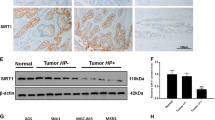
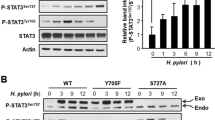
Abstract
Infection with Helicobacter pylori is one of the strongest risk factors for development of gastric cancer. Although these bacteria infect approximately half of the world’s population, only a small fraction of infected individuals develops gastric malignancies. Interactions between host and bacterial virulence factors are complex and interrelated, making it difficult to elucidate specific processes associated with H. pylori-induced tumorigenesis. In this study, we found that H. pylori inhibits p14ARF tumor suppressor by inducing its degradation. This effect was found to be strain-specific. Downregulation of p14ARF induced by H. pylori leads to inhibition of autophagy in a p53-independent manner in infected cells. We identified TRIP12 protein as E3 ubiquitin ligase that is upregulated by H. pylori, inducing ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of p14ARF protein. Using isogenic H. pylori mutants, we found that induction of TRIP12 is mediated by bacterial virulence factor CagA. Increased expression of TRIP12 protein was found in infected gastric epithelial cells in vitro and human gastric mucosa of H. pylori-infected individuals. In conclusion, our data demonstrate a new mechanism of ARF inhibition that may affect host–bacteria interactions and facilitate tumorigenic transformation in the stomach.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kodaman N, Pazos A, Schneider BG, Piazuelo MB, Mera R, Sobota RS, et al. Human and Helicobacter pylori coevolution shapes the risk of gastric disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:1455–60.
Odenbreit S, Puls J, Sedlmaier B, Gerland E, Fischer W, Haas R. Translocation of Helicobacter pylori CagA into gastric epithelial cells by type IV secretion. Science. 2000;287:1497–1500.
Zhu Y, Zhong X, Zheng S, Du Q, Xu W. Transformed immortalized gastric epithelial cells by virulence factor CagA of Helicobacter pylori through Erk mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Oncogene. 2005;24:3886–95.
Ohnishi N, Yuasa H, Tanaka S, Sawa H, Miura M, Matsui A, et al. Transgenic expression of Helicobacter pylori CagA induces gastrointestinal and hematopoietic neoplasms in mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:1003–8.
Sherr CJ. Ink4-Arf locus in cancer and aging. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2012;1:731–41.
Sato F, Meltzer SJ. CpG island hypermethylation in progression of esophageal and gastric cancer. Cancer. 2006;106:483–93.
Iida S, Akiyama Y, Nakajima T, Ichikawa W, Nihei Z, Sugihara K, et al. Alterations and hypermethylation of thep14(ARF) gene in gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 2000;87:654–8.
Kamijo T, Weber JD, Zambetti G, Zindy F, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ. Functional and physical interactions of the ARF tumor suppressor with p53 and Mdm2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:8292–7.
Wei J, Noto JM, Zaika E, Romero-Gallo J, Piazuelo MB, Schneider B, et al. Bacterial CagA protein induces degradation of p53 protein in a p14ARF-dependent manner. Gut. 2015;64:1040–8.
Sherr CJ, Bertwistle D, DENB W, Kuo ML, Sugimoto M, Tago K, et al. p53-Dependent and -independent functions of the Arf tumor suppressor. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2005;70:129–37.
Budina-Kolomets A, Hontz RD, Pimkina J, Murphy ME. A conserved domain in exon 2 coding for the human and murine ARF tumor suppressor protein is required for autophagy induction. Autophagy. 2013;9:1553–65.
Abida WM, Gu W. p53-Dependent and p53-independent activation of autophagy by ARF. Cancer Res. 2008;68:352–7.
Yang Z, Klionsky DJ. An overview of the molecular mechanism of autophagy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009;335:1–32.
Franco AT, Israel DA, Washington MK, Krishna U, Fox JG, Rogers AB, et al. Activation of beta-catenin by carcinogenic Helicobacter pylori. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:10646–51.
Fox JG, Rogers AB, Ihrig M, Taylor NS, Whary MT, Dockray G, et al. Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer in INS-GAS mice is gender specific. Cancer Res. 2003;63:942–50.
Mauvezin C, Neufeld TP. Bafilomycin A1 disrupts autophagic flux by inhibiting both V-ATPase-dependent acidification and Ca-P60A/SERCA-dependent autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Autophagy. 2015;11:1437–8.
Kuo ML, den Besten W, Sherr CJ. N-Terminal polyubiquitination of the ARF tumor suppressor, a natural lysine-less protein. Cell Cycle. 2004;3:1367–9.
