Abstract
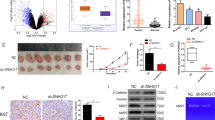
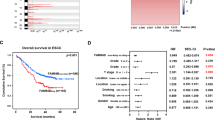
Esophageal cancer is a complex malignancy and the sixth leading cause of cancer death worldwide. In Eastern Asia including China, about 90% of all incident cases have esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Mounting evidence elucidates that aberrant expression of various non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) contributes to ESCC progression, but it remains unclear how small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are involved in ESCC development. We systemically screened clinically relevant snoRNAs in ESCC via integrative analyses of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data and validation in ESCC tissues. We found that snoRNA SNORD12B was one of the most evidently upregulated snoRNAs in ESCC specimens and its high expression was significantly associated with poor prognosis of patients. SNORD12B profoundly promoted proliferation, migration, invasion, and metastasis of ESCC cells in vitro and in vivo, indicating its oncogene nature. In particular, SNORD12B could interact with PP-1α, one of the three catalytic subunits of serine/threonine protein phosphatase 1, which is a major phosphatase that directly dephosphorylates AKT to suppress its activation. Interestingly, high levels of SNORD12B in ESCC cells could break interactions between 14-3-3ζ and PP-1α, abolish the retention of PP-1α in the cytosol by 14-3-3ζ and relocate PP-1α from the cytosol to the nucleus. This led to sequestered PP-1α in the nucleus, enhanced phosphorylation of AKT in the cytosol, activated AKT-mTOR-4EBP1 signaling, and, thus, ESCC progression. These insights would improve our understanding of how snoRNAs contribute to tumorigenesis and highlight the potential of snoRNAs as future therapeutic targets against cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34.
Abnet CC, Arnold M, Wei WQ. Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:360–73.
Tran GD, Sun XD, Abnet CC, Fan JH, Dawsey SM, Dong ZW, et al. Prospective study of risk factors for esophageal and gastric cancers in the Linxian general population trial cohort in China. Int J Cancer. 2005;113:456–63.
Islami F, Kamangar F, Aghcheli K, Fahimi S, Semnani S, Taghavi N, et al. Epidemiologic features of upper gastrointestinal tract cancers in Northeastern Iran. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:1402–6.
Wu M, Liu AM, Kampman E, Zhang ZF, Van’t Veer P, Wu DL, et al. Green tea drinking, high tea temperature and esophageal cancer in high- and low-risk areas of Jiangsu Province, China: a population-based case-control study. Int J Cancer. 2009;124:1907–13.
Chang J, Zhong R, Tian J, Li J, Zhai K, Ke J, et al. Exome-wide analyses identify low-frequency variant in CYP26B1 and additional coding variants associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2018;50:338–43.
Wu C, Wang Z, Song X, Feng XS, Abnet CC, He J, et al. Joint analysis of three genome-wide association studies of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese populations. Nat Genet. 2014;46:1001–6.
Wu C, Kraft P, Zhai K, Chang J, Wang Z, Li Y, et al. Genome-wide association analyses of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese identify multiple susceptibility loci and gene-environment interactions. Nat Genet. 2012;44:1090–7.
Abnet CC, Wang Z, Song X, Hu N, Zhou FY, Freedman ND, et al. Genotypic variants at 2q33 and risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in China: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:2132–41.
Wu C, Hu Z, He Z, Jia W, Wang F, Zhou Y, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies three new susceptibility loci for esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma in Chinese populations. Nat Genet. 2011;43:679–84.
Tanaka F, Yamamoto K, Suzuki S, Inoue H, Tsurumaru M, Kajiyama Y, et al. Strong interaction between the effects of alcohol consumption and smoking on oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma among individuals with ADH1B and/or ALDH2 risk alleles. Gut. 2010;59:1457–64.
Wang LD, Zhou FY, Li XM, Sun LD, Song X, Jin Y, et al. Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54. Nat Genet. 2010;42:759–63.
Abnet CC, Freedman ND, Hu N, Wang Z, Yu K, Shu XO, et al. A shared susceptibility locus in PLCE1 at 10q23 for gastric adenocarcinoma and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2010;42:764–7.
Cui R, Kamatani Y, Takahashi A, Usami M, Hosono N, Kawaguchi T, et al. Functional variants in ADH1B and ALDH2 coupled with alcohol and smoking synergistically enhance esophageal cancer risk. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:1768–75.
