Abstract
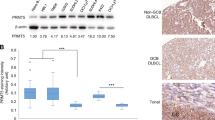
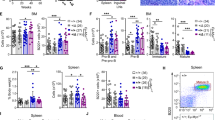
B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathways and interactions with the tumor microenvironment account for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) cells survival in lymphoid organs. In several MCL cases, the WNT/β-catenin canonical pathway is activated and β–catenin accumulates into the nucleus. As both BCR and β-catenin are important mediators of cell survival and interaction with the microenvironment, we investigated the crosstalk between BCR and WNT/β-catenin signaling and analyzed their impact on cellular homeostasis as well as their targeting by specific inhibitors. β-catenin was detected in all leukemic MCL samples and its level of expression rapidly increased upon BCR stimulation. This stabilization was hampered by the BCR-pathway inhibitor Ibrutinib, supporting β-catenin as an effector of the BCR signaling. In parallel, MCL cells as compared with normal B cells expressed elevated levels of WNT16, a NF-κB target gene. Its expression increased further upon BCR stimulation to participate to the stabilization of β-catenin. Upon BCR stimulation, β-catenin translocated into the nucleus but did not induce a Wnt-like transcriptional response, i.e., TCF/LEF dependent. β-catenin rather participated to the regulation of NF-κB transcriptional targets, such as IL6, IL8, and IL1. Oligo pull down and chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments demonstrated that β-catenin is part of a protein complex that binds the NF-κB DNA consensus sequence, strengthening the idea of an association between the two proteins. An inhibitor targeting β-catenin transcriptional interactions hindered both NF-κB DNA recruitment and induced primary MCL cells apoptosis. Thus, β-catenin likely represents another player through which BCR signaling impacts on MCL cell survival.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argatoff LH, Connors JM, Klasa RJ, Horsman DE, Gascoyne RD. Mantle cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic study of 80 cases. Blood. 1997;89:2067–78.
Orchard J, Garand R, Davis Z, Babbage G, Sahota S, Matutes E, et al. A subset of t(11;14) lymphoma with mantle cell features displays mutated IgVH genes and includes patients with good prognosis, nonnodal disease. Blood. 2003;101:4975–81.
Bosch F, Jares P, Campo E, Lopez-Guillermo A, Piris MA, Villamor N, et al. PRAD-1/cyclin D1 gene overexpression in chronic lymphoproliferative disorders: a highly specific marker of mantle cell lymphoma. Blood. 1994;84:2726–32.
Jares P, Colomer D, Campo E. Molecular pathogenesis of mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:3416–23.
Perez-Galan P, Dreyling M, Wiestner A. Mantle cell lymphoma: biology, pathogenesis, and the molecular basis of treatment in the genomic era. Blood. 2011;117:26–38.
Hadzidimitriou A, Agathangelidis A, Darzentas N, Murray F, Delfau-Larue MH, Pedersen LB, et al. Is there a role for antigen selection in mantle cell lymphoma? Immunogenetic support from a series of 807 cases. Blood. 2011;118:3088–95.
Saba NS, Liu D, Herman SE, Underbayev C, Tian X, Behrend D, et al. Pathogenic role of B-cell receptor signaling and canonical NF-kappaB activation in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood. 2016;128:82–92.
Rizzatti EG, Falcao RP, Panepucci RA, Proto-Siqueira R, Anselmo-Lima WT, Okamoto OK, et al. Gene expression profiling of mantle cell lymphoma cells reveals aberrant expression of genes from the PI3K-AKT, WNT and TGFbeta signalling pathways. Br J Haematol. 2005;130:516–26.
Kimura Y, Arakawa F, Kiyasu J, Miyoshi H, Yoshida M, Ichikawa A, et al. The Wnt signaling pathway and mitotic regulators in the initiation and evolution of mantle cell lymphoma: gene expression analysis. Int J Oncol. 2013;43:457–68.
Gelebart P, Anand M, Armanious H, Peters AC, Dien Bard J, Amin HM, et al. Constitutive activation of the Wnt canonical pathway in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood. 2008;112:5171–9.
Clevers H, Nusse R. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012;149:1192–205.
Cadigan KM, Nusse R. Wnt signaling: a common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 1997;11:3286–305.
Stamos JL, Weis WI. The beta-catenin destruction complex. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5:a007898.
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature. 1995;378:785–9.
Goode N, Hughes K, Woodgett JR, Parker PJ. Differential regulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta by protein kinase C isotypes. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:16878–82.
Christian SL, Sims PV, Gold MR. The B cell antigen receptor regulates the transcriptional activator beta-catenin via protein kinase C-mediated inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3. J Immunol. 2002;169:758–69.
Tetsu O, McCormick F. Beta-catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature. 1999;398:422–6.
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H, Zawel L, da Costa LT, et al. Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science. 1998;281:1509–12.
Jho EH, Zhang T, Domon C, Joo CK, Freund JN, Costantini F. Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling induces the transcription of Axin2, a negative regulator of the signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:1172–83.
Nicholson KM, Anderson NG. The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal. 2002;14:381–95.
Baran-Marszak F, Boukhiar M, Harel S, Laguillier C, Roger C, Gressin R, et al. Constitutive and B-cell receptor-induced activation of STAT3 are important signaling pathways targeted by bortezomib in leukemic mantle cell lymphoma. Haematologica. 2010;95:1865–72.
Bernard S, Danglade D, Gardano L, Laguillier C, Lazarian G, Roger C, et al. Inhibitors of BCR signalling interrupt the survival signal mediated by the micro-environment in mantle cell lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 2014;136:2761–74.
