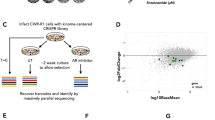
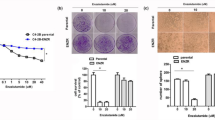
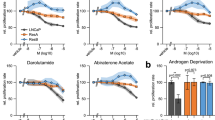
Abstract
Although enzalutamide improves the overall survival of patients with metastatic prostate cancers, enzalutamide resistance (ENZR) will be inevitably developed. Emerging evidence support that alternative oncogenic pathways may bypass the androgen receptor (AR) signaling to promote ENZR progression, however, the underpinning mechanisms remain poorly defined. Here, we report that the expression of RuvB like AAA ATPase 1 (RUVBL1) is upregulated in ENZR cells and xenograft models and prostate tumors in patients. Enzalutamide increases RUVBL1 accumulation in the cytoplasm, which in turn enhances the recruitment of CRAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase protein to plexin A1 (PLXNA1) and the subsequent activation of the downstream MAPK pathway. Co-overexpression of RUVBL1 and PLXNA1 defines a subgroup of prostate cancer (PCa) patients with a poor prognosis. Furthermore, pharmacological inhibition of RUVBL1 by CB-6644 suppresses ENZR cell proliferation and xenograft growth and allows re-sensitization of ENZR cells and xenografts to enzalutamide, indicating that RUVBL1 may act to substitute the AR signaling to promote cancer cell survival and ENZR development. Together, these findings may lead to the identification of RUVBL1 as a potential therapeutic target for ENZR tumors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watson PA, Arora VK, Sawyers CL. Emerging mechanisms of resistance to androgen receptor inhibitors in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15:701–11.
Tran C, Ouk S, Clegg NJ, Chen Y, Watson PA, Arora V, et al. Development of a second-generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Science. 2009;324:787–90.
Robinson D, Van Allen EM, Wu YM, Schultz N, Lonigro RJ, Mosquera JM, et al. Integrative clinical genomics of advanced prostate cancer. Cell. 2015;161:1215–28.
Mostaghel EA, Zhang A, Hernandez S, Marck BT, Zhang X, Tamae D, et al. Contribution of adrenal glands to intratumor androgens and growth of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:426–39.
Hu R, Dunn TA, Wei S, Isharwal S, Veltri RW, Humphreys E, et al. Ligand-independent androgen receptor variants derived from splicing of cryptic exons signify hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69:16–22.
He Y, Wei T, Ye Z, Orme JJ, Lin D, Sheng H, et al. A noncanonical AR addiction drives enzalutamide resistance in prostate cancer. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1521.
Arora VK, Schenkein E, Murali R, Subudhi SK, Wongvipat J, Balbas MD, et al. Glucocorticoid receptor confers resistance to antiandrogens by bypassing androgen receptor blockade. Cell. 2013;155:1309–22.
Carver BS, Chapinski C, Wongvipat J, Hieronymus H, Chen Y, Chandarlapaty S, et al. Reciprocal feedback regulation of PI3K and androgen receptor signaling in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2011;19:575–86.
Mulholland DJ, Tran LM, Li Y, Cai H, Morim A, Wang S, et al. Cell autonomous role of PTEN in regulating castration-resistant prostate cancer growth. Cancer Cell. 2011;19:792–804.
Bluemn EG, Coleman IM, Lucas JM, Coleman RT, Hernandez-Lopez S, Tharakan R, et al. Androgen receptor pathway-independent prostate cancer is sustained through FGF signaling. Cancer Cell. 2017;32:474–89.
Beltran H, Prandi D, Mosquera JM, Benelli M, Puca L, Cyrta J, et al. Divergent clonal evolution of castration-resistant neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Nat Med. 2016;22:298–305.
Mello T, Materozzi M, Zanieri F, Simeone I, Ceni E, Bereshchenko O, et al. Liver haploinsufficiency of RuvBL1 causes hepatic insulin resistance and enhances hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Int J Cancer. 2020;146:3410–22.
Fan W, Xie J, Xia J, Zhang Y, Yang M, Wang H, et al. RUVBL1-ITFG1 interaction is required for collective invasion in breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861:1788–1800.