Wang X, Li M, Wang Z, Han S, Tang X, Ge Y, et al. Silencing of long noncoding RNA MALAT1 by miR-101 and miR-217 inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:3925–35.
Chen Y, Lu Y, Ren Y, Yuan J, Zhang N, Kimball H, et al. Starvation-induced suppression of DAZAP1 by miR-10b integrates splicing control into TSC2-regulated oncogenic autophagy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Theranostics. 2020;10:4983–96.
Liu J, Liu ZX, Wu QN, Lu YX, Wong CW, Miao L, et al. Long noncoding RNA AGPG regulates PFKFB3-mediated tumor glycolytic reprogramming. Nat Commun. 2020;11:1507.
Zhang H, Hua Y, Jiang Z, Yue J, Shi M, Zhen X, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-promoted LncRNA DNM3OS confers radioresistance by regulating DNA damage response in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:1989–2000.
You BH, Yoon JH, Kang H, Lee EK, Lee SK, Nam JW. HERES, a lncRNA that regulates canonical and noncanonical Wnt signaling pathways via interaction with EZH2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:24620–9.
Zhang XD, Huang GW, Xie YH, He JZ, Guo JC, Xu XE, et al. The interaction of lncRNA EZR-AS1 with SMYD3 maintains overexpression of EZR in ESCC cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:1793–809.
Tan DSW, Chong FT, Leong HS, Toh SY, Lau DP, Kwang XL, et al. Long noncoding RNA EGFR-AS1 mediates epidermal growth factor receptor addiction and modulates treatment response in squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Med. 2017;23:1167–75.
Li J, Chen Z, Tian L, Zhou C, He MY, Gao Y, et al. LncRNA profile study reveals a three-lncRNA signature associated with the survival of patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gut. 2014;63:1700–10.
Fong LY, Taccioli C, Palamarchuk A, Tagliazucchi GM, Jing R, Smalley KJ, et al. Abrogation of esophageal carcinoma development in miR-31 knockout rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:6075–85.
Sudo K, Kato K, Matsuzaki J, Boku N, Abe S, Saito Y, et al. Development and validation of an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma detection model by large-scale MicroRNA profiling. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2:e194573.
Luo A, Zhou X, Shi X, Zhao Y, Men Y, Chang X, et al. Exosome-derived miR-339-5p mediates radiosensitivity by targeting Cdc25A in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 2019;38:4990–5006.
Matera AG, Terns RM, Terns MP. Non-coding RNAs: lessons from the small nuclear and small nucleolar RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:209–20.
Bratkovic T, Rogelj B. The many faces of small nucleolar RNAs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1839:438–43.
Dupuis-Sandoval F, Poirier M, Scott MS. The emerging landscape of small nucleolar RNAs in cell biology. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2015;6:381–97.
Baillat D, Hakimi MA, Naar AM, Shilatifard A, Cooch N, Shiekhattar R. Integrator, a multiprotein mediator of small nuclear RNA processing, associates with the C-terminal repeat of RNA polymerase II. Cell. 2005;123:265–76.
Huang C, Shi J, Guo Y, Huang W, Huang S, Ming S, et al. A snoRNA modulates mRNA 3’ end processing and regulates the expression of a subset of mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:8647–60.
Brameier M, Herwig A, Reinhardt R, Walter L, Gruber J. Human box C/D snoRNAs with miRNA like functions: expanding the range of regulatory RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:675–86.
Kishore S, Stamm S. The snoRNA HBII-52 regulates alternative splicing of the serotonin receptor 2C. Science. 2006;311:230–2.
Ender C, Krek A, Friedlander MR, Beitzinger M, Weinmann L, Chen W, et al. A human snoRNA with microRNA-like functions. Mol Cell. 2008;32:519–28.
Schubert T, Pusch MC, Diermeier S, Benes V, Kremmer E, Imhof A, et al. Df31 protein and snoRNAs maintain accessible higher-order structures of chromatin. Mol Cell. 2012;48:434–44.
Falaleeva M, Pages A, Matuszek Z, Hidmi S, Agranat-Tamir L, Korotkov K, et al. Dual function of C/D box small nucleolar RNAs in rRNA modification and alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:E1625–1634.
Siprashvili Z, Webster DE, Johnston D, Shenoy RM, Ungewickell AJ, Bhaduri A, et al. The noncoding RNAs SNORD50A and SNORD50B bind K-Ras and are recurrently deleted in human cancer. Nat Genet. 2016;48:53–58.
