Abstract
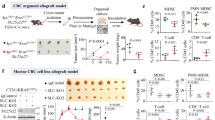
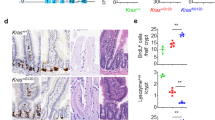
Childhood onset of colorectal signet-ring cell carcinoma (CR-SRCC) is extremely rare and featured as highly malignant with poor prognosis. Here we reported a CR-SRCC case of 11-year-old boy with a novel inherited X-linked KDM6AA694T mutation. The H3K27me3 demethylase KDM6A was frequently mutated in varieties of tumors and acts as a tumor suppressor. In vivo H3K27me3 demethylation assay demonstrated that KDM6AA694T had dampened H3K27me3 demethylase activity. Overexpression of KDM6AA694T in SRCC cell line KATO3 promoted cell proliferation, invasion and migration, which were further confirmed in vivo by constructing orthotopic tumor growth and lung metastasis model. Besides, expression of KDM6AA694T in immune cells suppresses inflammatory macrophage response and effector T cell response. In conclusion, we characterized a novel inherited KDM6AA694T mutant from a childhood-onset SRCC case and demonstrated that the mutant with impaired H3K27me3 demethylase activity could potentiate tumor malignancy and suppress antitumor immunity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw sequencing data have been deposited in the Chinese National Genomics Data Center (accession code HRA002692).
References
Shu Y, Zhang W, Hou Q, Zhao L, Zhang S, Zhou J, et al. Prognostic significance of frequent CLDN18-ARHGAP26/6 fusion in gastric signet-ring cell cancer. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2447.
Benesch MGK, Mathieson A. Epidemiology of signet ring cell adenocarcinomas. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12:1544.
Cancer Genome Atlas N. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature. 2012;487:330–7.
Korphaisarn K, Morris V, Davis JS, Overman MJ, Fogelman DR, Kee BK, et al. Signet ring cell colorectal cancer: genomic insights into a rare subpopulation of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2019;121:505–10.
Nam JY, Oh BY, Hong HK, Bae JS, Kim TW, Ha SY, et al. Molecular characterization of colorectal signet-ring cell carcinoma using whole-exome and RNA sequencing. Transl Oncol. 2018;11:836–44.
Li Y, Li J, Wang R, Zhang L, Fu G, Wang X, et al. Frequent RNF43 mutation contributes to moderate activation of Wnt signaling in colorectal signet-ring cell carcinoma. Protein Cell. 2020;11:292–8.
Alvi MA, Loughrey MB, Dunne P, McQuaid S, Turkington R, Fuchs MA, et al. Molecular profiling of signet ring cell colorectal cancer provides a strong rationale for genomic targeted and immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies. Br J Cancer. 2017;117:203–9.
Huang S, Wang Z, Zhou J, Huang J, Zhou L, Luo J, et al. EZH2 inhibitor GSK126 suppresses antitumor immunity by driving production of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Res. 2019;79:2009–20.
Revia S, Seretny A, Wendler L, Banito A, Eckert C, Breuer K, et al. Histone H3K27 demethylase KDM6A is an epigenetic gatekeeper of mTORC1 signalling in cancer. Gut. 2022;71:1613–28.
Kong N, Zhang R, Wu G, Sui X, Wang J, Kim NY, et al. Intravesical delivery of KDM6A-mRNA via mucoadhesive nanoparticles inhibits the metastasis of bladder cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2022;119:e2112696119.
Kalisz M, Bernardo E, Beucher A, Maestro MA, Del Pozo N, Millán I, et al. HNF1A recruits KDM6A to activate differentiated acinar cell programs that suppress pancreatic cancer. EMBO J. 2020;39:e102808.
Stief SM, Hanneforth AL, Weser S, Mattes R, Carlet M, Liu WH, et al. Loss of KDM6A confers drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2020;34:50–62.
Bosselut R. Pleiotropic functions of H3K27Me3 demethylases in immune cell differentiation. Trends Immunol. 2016;37:102–13.
Manna S, Kim JK, Bauge C, Cam M, Zhao Y, Shetty J, et al. Histone H3 Lysine 27 demethylases Jmjd3 and Utx are required for T-cell differentiation. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8152.