Yenerall P, Das AK, Wang S, Kollipara RK, Li LS, Villalobos P, et al. RUVBL1/RUVBL2 ATPase activity drives PAQosome maturation, DNA replication and radioresistance in lung cancer. Cell Chem Biol. 2020;27:105–21.
Venteicher AS, Meng Z, Mason PJ, Veenstra TD, Artandi SE. Identification of ATPases pontin and reptin as telomerase components essential for holoenzyme assembly. Cell. 2008;132:945–57.
Huber O, Menard L, Haurie V, Nicou A, Taras D, Rosenbaum J. Pontin and reptin, two related ATPases with multiple roles in cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68:6873–6.
Chen J, Liu G, Wu Y, Ma J, Wu H, Xie Z, et al. CircMYO10 promotes osteosarcoma progression by regulating miR-370-3p/RUVBL1 axis to enhance the transcriptional activity of beta-catenin/LEF1 complex via effects on chromatin remodeling. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:150.
Aramayo RJ, Willhoft O, Ayala R, Bythell-Douglas R, Wigley DB, Zhang X. Cryo-EM structures of the human INO80 chromatin-remodeling complex. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018;25:37–44.
Mao YQ, Houry WA. The role of pontin and reptin in cellular physiology and cancer etiology. Front Mol Biosci. 2017;4:58.
Dauden MI, Lopez-Perrote A, Llorca O. RUVBL1-RUVBL2 AAA-ATPase: a versatile scaffold for multiple complexes and functions. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021;67:78–85.
Clarke TL, Sanchez-Bailon MP, Chiang K, Reynolds JJ, Herrero-Ruiz J, Bandeiras TM, et al. PRMT5-dependent methylation of the TIP60 coactivator RUVBL1 is a key regulator of homologous recombination. Mol Cell. 2017;65:900–16.
Runge JS, Raab JR, Magnuson T. Identification of two distinct classes of the human INO80 complex genome-wide. G3 (Bethesda). 2018;8:1095–102.
Izumi N, Yamashita A, Hirano H, Ohno S. Heat shock protein 90 regulates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related protein kinase family proteins together with the RUVBL1/2 and Tel2-containing co-factor complex. Cancer Sci. 2012;103:50–57.
Wood MA, McMahon SB, Cole MD. An ATPase/helicase complex is an essential cofactor for oncogenic transformation by c-Myc. Mol Cell. 2000;5:321–30.
Bizarro J, Charron C, Boulon S, Westman B, Pradet-Balade B, Vandermoere F, et al. Proteomic and 3D structure analyses highlight the C/D box snoRNP assembly mechanism and its control. J Cell Biol. 2014;207:463–80.
Lauscher JC, Loddenkemper C, Kosel L, Grone J, Buhr HJ, Huber O. Increased pontin expression in human colorectal cancer tissue. Hum Pathol. 2007;38:978–85.
Zhang X, Ren J, Yan L, Tang Y, Zhang W, Li D, et al. Cytoplasmic expression of pontin in renal cell carcinoma correlates with tumor invasion, metastasis and patients’ survival. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0118659.
Guo H, Zhang XY, Peng J, Huang Y, Yang Y, Liu Y, et al. RUVBL1, a novel C-RAF-binding protein, activates the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway to promote lung cancer tumorigenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;498:932–9.
Yuan XS, Wang ZT, Hu YJ, Bao FC, Yuan P, Zhang C, et al. Downregulation of RUVBL1 inhibits proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma cells by G1/S phase cell cycle arrest via multiple mechanisms. Tumor Biol (Artic). 2016;37:16015–27.
Taniuchi K, Furihata M, Iwasaki S, Tanaka K, Shimizu T, Saito M, et al. RUVBL1 directly binds actin filaments and induces formation of cell protrusions to promote pancreatic cancer cell invasion. Int J Oncol. 2014;44:1945–54.
Thomas C, Lamoureux F, Crafter C, Davies BR, Beraldi E, Fazli L, et al. Synergistic targeting of PI3K/AKT pathway and androgen receptor axis significantly delays castration-resistant prostate cancer progression in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12:2342–55.
