Abstract
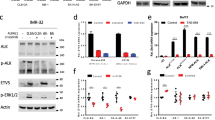
The identification of molecular events underlying the pathogenesis of neuroblastoma can likely result in improved clinical outcomes for this disease. In this study, a translocation within chromosome 2p and 4q was found to bring about the formation of an in-frame fusion gene that was composed of portions of the teneurin transmembrane protein 3 (TENM3, also known as ODZ3) gene and the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene in tumor cells from patients with neuroblastoma. Expression of the full length TENM3–ALK cDNA in NIH-3T3 cells led to the formation of a fusion protein that: (1) possesses constitutive tyrosine kinase activity, (2) induces strong activation of the downstream targets of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), protein kinase B (a.k.a. AKT), and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), (3) provokes oncogenic transformation in NOD.Cg-PrkdcscidIl2rgtm1Sug/ShiJic mice, and (4) possesses sensitivity to ALK inhibitors in vitro and in vivo. Our findings demonstrated that patients with neuroblastoma may express a transforming fusion kinase, which is a promising candidate for a therapeutic target and a diagnostic molecular marker for neuroblastoma. The in-frame 5′ partner gene that fuses with ALK has not been reported previously in neuroblastoma. Our data provide novel biological insights into the mechanism of ALK activation due to translocation, with implications for neuroblastoma tumorigenesis, and could be useful as a vital marker for the accurate diagnosis of this type of neuroblastoma.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maris JM. Recent advances in neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2202–11.
Mazzocco K, Defferrari R, Sementa AR, Garaventa A, Longo L, De Mariano M, et al. Genetic abnormalities in adolescents and young adults with neuroblastoma: a report from the Italian Neuroblastoma group. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2015;62:1725–32.
Mossé YP, Deyell RJ, Berthold F, Nagakawara A, Ambros PF, Monclair T, et al. Neuroblastoma in older children, adolescents and young adults: a report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group project. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2014;61:627–35.
Pinto NR, Applebaum MA, Volchenboum SL, Matthay KK, London WB, Ambros PF, et al. Advances in risk classification and treatment strategies for neuroblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:3008–17.
Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB, Dittmer KG, Shapiro DN, Saltman DL, et al. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science. 1994;263:1281–4.
Roskoski R. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK): structure, oncogenic activation, and pharmacological inhibition. Pharmacol Res. 2013;68:68–94.
Della Corte CM, Viscardi G, Di Liello R, Fasano M, Martinelli E, Troiani T. et al. Role and targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0776-2.
Okubo J, Takita J, Chen Y, Oki K, Nishimura R, Kato M, et al. Aberrant activation of ALK kinase by a novel truncated form ALK protein in neuroblastoma. Oncogene. 2012;31:4667–76.
Cazes A, Louis-Brennetot C, Mazot P, Dingli F, Lombard B, Boeva V, et al. Characterization of rearrangements involving the ALK gene reveals a novel truncated form associated with tumor aggressiveness in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2013;73:195–204.
Fransson S, Hansson M, Ruuth K, Djos A, Berbegall A, Javanmardi N, et al. Intragenic anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements: translocations as a novel mechanism of ALK activation in neuroblastoma tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2015;54:99–109.
Matsuno R, Akiyama K, Toyama D, Ikeda H, Yamamoto S. Adolescent pulmonary metastatic neuroblastoma with ALK rearrangement: a case report. Pediatr Int. 2020;62:507–9.
Seki M, Nishimura R, Yoshida K, Shimamura T, Shiraishi Y, Sato Y, et al. Integrated genetic and epigenetic analysis defines novel molecular subgroups in rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7557.
Tang Z, Wang L, Tang G, Medeiros LJ. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) for detecting anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:3939.
Seki M, Kimura S, Isobe T, Yoshida K, Ueno H, Nakajima-Takagi Y, et al. Recurrent SPI1 (PU.1) fusions in high-risk pediatric T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet. 2017;49:1274–81.
Kitamura T, Koshino Y, Shibata F, Oki T, Nakajima H, Nosaka T, et al. Retrovirus-mediated gene transfer and expression cloning: powerful tools in functional genomics. Exp Hematol. 2003;31:1007–14.
Ceccon M, Metrlo MEB, Mologni L, Poggio T, Varecio LM, Menotti M, et al. Excess of NPM-ALK oncogenic signaling promotes cellular apoptosis and drug dependency. Oncogene. 2016;35:3854–65.
Christensen JG, Zou HY, Arango ME, Li Q, Lee JH, McDonnell SR, et al. Cytoreductive antitumor activity of PF-2341066, a novel inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase and c-Met, in experimental models of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:3314–22.
