M, Liu X, Wan P, Hu Y, et al. Hypoxia inducible lncRNA-CBSLR modulates ferroptosis through m6A-YTHDF2-dependent modulation of CBS in gastric cancer. J Adv Res. 2022;37:91–106.
Sun S, Guo C, Gao T, Ma D, Su X, Pang Q, et al. Hypoxia enhances glioma resistance to sulfasalazine-induced ferroptosis by upregulating SLC7A11 via PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α axis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:7862430.
Chen Z, Han F, Du Y, Shi H, Zhou W. Hypoxic microenvironment in cancer: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8:70.
Liao C, Liu X, Zhang C, Zhang Q. Tumor hypoxia: from basic knowledge to therapeutic implications. Semin Cancer Biol. 2023;88:172–86.
Tang Z, Jiang W, Mao M, Zhao J, Chen J, Cheng N. Deubiquitinase USP35 modulates ferroptosis in lung cancer via targeting ferroportin. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11:e390.
Meng C, Zhan J, Chen D, Shao G, Zhang H, Gu W, et al. The deubiquitinase USP11 regulates cell proliferation and ferroptotic cell death via stabilization of NRF2 USP11 deubiquitinates and stabilizes NRF2. Oncogene. 2021;40:1706–20.
Hou W, Xie Y, Song X, Sun X, Lotze MT, Zeh HJ 3rd, et al. Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin. Autophagy. 2016;12:1425–8.
Jain V, Amaravadi RK. Pumping iron: ferritinophagy promotes survival and therapy resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:2023–5.
Mancias JD, Wang X, Gygi SP, Harper JW, Kimmelman AC. Quantitative proteomics identifies NCOA4 as the cargo receptor mediating ferritinophagy. Nature. 2014;509:105–9.
Li C, Zhang J, Xu H, Chang M, Lv C, Xue W, et al. Retigabine ameliorates acute stress-induced impairment of spatial memory retrieval through regulating USP2 signaling pathways in hippocampal CA1 area. Neuropharmacology. 2018;135:151–62.
Latunde-Dada GO. Ferroptosis: Role of lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861:1893–1900.
Li K, Chen B, Xu A, Shen J, Li K, Hao K, et al. TRIM7 modulates NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in glioblastoma cells. Redox Biol. 2022;56:102451.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Core Facility of Jiangsu Provincial People’s Hospital for its help in the detection of experimental samples.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20201080), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82003228, 82003235, 82102830, 82102831), and the Research project of clinical medical science and technology development fund of Jiangsu University (No:JLY2021097), and the Court-level Natural Science Foundation Project of Jurong People’s Hospital (Nos. JY20221001, JY20231005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JS, XD, JZ and QL contributed to the design of the study. JS, JZ, YS, and QG performed the experiments. HC, MZ, CZ and LL analyzed and interpreted the data. JZ, YZ and WW prepared all figures. JS, XD, JZ and QL contributed to the writing and revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Zhang, J., Shi, Y. et al. Hypoxia inhibits ferritinophagy-mediated ferroptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via the USP2-NCOA4 axis. Oncogene (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-024-03050-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-024-03050-z