Advani SJ, Camargo MF, Seguin L, Mielgo A, Anand S, Hicks AM, et al. Kinase-independent role for CRAF-driving tumour radioresistance via CHK2. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8154.
Assimon VA, Tang Y, Vargas JD, Lee GJ, Wu ZY, Lou K, et al. CB-6644 is a selective inhibitor of the RUVBL1/2 complex with anticancer activity. ACS Chem Biol. 2019;14:236–44.
Li S, Fong KW, Gritsina G, Zhang A, Zhao JC, Kim J, et al. Activation of MAPK signaling by CXCR7 leads to enzalutamide resistance in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2019;79:2580–92.
Verras M, Lee J, Xue H, Li TH, Wang Y, Sun Z. The androgen receptor negatively regulates the expression of c-Met: implications for a novel mechanism of prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2007;67:967–75.
Zhang A, Zhao JC, Kim J, Fong KW, Yang YA, Chakravarti D, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR enhances the androgen-receptor-mediated transcriptional program and drives castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cell Rep. 2015;13:209–21.
Zhao JC, Yu J, Runkle C, Wu L, Hu M, Wu D, et al. Cooperation between Polycomb and androgen receptor during oncogenic transformation. Genome Res. 2012;22:322–31.
Tellman TV, Cruz LA, Grindel BJ, Farach-Carson MC. Cleavage of the perlecan-semaphorin 3A-Plexin A1-Neuropilin-1 (PSPN) complex by matrix metalloproteinase 7/matrilysin triggers prostate cancer cell dyscohesion and migration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:3218.
Ren S, Wei GH, Liu D, Wang L, Hou Y, Zhu S, et al. Whole-genome and transcriptome sequencing of prostate cancer identify new genetic alterations driving disease progression. Eur Urol. 2018;73:322–39.
Gao L, Zhang W, Zhang J, Liu J, Sun F, Liu H, et al. KIF15-mediated stabilization of AR and AR-V7 contributes to enzalutamide resistance in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2021;81:1026–39.
Qi M, Jiao M, Li X, Hu J, Wang L, Zou Y, et al. CUL4B promotes gastric cancer invasion and metastasis-involvement of upregulation of HER2. Oncogene. 2018;37:1075–85.
Wang L, Zhang J, Yang X, Chang YW, Qi M, Zhou Z, et al. SOX4 is associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2013;16:301–7.
Hu J, Sun F, Chen W, Zhang J, Zhang T, Qi M, et al. BTF3 sustains cancer stem-like phenotype of prostate cancer via stabilization of BMI1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:227.
Wang L, Song G, Zhang X, Feng T, Pan J, Chen W, et al. PADI2-mediated citrullination promotes prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2017;77:5755–68.
Funding
This work was supported by the Joint Research Fund of Natural Science, Shandong Province (ZR2019LZL014), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81972416, 82172818), Major Science and Technology Innovation Project of Shandong Province (2018CXGC1210), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC0114703), and The Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University (2018JC016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study concept and design: FS, XD, and BH. Data acquisition: FS, XW, TF, LG, WZ, XW, ZY, BD, and XW. Analysis and interpretation of the data: FS, XW, JL, WJ, Hl, KL, YS. Paper preparation: FS, BH, and XD. Critical review: BH, FS, XW, and XD.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, F., Wang, X., Hu, J. et al. RUVBL1 promotes enzalutamide resistance of prostate tumors through the PLXNA1-CRAF-MAPK pathway. Oncogene 41, 3239–3250 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02332-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02332-8
This article is cited by
-
RUVBL1 ubiquitination by DTL promotes RUVBL1/2-β-catenin-mediated transcriptional regulation of NHEJ pathway and enhances radiation resistance in breast cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2024)
-
Targeting PHB1 to inhibit castration-resistant prostate cancer progression in vitro and in vivo
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)
-
RUVBL1-modulated chromatin remodeling alters the transcriptional activity of oncogenic CTNNB1 in uveal melanoma
Cell Death Discovery (2023)