Abstract
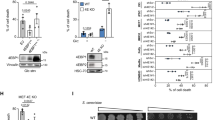
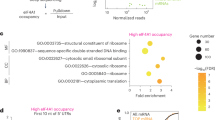
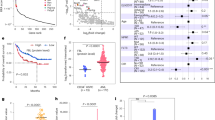
eIF3a (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3a), a subunit of the eIF3 complex, has been suggested to play a regulatory role in protein synthesis and in cellular response to DNA-damaging treatments. S6K1 is an effector and a mediator of mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) in regulating protein synthesis and integrating diverse signals into control of cell growth and response to stress. Here, we show that eIF3a regulates S6K1 activity by inhibiting mTORC1 kinase via regulating Raptor synthesis. The regulation of Raptor synthesis is via eIF3a interaction with HuR (human antigen R) and binding of the eIF3a-HuR complex to the 5ʹ-UTR of Raptor mRNA. Furthermore, mTORC1 may mediate eIF3a function in cellular response to cisplatin by regulating synthesis of NER proteins and NER activity. Taken together, we conclude that the mTOR signaling pathway may also be regulated by translational control and mediate eIF3a regulation of cancer cell response to cisplatin by regulating NER protein synthesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clemens MJ, Bommer UA. Translational control: the cancer connection. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;31:1–23.
Dong Z, Zhang JT. Initiation factor eIF3 and regulation of mRNA translation, cell growth, and cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2006;59:169–80.
Yin JY, Dong Z, Liu ZQ, Zhang JT. Translational control gone awry: a new mechanism of tumorigenesis and novel targets of cancer treatments. Biosci Rep. 2011;31:1–15.
Yin JY, Zhang JT, Zhang W, Zhou HH, Liu ZQ. eIF3a: A new anticancer drug target in the eIF family. Cancer Lett. 2018;412:81–87.
Yin JY, Shen J, Dong ZZ, Huang Q, Zhong MZ, Feng DY, et al. Effect of eIF3a on response of lung cancer patients to platinum-based chemotherapy by regulating DNA repair. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:4600–9.
Liu RY, Dong Z, Liu J, Yin JY, Zhou L, Wu X, et al. Role of eIF3a in regulating cisplatin sensitivity and in translational control of nucleotide excision repair of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene. 2011;30:4814–23.
Chen J, Liu JY, Dong ZZ, Zou T, Wang Z, Shen Y, et al. The effect of eIF3a on anthracycline-based chemotherapy resistance by regulating DSB DNA repair. Biochem Pharm. 2021;190:114616.
Tumia R, Wang CJ, Dong T, Ma S, Beebe J, Chen J, et al. eIF3a Regulation of NHEJ Repair Protein Synthesis and Cellular Response to Ionizing Radiation. Front cell developmental Biol. 2020;8:753.
Dunlop EA, Tee AR. Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1: signalling inputs, substrates and feedback mechanisms. Cell Signal. 2009;21:827–35.
Hara K, Maruki Y, Long X, Yoshino K, Oshiro N, Hidayat S, et al. Raptor, a binding partner of target of rapamycin (TOR), mediates TOR action. Cell. 2002;110:177–89.
Kim DH, Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Latek RR, Guntur KV, Erdjument-Bromage H, et al. GbetaL, a positive regulator of the rapamycin-sensitive pathway required for the nutrient-sensitive interaction between raptor and mTOR. Mol Cell. 2003;11:895–904.
Loewith R, Jacinto E, Wullschleger S, Lorberg A, Crespo JL, Bonenfant D, et al. Two TOR complexes, only one of which is rapamycin sensitive, have distinct roles in cell growth control. Mol Cell. 2002;10:457–68.
Peterson TR, Laplante M, Thoreen CC, Sancak Y, Kang SA, Kuehl WM, et al. DEPTOR is an mTOR inhibitor frequently overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells and required for their survival. Cell. 2009;137:873–86.
Sancak Y, Thoreen CC, Peterson TR, Lindquist RA, Kang SA, Spooner E, et al. PRAS40 is an insulin-regulated inhibitor of the mTORC1 protein kinase. Mol Cell. 2007;25:903–15.
Fingar DC, Blenis J. Target of rapamycin (TOR): an integrator of nutrient and growth factor signals and coordinator of cell growth and cell cycle progression. Oncogene. 2004;23:3151–71.
Wullschleger S, Loewith R, Hall MN. TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell. 2006;124:471–84.
Feng Z, Zhang H, Levine AJ, Jin S. The coordinate regulation of the p53 and mTOR pathways in cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:8204–9.
Beuvink I, Boulay A, Fumagalli S, Zilbermann F, Ruetz S, O’Reilly T, et al. The mTOR inhibitor RAD001 sensitizes tumor cells to DNA-damaged induced apoptosis through inhibition of p21 translation. Cell. 2005;120:747–59.
