Abstract
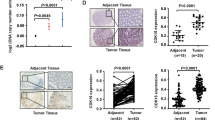
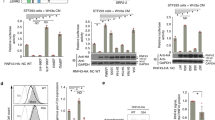
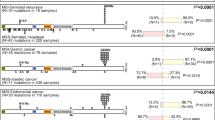
Wnt signaling dysregulation promotes tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer (CRC). We investigated the role of PTPRF, a receptor-type tyrosine phosphatase, in regulating Wnt signaling in CRC. Knockdown of PTPRF decreased cell proliferation in patient-derived primary colon cancer cells and established CRC cell lines. In addition, the rate of proliferation as well as colony formation ability were significantly decreased in tumor organoids grown in 3D, whereas the number of differentiated tumor organoids were markedly increased. Consistently, knockdown of PTPRF resulted in a decrease in the expression of genes associated with cancer stem cells downstream of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Treating PTPRF knockdown cells with GSK3 inhibitor rescued the expression of Wnt target genes suggesting that PTPRF functions upstream of the β-catenin destruction complex. PTPRF was found to interact with LRP6 and silencing PTPRF largely decreased the activation of LRP6. Interestingly, this PTPRF-mediated activation of Wnt signaling was blocked in cells treated with clathrin endocytosis inhibitor. Furthermore, knockdown of PTPRF inhibited xenograft tumor growth in vivo and decreased the expression of Wnt target genes. Taken together, our studies identify a novel role of PTPRF as an oncogenic protein phosphatase in supporting the activation of Wnt signaling in CRC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
29 July 2021
The name of B. Mark Evers was given incorrect in HTML version of the article. Correct is: Given name: B. Mark Family name: Evers
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30.
Smith RA, Andrews KS, Brooks D, Fedewa SA, Manassaram-Baptiste D, Saslow D, et al. Cancer screening in the United States, 2018: A review of current American Cancer Society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:297–316.
O’Connell JB, Maggard MA, Livingston EH, Yo CK. Colorectal cancer in the young. Am J Surg. 2004;187:343–8.
Reya T, Clevers H. Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature. 2005;434:843–50.
Schatoff EM, Leach BI, Dow LE. Wnt signaling and colorectal cancer. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep. 2017;13:101–10.
Niehrs C. The complex world of WNT receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:767–79.
Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–80.
Nusse R, Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell. 2017;169:985–99.
Komiya Y, Habas R. Wnt signal transduction pathways. Organogenesis. 2008;4:68–75.
Stamos JL, Weis WI. The beta-catenin destruction complex. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5:a007898.
Julien SG, Dube N, Hardy S, Tremblay ML. Inside the human cancer tyrosine phosphatome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:35–49.
Virshup DM, Shenolikar S. From promiscuity to precision: protein phosphatases get a makeover. Mol Cell. 2009;33:537–45.
Alonso A, Sasin J, Bottini N, Friedberg I, Friedberg I, Osterman A, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome. Cell. 2004;117:699–711.
Johnson KG, Van, Vactor D. Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases in nervous system development. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:1–24.
Barlan K, Cetera M, Horne-Badovinac S. Fat2 and Lar define a basally localized planar signaling system controlling collective cell migration. Dev Cell. 2017;40:467–77. e465.
Du WW, Fang L, Li M, Yang X, Liang Y, Peng C, et al. MicroRNA miR-24 enhances tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting PTPN9 and PTPRF to promote EGF signaling. J Cell Sci. 2013;126:1440–53.
Nunes-Xavier CE, Martin-Perez J, Elson A, Pulido R. Protein tyrosine phosphatases as novel targets in breast cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1836:211–26.
Levea CM, McGary CT, Symons JR, Mooney RA. PTP LAR expression compared to prognostic indices in metastatic and non-metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2000;64:221–8.
Wang Z, Shen D, Parsons DW, Bardelli A, Sager J, Szabo S, et al. Mutational analysis of the tyrosine phosphatome in colorectal cancers. Science. 2004;304:1164–6.
Bera R, Chiou CY, Yu MC, Peng JM, He CR, Hsu CY, et al. Functional genomics identified a novel protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type F-mediated growth inhibition in hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. 2014;59:2238–50.
DaSilva JO, Amorino GP, Casarez EV, Pemberton B, Parsons SJ. Neuroendocrine-derived peptides promote prostate cancer cell survival through activation of IGF-1R signaling. Prostate. 2013;73:801–12.
Bujko M, Kober P, Mikula M, Ligaj M, Ostrowski J, Siedlecki JA. Expression changes of cell-cell adhesion-related genes in colorectal tumors. Oncol Lett. 2015;9:2463–70.
Wen YA, Xiong X, Zaytseva YY, Napier DL, Vallee E, Li AT, et al. Downregulation of SREBP inhibits tumor growth and initiation by altering cellular metabolism in colon cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:265.
Streuli M, Krueger NX, Ariniello PD, Tang M, Munro JM, Blattler WA, et al. Expression of the receptor-linked protein tyrosine phosphatase LAR: proteolytic cleavage and shedding of the CAM-like extracellular region. EMBO J. 1992;11:897–907.
Barr AJ, Ugochukwu E, Lee WH, King ON, Filippakopoulos P, Alfano I, et al. Large-scale structural analysis of the classical human protein tyrosine phosphatome. Cell. 2009;136:352–63.
Wen YA, Xiong X, Harris JW, Zaytseva YY, Mitov MI, Napier DL, et al. Adipocytes activate mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and autophagy to promote tumor growth in colon cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8:e2593.
Kreso A, van Galen P, Pedley NM, Lima-Fernandes E, Frelin C, Davis T, et al. Self-renewal as a therapeutic target in human colorectal cancer. Nat Med. 2014;20:29–36.