Northrup D, Yagi R, Cui K, Proctor WR, Wang C, Placek K, et al. Histone demethylases UTX and JMJD3 are required for NKT cell development in mice. Cell Biosci. 2017;7:25.
Cook KD, Shpargel KB, Starmer J, Whitfield-Larry F, Conley B, Allard DE, et al. T follicular helper cell-dependent clearance of a persistent virus infection requires T cell expression of the histone demethylase UTX. Immunity. 2015;43:703–14.
Itoh Y, Golden LC, Itoh N, Matsukawa MA, Ren E, Tse V, et al. The X-linked histone demethylase Kdm6a in CD4+ T lymphocytes modulates autoimmunity. J Clin Investig. 2019;129:3852–63.
Gao J, Gu J, Pan X, Gan X, Ju Z, Zhang S, et al. Blockade of miR-142-3p promotes anti-apoptotic and suppressive function by inducing KDM6A-mediated H3K27me3 demethylation in induced regulatory T cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:332.
Li X, Zhang Q, Shi Q, Liu Y, Zhao K, Shen Q, et al. Demethylase Kdm6a epigenetically promotes IL-6 and IFN-beta production in macrophages. J Autoimmun. 2017;80:85–94.
Chen J, Xu X, Li Y, Li F, Zhang J, Xu Q, et al. Kdm6a suppresses the alternative activation of macrophages and impairs energy expenditure in obesity. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28:1688–704.
Kobatake K, Ikeda KI, Nakata Y, Yamasaki N, Ueda T, Kanai A, et al. Kdm6a deficiency activates inflammatory pathways, promotes M2 macrophage polarization, and causes bladder cancer in cooperation with p53 dysfunction. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26:2065–79.
Kim KH, Roberts CW. Targeting EZH2 in cancer. Nat Med. 2016;22:128–34.
Schulz WA, Lang A, Koch J, Greife A. The histone demethylase UTX/KDM6A in cancer: progress and puzzles. Int J Cancer. 2019;145:614–20.
Rodriguez-Vida A, Lerner SP, Bellmunt J. The cancer genome atlas project in bladder cancer. Cancer Treat Res. 2018;175:259–71.
Wilcox AN, Silverman DT, Friesen MC, Locke SJ, Russ DE, Hyun N, et al. Smoking status, usual adult occupation, and risk of recurrent urothelial bladder carcinoma: data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Project. Cancer Causes Control. 2016;27:1429–35.
Wang L, Shilatifard A. UTX mutations in human cancer. Cancer Cell. 2019;35:168–76.
Revia S, Seretny A, Wendler L, Banito A, Eckert C, Breuer K, et al. Histone H3K27 demethylase KDM6A is an epigenetic gatekeeper of mTORC1 signalling in cancer. Gut. 2022;71:1613–1628.
Lee MG, Villa R, Trojer P, Norman J, Yan KP, Reinberg D, et al. Demethylation of H3K27 regulates polycomb recruitment and H2A ubiquitination. Science. 2007;318:447–50.
Ler LD, Ghosh S, Chai X, Thike AA, Heng HL, Siew EY, et al. Loss of tumor suppressor KDM6A amplifies PRC2-regulated transcriptional repression in bladder cancer and can be targeted through inhibition of EZH2. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9:eaai8312.
Liu Y, Qiu N, Shen L, Liu Q, Zhang J, Cheng YY, et al. Nanocarrier-mediated immunogenic chemotherapy for triple negative breast cancer. J Control Release. 2020;323:431–41.
Bhattacharya S, Ghosh A, Maiti S, Ahir M, Debnath GH, Gupta P, et al. Delivery of thymoquinone through hyaluronic acid-decorated mixed Pluronic® nanoparticles to attenuate angiogenesis and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer. J Control Release. 2020;322:357–74.
Ceccaldi R, Sarangi P, D’Andrea AD. The Fanconi anaemia pathway: new players and new functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17:337–49.
Cribbs AP, Terlecki-Zaniewicz S, Philpott M, Baardman J, Ahern D, Lindow M, et al. Histone H3K27me3 demethylases regulate human Th17 cell development and effector functions by impacting on metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:6056–66.