Babichev Y, Kabaroff L, Datti A, Uehling D, Isaac M, Al-Awar R, et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibition in combination with doxorubicin is an effective therapy for leiomyosarcoma. J Transl Med. 2016;14:67.
Grunwald V, DeGraffenried L, Russel D, Friedrichs WE, Ray RB, Hidalgo M. Inhibitors of mTOR reverse doxorubicin resistance conferred by PTEN status in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6141–5.
Wei F, Liu Y, Guo Y, Xiang A, Wang G, Xue X, et al. miR-99b-targeted mTOR induction contributes to irradiation resistance in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:81.
Nassim R, Mansure JJ, Chevalier S, Cury F, Kassouf W. Combining mTOR inhibition with radiation improves antitumor activity in bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo: a novel strategy for treatment. PLoS One. 2013;8:e65257.
Yuan HX, Guan KL. Structural insights of mTOR complex 1. Cell Res. 2016;26:267–8.
Espeillac C, Mitchell C, Celton-Morizur S, Chauvin C, Koka V, Gillet C, et al. S6 kinase 1 is required for rapamycin-sensitive liver proliferation after mouse hepatectomy. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:2821–32.
Su B, Jacinto E. Mammalian TOR signaling to the AGC kinases. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2011;46:527–47.
Magnuson B, Ekim B, Fingar DC. Regulation and function of ribosomal protein S6 kinase (S6K) within mTOR signalling networks. Biochem J. 2012;441:1–21.
Carriere A, Cargnello M, Julien LA, Gao H, Bonneil E, Thibault P, et al. Oncogenic MAPK signaling stimulates mTORC1 activity by promoting RSK-mediated raptor phosphorylation. Curr Biol: CB. 2008;18:1269–77.
Gwinn DM, Shackelford DB, Egan DF, Mihaylova MM, Mery A, Vasquez DS, et al. AMPK phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Mol cell. 2008;30:214–26.
Gwinn DM, Asara JM, Shaw RJ. Raptor is phosphorylated by cdc2 during mitosis. PloS one. 2010;5:e9197.
Ramirez-Valle F, Badura ML, Braunstein S, Narasimhan M, Schneider RJ. Mitotic raptor promotes mTORC1 activity, G(2)/M cell cycle progression, and internal ribosome entry site-mediated mRNA translation. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30:3151–64.
Carriere A, Romeo Y, Acosta-Jaquez HA, Moreau J, Bonneil E, Thibault P, et al. ERK1/2 phosphorylate Raptor to promote Ras-dependent activation of mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1). The. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:567–77.
Kwak D, Choi S, Jeong H, Jang JH, Lee Y, Jeon H, et al. Osmotic stress regulates mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) complex 1 via c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK)-mediated Raptor protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:18398–407.
Kim DH, Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, King JE, Latek RR, Erdjument-Bromage H, et al. mTOR interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell. 2002;110:163–75.
Foster KG, Acosta-Jaquez HA, Romeo Y, Ekim B, Soliman GA, Carriere A, et al. Regulation of mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) by raptor Ser863 and multisite phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:80–94.
Dong Z, Liu J, Zhang JT. Translational regulation of Chk1 expression by eIF3a via interaction with the RNA-binding protein HuR. Biochem J. 2020;477:1939–50.
Zoncu R, Efeyan A, Sabatini DM. mTOR: from growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12:21–35.
Kovacina KS, Park GY, Bae SS, Guzzetta AW, Schaefer E, Birnbaum MJ, et al. Identification of a proline-rich Akt substrate as a 14-3-3 binding partner. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:10189–94.
Vander Haar E, Lee SI, Bandhakavi S, Griffin TJ, Kim DH. Insulin signalling to mTOR mediated by the Akt/PKB substrate PRAS40. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:316–23.
Peng DJ, Wang J, Zhou JY, Wu GS. Role of the Akt/mTOR survival pathway in cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;394:600–5.
Altomare DA, Wang HQ, Skele KL, De Rienzo A, Klein-Szanto AJ, Godwin AK, et al. AKT and mTOR phosphorylation is frequently detected in ovarian cancer and can be targeted to disrupt ovarian tumor cell growth. Oncogene. 2004;23:5853–7.
Qiao Y, Spitz MR, Guo Z, Hadeyati M, Grossman L, Kraemer KH, et al. Rapid assessment of repair of ultraviolet DNA damage with a modified host-cell reactivation assay using a luciferase reporter gene and correlation with polymorphisms of DNA repair genes in normal human lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 2002;509:165–74.
Ahn B, Kang D, Kim H, Wei Q. Repair of mitomycin C cross-linked DNA in mammalian cells measured by a host cell reactivation assay. Mol Cells. 2004;18:249–55.