Gold MR, Ingham RJ, McLeod SJ, Christian SL, Scheid MP, Duronio V, et al. Targets of B-cell antigen receptor signaling: the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling pathway and the Rap1 GTPase. Immunol Rev. 2000;176:47–68.
Dal Col J, Dolcetti R. GSK-3beta inhibition: at the crossroad between Akt and mTOR constitutive activation to enhance cyclin D1 protein stability in mantle cell lymphoma. Cell Cycle. 2008;7:2813–6.
Gold MR, Scheid MP, Santos L, Dang-Lawson M, Roth RA, Matsuuchi L, et al. The B cell antigen receptor activates the Akt (protein kinase B)/glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling pathway via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Immunol. 1999;163:1894–905.
Boukhiar MA, Roger C, Tran J, Gressin R, Martin A, Ajchenbaum-Cymbalista F, et al. Targeting early B-cell receptor signaling induces apoptosis in leukemic mantle cell lymphoma. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2013;2:4.
Bognar MK, Vincendeau M, Erdmann T, Seeholzer T, Grau M, Linnemann JR, et al. Oncogenic CARMA1 couples NF-kappaB and beta-catenin signaling in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Oncogene. 2016;35:4269–81.
Chen FE, Huang DB, Chen YQ, Ghosh G. Crystal structure of p50/p65 heterodimer of transcription factor NF-kappaB bound to DNA. Nature. 1998;391:410–3.
Raskatov JA, Meier JL, Puckett JW, Yang F, Ramakrishnan P, Dervan PB. Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent gene transcription using programmable DNA minor groove binders. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:1023–8.
Lepourcelet M, Chen YN, France DS, Wang H, Crews P, Petersen F, et al. Small-molecule antagonists of the oncogenic Tcf/beta-catenin protein complex. Cancer Cell. 2004;5:91–102.
Khan NI, Bradstock KF, Bendall LJ. Activation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway mediates growth and survival in B-cell progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2007;138:338–48.
Gandhirajan RK, Poll-Wolbeck SJ, Gehrke I, Kreuzer KA. Wnt/beta-catenin/LEF-1 signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): a target for current and potential therapeutic options. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2010;10:716–27.
Spaargaren M, de Rooij MF, Kater AP, Eldering E. BTK inhibitors in chronic leukemia: a glimpse to the future. Oncogene. 2015;34:2426–36.
Lindvall J, Islam TC. Interaction of Btk and Akt in B cell signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;293:1319–26.
de Rooij MF, Kuil A, Kater AP, Kersten MJ, Pals ST, Spaargaren M. Ibrutinib and idelalisib synergistically target BCR-controlled adhesion in MCL and CLL: a rationale for combination therapy. Blood. 2015;125:2306–9.
Sun Y, Campisi J, Higano C, Beer TM, Porter P, Coleman I, et al. Treatment-induced damage to the tumor microenvironment promotes prostate cancer therapy resistance through WNT16B. Nat Med. 2012;18:1359–68.
Sun Y, Zhu D, Chen F, Qian M, Wei H, Chen W, et al. SFRP2 augments WNT16B signaling to promote therapeutic resistance in the damaged tumor microenvironment. Oncogene. 2016;35:4321–34.
Lovatt M, Bijlmakers MJ. Stabilisation of beta-catenin downstream of T cell receptor signalling. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e12794.
Koopmans T, Eilers R, Menzen M, Halayko A, Gosens R. beta-catenin directs nuclear Factor-kappaB p65 output via CREB-binding protein/p300 in human airway smooth muscle. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1086.
Ma B, Hottiger MO. Crosstalk between Wnt/beta-Catenin and NF-kappaB signaling pathway during Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2016;7:378.
Valenta T, Hausmann G, Basler K. The many faces and functions of beta-catenin. EMBO J. 2012;31:2714–36.
Zhang X, Hao J. Development of anticancer agents targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Am J Cancer Res. 2015;5:2344–60.
Mathur R, Sehgal L, Braun FK, Berkova Z, Romaguerra J, Wang M, et al. Targeting Wnt pathway in mantle cell lymphoma-initiating cells. J Hematol Oncol. 2015;8:63.
Hallett RM, Kondratyev MK, Giacomelli AO, Nixon AM, Girgis-Gabardo A, Ilieva D, et al. Small molecule antagonists of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway target breast tumor-initiating cells in a Her2/Neu mouse model of breast cancer. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e33976.
Mazieres J, You L, He B, Xu Z, Lee AY, Mikami I, et al. Inhibition of Wnt16 in human acute lymphoblastoid leukemia cells containing the t(1;19) translocation induces apoptosis. Oncogene. 2005;24:5396–400.
Acknowledgements
CF was the recipient of a “Année Recherche” support from APHP. AQ was the recipient of a Jansen fellowship. This project was funded by a “Bonus Qualité Recherche” grant from University Paris 13 and benefited from the financial support of INSERM, University Paris 13 and the Labex INFLAMEX, contract ANR11 IDEX00502. We thank Dr C. Leroy for reading the manuscript, Dr L. Guittat for helpful discussion during the experimental work and Dr B. Papp for initiating collaboration with Dr P. Gelebart.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazarian, G., Friedrich, C., Quinquenel, A. et al. Stabilization of β-catenin upon B-cell receptor signaling promotes NF-kB target genes transcription in mantle cell lymphoma. Oncogene 39, 2934–2947 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-1183-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-1183-x
This article is cited by
-
PAX5 aberrant expression incorporated in MIPI-SP risk scoring system exhibits additive value in mantle cell lymphoma
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in uterine leiomyoma: role in tumor biology and targeting opportunities
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2021)
-
Interaction of NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathways in Alzheimer’s Disease and Potential Active Drug Treatments
Neurochemical Research (2021)