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, et al. Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med. 2004;10:942–9.
Shin HM, Kapoor VN, Kim G, Li P, Kim HR, Suresh M, et al. Transient expression of ZBTB32 in anti-viral CD8+ T cells limits the magnitude of the effector response and the generation of memory. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13:e1006544.
Li Y, Zhai P, Zheng Y, Zhang J, Kellum JA, Peng Z. Csf2 attenuated sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by promoting alternative macrophage transition. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1415.
Shi B, Li W, Song Y, Wang Z, Ju R, Ulman A, et al. UTX condensation underlies its tumour-suppressive activity. Nature. 2021;597:726–31.
Van der Meulen J, Sanghvi V, Mavrakis K, Durinck K, Fang F, Matthijssens F, et al. The H3K27me3 demethylase UTX is a gender-specific tumor suppressor in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2015;125:13–21.
Beke A, Laplane L, Riviere J, Yang Q, Torres-Martin M, Dayris T, et al. Multilayer intraclonal heterogeneity in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Haematologica. 2020;105:112–23.
Yi J, Shi X, Xuan Z, Wu J. Histone demethylase UTX/KDM6A enhances tumor immune cell recruitment, promotes differentiation and suppresses medulloblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2021;499:188–200.
Grasso CS, Wu YM, Robinson DR, Cao X, Dhanasekaran SM, Khan AP, et al. The mutational landscape of lethal castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature. 2012;487:239–43.
Dalgliesh GL, Furge K, Greenman C, Chen L, Bignell G, Butler A, et al. Systematic sequencing of renal carcinoma reveals inactivation of histone modifying genes. Nature. 2010;463:360–3.
Crompton JG, Sukumar M, Restifo NP. Uncoupling T-cell expansion from effector differentiation in cell-based immunotherapy. Immunol Rev. 2014;257:264–76.
Rao RC, Dou Y. Hijacked in cancer: the KMT2 (MLL) family of methyltransferases. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15:334–46.
Miller SA, Mohn SE, Weinmann AS. Jmjd3 and UTX play a demethylase-independent role in chromatin remodeling to regulate T-box family member-dependent gene expression. Mol Cell. 2010;40:594–605.
Gounder M, Schoffski P, Jones RL, Agulnik M, Cote GM, Villalobos VM, et al. Tazemetostat in advanced epithelioid sarcoma with loss of INI1/SMARCB1: an international, open-label, phase 2 basket study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:1423–32.
Piunti A, Meghani K, Yu Y, Robertson AG, Podojil JR, McLaughlin KA, et al. Immune activation is essential for the antitumor activity of EZH2 inhibition in urothelial carcinoma. Sci Adv. 2022;8:eabo8043.
Ying W, Cheruku PS, Bazer FW, Safe SH, Zhou B. Investigation of macrophage polarization using bone marrow derived macrophages. J Vis Exp. 2013;23:50323.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grant from National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070918 from JW), Outstanding Youth Fund of Guangdong Province (2022B1515020109 from JW), Start-up funding for the Pediatric Research Institute of Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center (3001082 from JW), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong (ZR202110280038 from MF), Postdoctoral Innovation Project of Shandong Province (SDCX-ZG-202203028 from MF) and Municipal School (College) Joint Funding Project (202201020594 from CC and 202201020591 from QW). Finally, we sincerely thank BioRender (https://biorender.com/) for the elements within the experimental design diagram and graphical abstract.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW, QW and CC conceived the study cooperatively. JW and MF designed the research strategy. QW, CC, YL, and HZ provided the human tissue and blood samples and necessary interpretation of the clinical data. MF, XH and WX performed most of the experiments and data analysis with the help from Xiaojiang Lai, Xiaojie Liu and WT. WT performed the pedigree analysis of WES sequencing data. NG and GP finished the work of filing and deposition of the human genetic data. JW, MF and WX wrote the manuscript with constructive suggestions from QW and CC.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, M., Chai, C., Hao, X. et al. Inherited KDM6AA649T facilitates tumor-immune escape and exacerbates colorectal signet-ring cell carcinoma outcomes. Oncogene (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-024-03029-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-024-03029-w