Wu D, Pan W. GSK3: a multifaceted kinase in Wnt signaling. Trends Biochemical Sci. 2010;35:161–8.
Stewart K, Uetani N, Hendriks W, Tremblay ML, Bouchard M. Inactivation of LAR family phosphatase genes Ptprs and Ptprf causes craniofacial malformations resembling Pierre-Robin sequence. Development. 2013;140:3413–22.
Voloshanenko O, Erdmann G, Dubash TD, Augustin I, Metzig M, Moffa G, et al. Wnt secretion is required to maintain high levels of Wnt activity in colon cancer cells. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2610.
Flanagan DJ, Vincan E, Phesse TJ. Wnt signaling in cancer: not a binary ON:OFF switch. Cancer Res. 2019;79:5901–6.
Flanagan DJ, Barker N, Costanzo NSD, Mason EA, Gurney A, Meniel VS, et al. Frizzled-7 is required for Wnt signaling in gastric tumors with and without Apc mutations. Cancer Res. 2019;79:970–81.
Vermeulen L, Morrissey E, van der Heijden M, Nicholson AM, Sottoriva A, Buczacki S, et al. Defining stem cell dynamics in models of intestinal tumor initiation. Science. 2013;342:995–8.
Vermeulen L, De Sousa EMF, van der Heijden M, Cameron K, de Jong JH, Borovski T, et al. Wnt activity defines colon cancer stem cells and is regulated by the microenvironment. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12:468–76.
Yamamoto H, Komekado H, Kikuchi A. Caveolin is necessary for Wnt-3a-dependent internalization of LRP6 and accumulation of beta-catenin. Dev Cell. 2006;11:213–23.
Saito-Diaz K, Benchabane H, Tiwari A, Tian A, Li B, Thompson JJ, et al. APC inhibits ligand-independent Wnt signaling by the clathrin endocytic pathway. Dev Cell. 2018;44:566–81. e568.
Kim I, Pan W, Jones SA, Zhang Y, Zhuang X. Wu D. Clathrin and AP2 are required for PtdIns(4,5)P2-mediated formation of LRP6 signalosomes. J Cell Biol. 2013;200:419–28.
Hagemann AI, Kurz J, Kauffeld S, Chen Q, Reeves PM, Weber S, et al. In vivo analysis of formation and endocytosis of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling complex in zebrafish embryos. J Cell Sci. 2014;127:3970–82.
Mana G, Clapero F, Panieri E, Panero V, Bottcher RT, Tseng HY, et al. PPFIA1 drives active alpha5beta1 integrin recycling and controls fibronectin fibrillogenesis and vascular morphogenesis. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13546.
Tian X, Yang C, Yang L, Sun Q, Liu N. PTPRF as a novel tumor suppressor through deactivation of ERK1/2 signaling in gastric adenocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:7795–803.
Harder KW, Saw J, Miki N, Jirik F. Coexisting amplifications of the chromosome 1p32 genes (PTPRF and MYCL1) encoding protein tyrosine phosphatase LAR and L-myc in a small cell lung cancer line. Genomics. 1995;27:552–3.
Yang T, Zhang JS, Massa SM, Han X, Longo FM. Leukocyte common antigen-related tyrosine phosphatase receptor: increased expression and neuronal-type splicing in breast cancer cells and tissue. Mol Carcinogenesis. 1999;25:139–49.
Konishi N, Tsujikawa K, Yamamoto H, Ishida E, Nakamura M, Shimada K, et al. Overexpression of leucocyte common antigen (LAR) P-subunit in thyroid carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 2003;88:1223–8.
Soulieres D, Hirsch FR, Shepherd FA, Bordogna W, Delmar P, Shames DS, et al. PTPRF expression as a potential prognostic/predictive marker for treatment with erlotinib in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10:1364–9.
Liu J, Weiss HL, Rychahou P, Jackson LN, Evers BM, Gao T. Loss of PHLPP expression in colon cancer: role in proliferation and tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2009;28:994–1004.
Li X, Stevens PD, Liu J, Yang H, Wang W, Wang C et al. PHLPP is a negative regulator of RAF1, which reduces colorectal cancer cell motility and prevents tumor progression in mice. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:1301–12. e1301-1310.
Stevens PD, Wen YA, Xiong X, Zaytseva YY, Li AT, Wang C, et al. Erbin suppresses KSR1-mediated RAS/RAF signaling and tumorigenesis in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2018;78:4839–52.
Mao B, Wu W, Davidson G, Marhold J, Li M, Mechler BM, et al. Kremen proteins are Dickkopf receptors that regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Nature. 2002;417:664–7.
Chen M, Wang J, Lu J, Bond MC, Ren XR, Lyerly HK, et al. The anti-helminthic niclosamide inhibits Wnt/Frizzled1 signaling. Biochemistry. 2009;48:10267–74.
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:15545–50.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funding grants R01CA133429 (TG), R01CA208343 (BME and TG), T32CA160003 (BME), and F31CA196219 (PDS). This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Award (#1839289). The studies were conducted with support provided by the Biospecimen Procurement and Translational Pathology and Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Shared Resource Facilities of the University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center (P30CA177558) at the University of Kentucky.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, T., Stevens, A.T., Xiong, X. et al. Inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type F suppresses Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 39, 6789–6801 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01472-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01472-z
This article is cited by
-
Activation of Drp1 promotes fatty acids-induced metabolic reprograming to potentiate Wnt signaling in colon cancer
Cell Death & Differentiation (2022)
-
FSCN1 induced PTPRF-dependent tumor microenvironment inflammatory reprogramming promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression via regulating macrophagic glycolysis
Cellular Oncology (2022)