Johnson TW, Richardson PF, Bailey S, Brooun A, Burke BJ, Collins MR, et al. Discovery of (10R)-7-amino-12-fluoro-2,10,16-trimethyl-15-oxo-10,15,16,17-tetrahydro-2H-8,4-(metheno)pyrazolo[4,3-h][2,5,11]-benzoxadiazacyclotetradecine-3-carbonitrile (PF-06463922), a macrocyclic inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) and c-ros oncogene 1 (ROS1) with preclinical brain exposure and broad-spectrum potency against ALK-resistant mutations. J Med Chem. 2014;57:4720–44.
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Solomon B, Maki RG, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1693–703.
Ito M, Hiramatsu H, Kobayashi K, Suzue K, Kawahata M, Hioki K, et al. NOD/SCID/gamma(c)(null) mouse: an excellent recipient mouse model for engraftment of human cells. Blood. 2002;100:3175–82.
Arregui CO, Balsamo J, Lilien J. Regulation of signaling by protein-tyrosine phosphatases: potential roles in the nervous system. Neurochem Res. 2000;25:95–105.
Young TR, Leamey CA. Teneurins: important regulators of neural circuitry. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;41:990–3.
Ziegler A, Corvalán A, Roa I, Brañes JA, Wollscheid B. Teneurin protein family: an emerging role in human tumorigenesis and drug resistance. Cancer Lett. 2012;326:1–7.
Molenaar JJ, Koster J, Zwijnenburg DA, van Sluis P, Valentijn LJ, van der Ploeg I, et al. Sequencing of neuroblastoma identifies chromothripsis and defects in neuritogenesis genes. Nature. 2012;483:589–93.
Feng K, Zhou XH, Oohashi T, Mörgelin M, Lustig A, Hirakawa S, et al. All four members of the Ten-m/Odz family of transmembrane proteins form dimers. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:26128–35.
Stein H, Foss HD, Dürkop H, Marafioti T, Delsol G, Pulford K, et al. CD30(+) anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a review of its histopathologic, genetic, and clinical features. Blood. 2000;96:3681–95.
Martelli MP, Sozzi G, Hernandez L, Pettirossi V, Navarro A, Conte D, et al. EML4-ALK rearrangement in non-small cell lung cancer and non-tumor lung tissues. Am J Pathol. 2009;174:661–70.
Shiota M, Fujimoto J, Semba T, Satoh H, Yamamoto T, Mori S. Hyperphosphorylation of a novel 80 kDa protein-tyrosine kinase similar to Ltk in a human Ki-1 lymphoma cell line, AMS3. Oncogene. 1994;9:1567–74.
Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–6.
Rikova K, Guo A, Zeng Q, Possemato A, Yu J, Haack H, et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell. 2007;131:1190–203.
Tabbó F, Barreca A, Piva R, Inghirami G. Group ET-CLS. ALK Signaling and target therapy in anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Front Oncol. 2012;2:41.
Duyster J, Bai RY, Morris SW. Translocations involving anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). Oncogene. 2001;20:5623–37.
Mano H. Non-solid oncogenes in solid tumors: EML4-ALK fusion genes in lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008;99:2349–55.
Richards MW, Law EW, Rennalls LP, Busacca S, O’Regan L, Fry AM, et al. Crystal structure of EML1 reveals the basis for Hsp90 dependence of oncogenic EML4-ALK by disruption of an atypical β-propeller domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:5195–200.
Richards MW, O’Regan L, Roth D, Montgomery JM, Straube A, Fry AM, et al. Microtubule association of EML proteins and the EML4-ALK variant 3 oncoprotein require an N-terminal trimerization domain. Biochem J. 2015;467:529–36.
Takeuchi K, Choi YL, Soda M, Inamura K, Togashi Y, Hatano S, et al. Multiplex reverse transcription-PCR screening for EML4-ALK fusion transcripts. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:6618–24.
Choi YL, Lira ME, Hong M, Kim RN, Choi SJ, Song JY, et al. A novel fusion of TPR and ALK in lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9:563–6.
Amano Y, Ishikawa R, Sakatani T, Ichinose J, Sunohara M, Watanabe K, et al. Oncogenic TPM3-ALK activation requires dimerization through the coiled-coil structure of TPM3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;457:457–60.
Grande E, Bolós MV, Arriola E. Targeting oncogenic ALK: a promising strategy for cancer treatment. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:569–79.
Oohashi T, Zhou XH, Feng K, Richter B, Mörgelin M, Perez MT, et al. Mouse ten-m/Odz is a new family of dimeric type II transmembrane proteins expressed in many tissues. J Cell Biol. 1999;145:563–77.