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 2005;307:1098–101.
Kocalis HE, Hagan SL, George L, Turney MK, Siuta MA, Laryea GN, et al. Rictor/mTORC2 facilitates central regulation of energy and glucose homeostasis. Mol Metab. 2014;3:394–407.
Stronach EA, Chen M, Maginn EN, Agarwal R, Mills GB, Wasan H, et al. DNA-PK mediates AKT activation and apoptosis inhibition in clinically acquired platinum resistance. Neoplasia. 2011;13:1069–80.
Bozulic L, Surucu B, Hynx D, Hemmings BA. PKBalpha/Akt1 acts downstream of DNA-PK in the DNA double-strand break response and promotes survival. Mol Cell. 2008;30:203–13.
Wagner S, Herrmannova A, Malik R, Peclinovska L, Valasek LS. Functional and biochemical characterization of human eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 in living cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2014;34:3041–52.
Dong Z, Qi J, Peng H, Liu J, Zhang JT. Spectrin Domain of Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 3a Is the Docking Site for Formation of the a:b:i:g Subcomplex. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:27951–9.
Chaudhuri J, Chakrabarti A, Maitra U. Biochemical characterization of mammalian translation initiation factor 3 (eIF3). Molecular cloning reveals that p110 subunit is the mammalian homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein Prt1. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:30975–83.
Dong Z, Zhang JT. EIF3 p170, a Mediator of Mimosine Effect on Protein Synthesis and Cell Cycle Progression. Mol Biol Cell. 2003;14:3942–51.
Wagner S, Herrmannova A, Sikrova D, Valasek LS. Human eIF3b and eIF3a serve as the nucleation core for the assembly of eIF3 into two interconnected modules: the yeast-like core and the octamer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:10772–88.
Dong Z, Liu LH, Han B, Pincheira R, Zhang JT. Role of eIF3 p170 in controlling synthesis of ribonucleotide reductase M2 and cell growth. Oncogene. 2004;23:3790–801.
Nouspikel T. DNA repair in mammalian cells: Nucleotide excision repair: variations on versatility. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009;66:994–1009.
Neher TM, Rechkunova NI, Lavrik OI, Turchi JJ. Photo-cross-linking of XPC-Rad23B to cisplatin-damaged DNA reveals contacts with both strands of the DNA duplex and spans the DNA adduct. Biochemistry. 2010;49:669–78.
Neher TM, Shuck SC, Liu JY, Zhang JT, Turchi JJ. Identification of novel small molecule inhibitors of the XPA protein using in silico based screening. ACS Chem Biol. 2010;5:953–65.
Saxton RA, Sabatini DM. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell. 2017;168:960–76.
Dong Z, Liu Y, Zhang JT. Regulation of ribonucleotide reductase M2 expression by the upstream AUGs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:2715–25.
Yin JY, Dong ZZ, Liu RY, Chen J, Liu ZQ, Zhang JT. Translational regulation of RPA2 via internal ribosomal entry site and by eIF3a. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34:1224–31.
Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–54.
Qi J, Dong Z, Liu J, Zhang JT. EIF3i promotes colon oncogenesis by regulating COX-2 protein synthesis and beta-catenin activation. Oncogene. 2014;33:4156–63.
Vandamme T, Beyens M, de Beeck KO, Dogan F, van Koetsveld PM, Pauwels P, et al. Long-term acquired everolimus resistance in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours can be overcome with novel PI3K-AKT-mTOR inhibitors. Br J Cancer. 2016;114:650–8.
Peery R, Kyei-Baffour K, Dong Z, Liu J, de Andrade Horn P, Dai M, et al. Synthesis and identification of a novel lead targeting survivin dimerization for proteasome-dependent degradation. J Med Chem. 2020;63:7243–51.
Huang W, Dong Z, Chen Y, Wang F, Wang CJ, Peng H, et al. Small-molecule inhibitors targeting the DNA-binding domain of STAT3 suppress tumor growth, metastasis and STAT3 target gene expression in vivo. Oncogene. 2016;35:783–92.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the NIH grant R01 CA211904.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SM, ZD and JTZ: designed research; SM: performed research; SM, YH and JL: analyzed data; SM and JTZ: wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, S., Dong, Z., Huang, Y. et al. eIF3a regulation of mTOR signaling and translational control via HuR in cellular response to DNA damage. Oncogene 41, 2431–2443 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02262-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-022-02262-5
This article is cited by
-
Analysis of m6A regulators related immune characteristics in ankylosing spondylitis by integrated bioinformatics and computational strategies
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment increases intestinal stem cell proliferation through the mTORC1/S6K1 signaling pathway in Mus musculus
Biological Research (2023)
-
Theranostic imaging and multimodal photodynamic therapy and immunotherapy using the mTOR signaling pathway
Nature Communications (2023)