Xu L, Ziegelbauer J, Wang R, Wu WW, Shen RF, Juhl H, et al. Distinct profiles for mitochondrial t-RNAs and small nucleolar RNAs in locally invasive and metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:773–84.
Zhou F, Liu Y, Rohde C, Pauli C, Gerloff D, Kohn M, et al. AML1-ETO requires enhanced C/D box snoRNA/RNP formation to induce self-renewal and leukaemia. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19:844–55.
Gong J, Li Y, Liu CJ, Xiang Y, Li C, Ye Y, et al. A Pan-cancer analysis of the expression and clinical relevance of small nucleolar RNAs in human cancer. Cell Rep. 2017;21:1968–81.
Cao P, Yang A, Wang R, Xia X, Zhai Y, Li Y, et al. Germline duplication of SNORA18L5 increases risk for HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma by altering localization of ribosomal proteins and decreasing levels of p53. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:542–56.
Fan RH, Guo JN, Yan W, Huang MD, Zhu CL, Yin YM, et al. Small nucleolar host gene 6 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation and inhibits cell apoptosis. Oncol Lett. 2018;15:6497–502.
Xiao L, Gong LL, Yuan D, Deng M, Zeng XM, Chen LL, et al. Protein phosphatase-1 regulates Akt1 signal transduction pathway to control gene expression, cell survival and differentiation. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:1448–62.
Jérôme M, Paudel HK. 14-3-3ζ regulates nuclear trafficking of protein phosphatase 1α (PP1α) in HEK-293 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014;558:28–35.
Saxton RA, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell. 2017;168:960–76.
Hsieh AC, Costa M, Zollo O, Davis C, Feldman ME, Testa JR, et al. Genetic dissection of the oncogenic mTOR pathway reveals druggable addiction to translational control via 4EBP-eIF4E. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:249–61.
Hsieh AC, Liu Y, Edlind MP, Ingolia NT, Janes MR, Sher A, et al. The translational landscape of mTOR signalling steers cancer initiation and metastasis. Nature. 2012;485:55–61.
Zhang N, Song Y, Xu Y, Liu J, Shen Y, Zhou L, et al. MED13L integrates Mediator-regulated epigenetic control into lung cancer radiosensitivity. Theranostics. 2020;10:9378–94.
Zhang N, Li Y, Xie M, Song Y, Liu J, Lei T, et al. DACT2 modulated by TFAP2A-mediated allelic transcription promotes EGFR-TKIs efficiency in advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020;172:113772.
Li Y, Zhang N, Zhang L, Song Y, Liu J, Yu J, et al. Oncogene HSPH1 modulated by the rs2280059 genetic variant diminishes EGFR-TKIs efficiency in advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 2020;41:1195–202.
Yuan J, Song Y, Pan W, Li Y, Xu Y, Xie M, et al. LncRNA SLC26A4-AS1 suppresses the MRN complex-mediated DNA repair signaling and thyroid cancer metastasis by destabilizing DDX5. Oncogene. 2020;39:6664–76.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31671300, 31871306); Taishan Scholars Program of Shandong Province (tsqn20161060); Program of Science and Technology for the youth innovation team in universities of Shandong Province (2020KJL001); Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Plan of Shandong Province (2019WS202); Youth Foundation Programs of Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences (2018-28). The authors would like to thank the many individuals who participated in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, B., Liu, J., Zhang, N. et al. Oncogenic SNORD12B activates the AKT-mTOR-4EBP1 signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via nucleus partitioning of PP-1α. Oncogene 40, 3734–3747 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01809-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-01809-2
This article is cited by
-
A novel peptide PDHK1-241aa encoded by circPDHK1 promotes ccRCC progression via interacting with PPP1CA to inhibit AKT dephosphorylation and activate the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway
Molecular Cancer (2024)
-
TEP SNORD12B, SNORA63, and SNORD14E as novel biomarkers for hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HBV-related HCC)
Cancer Cell International (2024)
-
U2AF2-SNORA68 promotes triple-negative breast cancer stemness through the translocation of RPL23 from nucleoplasm to nucleolus and c-Myc expression
Breast Cancer Research (2024)
-
SNORD88C guided 2′-O-methylation of 28S rRNA regulates SCD1 translation to inhibit autophagy and promote growth and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
YBX1 regulates the survival of chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells by modulating m6A-mediated YWHAZ stability
Cellular Oncology (2023)