Chen D, Shan J, Zhu WG, Qin J, Gu W. Transcription-independent ARF regulation in oncogenic stress-mediated p53 responses. Nature. 2010;464:624–7.
Ko A, Shin JY, Seo J, Lee KD, Lee EW, Lee MS, et al. Acceleration of gastric tumorigenesis through MKRN1-mediated posttranslational regulation of p14ARF. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104:1660–72.
Wang X, Zha M, Zhao X, Jiang P, Du W, Tam AY, et al. Siva1 inhibits p53 function by acting as an ARF E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1551.
Argent RH, Thomas RJ, Letley DP, Rittig MG, Hardie KR, Atherton JC. Functional association between the Helicobacter pylori virulence factors VacA and CagA. J Med Microbiol. 2008;57:145–50.
Brandt S, Kwok T, Hartig R, Konig W, Backert S. NF-kappaB activation and potentiation of proinflammatory responses by the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:9300–5.
Pimkina J, Murphy ME. ARF, autophagy and tumor suppression. Autophagy. 2009;5:397–9.
Reef S, Zalckvar E, Shifman O, Bialik S, Sabanay H, Oren M, et al. A short mitochondrial form of p19ARF induces autophagy and caspase-independent cell death. Mol Cell. 2006;22:463–75.
Balaburski GM, Hontz RD, Murphy ME. p53 and ARF: unexpected players in autophagy. Trends Cell Biol. 2010;20:363–9.
Buchholz M, Braun M, Heidenblut A, Kestler HA, Kloppel G, Schmiegel W, et al. Transcriptome analysis of microdissected pancreatic intraepithelial neoplastic lesions. Oncogene. 2005;24:6626–36.
Finak G, Bertos N, Pepin F, Sadekova S, Souleimanova M, Zhao H, et al. Stromal gene expression predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer. Nat Med. 2008;14:518–27.
Whitehead RH, Robinson PS. Establishment of conditionally immortalized epithelial cell lines from the intestinal tissue of adult normal and transgenic mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009;296:G455–460.
Peek RM Jr., Blaser MJ, Mays DJ, Forsyth MH, Cover TL, Song SY, et al. Helicobacter pylori strain-specific genotypes and modulation of the gastric epithelial cell cycle. Cancer Res. 1999;59:6124–31.
Treier M, Staszewski LM, Bohmann D. Ubiquitin-dependent c-Jun degradation in vivo is mediated by the delta domain. Cell. 1994;78:787–98.
Wei J, Nagy TA, Vilgelm A, Zaika E, Ogden SR, Romero-Gallo J, et al. Regulation of p53 tumor suppressor by Helicobacter pylori in gastric epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:1333–43.
N’Diaye EN, Kajihara KK, Hsieh I, Morisaki H, Debnath J, Brown EJ. PLIC proteins or ubiquilins regulate autophagy-dependent cell survival during nutrient starvation. EMBO Rep. 2009;10:173–9.
de Sablet T, Piazuelo MB, Shaffer CL, Schneider BG, Asim M, Chaturvedi R, et al. Phylogeographic origin of Helicobacter pylori is a determinant of gastric cancer risk. Gut. 2011;60:1189–95.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Maria B. Piazuelo and Alberto G. Delgado for help with tissue processing. This work was supported by grants from the National Cancer Institute CA206564, R01 CA138833, the Department of Veterans Affairs BX002115, Vanderbilt Ingram Cancer Center (P30 CA68485), and the Vanderbilt Digestive Disease Research Center (DK058404). The contents of this work are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the Department of Veterans Affairs, National Institutes of Health, Vanderbilt University, or University of Miami Health Centers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horvat, A., Noto, J.M., Ramatchandirin, B. et al. Helicobacter pylori pathogen regulates p14ARF tumor suppressor and autophagy in gastric epithelial cells. Oncogene 37, 5054–5065 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0343-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0343-8
This article is cited by
-
Role of Helicobacter pylori virulence factors and alteration of the Tumor Immune Microenvironment: challenges and opportunities for Cancer Immunotherapy
Archives of Microbiology (2024)
-
Helicobacter pylori-induced fibroblast-derived Serpin E1 promotes gastric cancer growth and peritoneal dissemination through p38 MAPK/VEGFA-mediated angiogenesis
Cancer Cell International (2023)
-
Enterobacteria impair host p53 tumor suppressor activity through mRNA destabilization
Oncogene (2022)
-
Manifold role of ubiquitin in Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
Inhibition of EZH2 and activation of ERRγ synergistically suppresses gastric cancer by inhibiting FOXM1 signaling pathway
Gastric Cancer (2021)