Chiarle R, Voena C, Ambrogio C, Piva R, Inghirami G. The anaplastic lymphoma kinase in the pathogenesis of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:11–23.
Pulford K, Morris SW, Turturro F. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase proteins in growth control and cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2004;199:330–58.
Bischof D, Pulford K, Mason DY, Morris SW. Role of the nucleophosmin (NPM) portion of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma-asscociated NPM-anaplastic lymphoma kinase fusion protein in oncogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:2312–25.
Mason DY, Pulford KA, Bischof D, Kuefer MU, Butler LH, Lamant L, et al. Nuclear localization of the nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase is not required for malignant transformation. Cancer Res. 1998;58:1057–62.
Chen Y, Takita J, Choi YL, Kato M, Ohira M, Sanada M, et al. Oncogenic mutations of ALK kinase in neuroblastoma. Nature. 2008;455:971–4.
Mossé YP, Laudenslager M, Longo L, Cole KA, Wood A, Attiyeh EF, et al. Identification of ALK as a major familial neuroblastoma predisposition gene. Nature. 2008;455:930–5.
Carén H, Abel F, Kogner P, Martinsson T. High incidence of DNA mutations and gene amplifications of the ALK gene in advanced sporadic neuroblastoma tumours. Biochem J. 2008;416:153–9.
George RE, Sanda T, Hanna M, Fröhling S, Luther W 2nd, Zhang J, et al. Activating mutations in ALK provide a therapeutic target in neuroblastoma. Nature. 2008;455:975–8.
Janoueix-Lerosey I, Lequin D, Brugières L, Ribeiro A, de Pontual L, Combaret V, et al. Somatic and germline activating mutations of the ALK kinase receptor in neuroblastoma. Nature. 2008;455:967–70.
Takita J. The role of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in pediatric cancers. Cancer Sci. 2017;108:1913–20.
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Cambridge DR, Shaw AT, Solomon B, Maki RG, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1693–703.
Cambridge DR, Kim HR, Ahn MJ, Yang JC, Han JY, Lee JS, et al. Brigatinib versus Crizotinib in ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2027–39.
Infarinato NR, Park JH, Krytska K, Ryles HT, Sano R, Szigety KM, et al. The ALK/ROS1 inhibitor PF-06463922 overcomes primary resistance to crizotinib in ALK-Driven neuroblastoma. Cancer Discov. 2016;6:96–107.
Passoni L, Longo L, Collini P, Coluccia AM, Bozzi F, Podda M, et al. Mutation-independent anaplastic lymphoma kinase overexpression in poor prognosis neuroblastoma patients. Cancer Res. 2009;69:7338–46.
Hiwatari M, Taki T, Taketani T, Taniwaki M, Sugita K, Okuya M, et al. Fusion of an AF4-related gene, LAF4, to MLL in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia with t(2;11)(q11;q23). Oncogene. 2003;22:2851–5.
Li Z, Dacic S, Pantanowitz L, Khalbuss WE, Nikiforova MN, Monaco SE. Correlation of cytomorphology and molecular findings in EGFR+, KRAS+, and ALK+ lung carcinomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 2014;141:420–8.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank M. Matsumura, K. Yin, and F. Saito for their excellent technical assistance, Dr. T. Kitamura (Division of Cellular Therapy/Division of Stem Cell Signaling, The Institute of Medical Sciences, The University of Tokyo, Japan) for the kind gift of expression vector pMYs-IRES-Neo. The authors also wish to express their appreciation to K. Chiba and H. Tanaka (The University of Tokyo) for the supercomputer. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP19J11112, JP17H04224, JP18K19467, and JP20H00528; Project for Cancer Research and Therapeutic Evolution (P-CREATE; grant no. JP19cm0106509h9904), and Practical Research for Innovative Cancer Control (grant no. JP19ck0106468h001) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED); Princess Takamatsu Cancer Research Fund. This research also used the computational resources of the K computer provided by the RIKEN Advanced Institute for Computational Science through the HPCI System Research project (hp140230, hp160219, and hp150232) (SM and SO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MH and JT wrote the paper; MH, TN, and MS analyzed the data; MH performed the experiments; RM and SY analyzed the FISH data; KY, SM, and SO developed the bioinformatics pipelines; MK, ASO, MS, KW, and JT provided conceptual advice; and MH and JT designed the study. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiwatari, M., Seki, M., Matsuno, R. et al. Novel TENM3–ALK fusion is an alternate mechanism for ALK activation in neuroblastoma. Oncogene 41, 2789–2797 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02301-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02301-1