Abstract
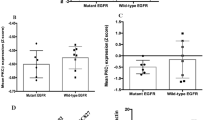
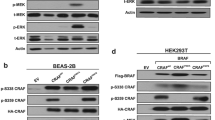
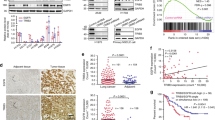
BRAF is one of the most frequently mutated genes across a number of different cancers, with the best-characterized mutation being V600E. Despite the successes of treating BRAF mutant V600E lung cancer with BRAF pathway inhibitors, treatment strategies targeting tumors with non-V600E mutations are yet to be established. We studied cellular signaling differences between lung cancers with different BRAF mutations and determined their sensitivities to BRAF pathway inhibitors. Here, we observed that MEK inhibition induced feedback activation of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) EGFR, and in some cases the RTK FGFR, resulting in transient suppression of ERK phosphorylation in BRAF non-V600E, but not BRAF V600E, mutant cells. Furthermore, we found that both EGFR and FGFR activated the MEK/ERK pathway, despite the presence of BRAF non-V600E mutations with elevated kinase activity. Moreover, in BRAF non-V600E mutants with impaired kinase activities, EGFR had even greater control over the MEK/ERK pathway, essentially contributing completely to the tonic mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signal. Accordingly, the combination of MEK inhibitor with EGFR inhibitor was effective at shrinking tumors in mouse model of BRAF non-V600E mutant lung cancer. Furthermore, the results were recapitulated with a clinically relevant dual inhibitor of EGFR and RAF, BGB-283. Overall, although BRAF V600E mutant cells are sensitive to BRAF inhibition, non-V600E mutant cancer cells are reliant on RTKs for their MAPK activation and inhibiting both MEK and RTKs are necessary in these cancers. Our findings provide evidence of critical survival signals in BRAF non-V600E mutant cancers, which could pave the way for effective treatment of these cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949–54.
Holderfield M, Deuker MM, McCormick F, McMahon M. Targeting RAF kinases for cancer therapy: BRAF-mutated melanoma and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 2014;14:455–67.
Paik PK, Arcila ME, Fara M, Sima CS, Miller VA, Kris MG, et al. Clinical characteristics of patients with lung adenocarcinomas harboring BRAF mutations. J Clin Oncol 2011;29:2046–51.
Marchetti A, Felicioni L, Malatesta S, Grazia Sciarrotta M, Guetti L, Chella A, et al. Clinical features and outcome of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring BRAF mutations. J Clin Oncol 2011;29:3574–9.
de Langen AJ, Smit EF. Therapeutic approach to treating patients with BRAF-mutant lung cancer: latest evidence and clinical implications. Ther Adv Med Oncol 2017;9:46–58.
Planchard D, Kim TM, Mazieres J, Quoix E, Riely G, Barlesi F, et al. Dabrafenib in patients with BRAF(V600E)-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a single-arm, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:642–50.
Planchard D, Besse B, Groen HJ, Souquet PJ, Quoix E, Baik CS, et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with previously treated BRAF(V600E)-mutant metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: an open-label, multicentre phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 2016;17:984–93.
Carter J, Tseng LH, Zheng G, Dudley J, Illei P, Gocke CD, et al. Non-p.V600E BRAF mutations are common using a more sensitive and broad detection tool. Am J Clin Pathol 2015;144:620–8.
Zheng G, Tseng LH, Chen G, Haley L, Illei P, Gocke CD, et al. Clinical detection and categorization of uncommon and concomitant mutations involving BRAF. BMC Cancer 2015;15:779.
Nguyen-Ngoc T, Bouchaab H, Adjei AA, Peters S. BRAF alterations as therapeutic targets in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2015;10:1396–403.
Wan PT, Garnett MJ, Roe SM, Lee S, Niculescu-Duvaz D, Good VM, et al. Mechanism of activation of the RAF-ERK signaling pathway by oncogenic mutations of B-RAF. Cell. 2004;116:855–67.
Yao Z, Torres NM, Tao A, Gao Y, Luo L, Li Q, et al. BRAF mutants evade ERK-dependent feedback by different mechanisms that determine their sensitivity to pharmacologic inhibition. Cancer Cell 2015;28:370–83.
Haling JR, Sudhamsu J, Yen I, Sideris S, Sandoval W, Phung W, et al. Structure of the BRAF-MEK complex reveals a kinase activity independent role for BRAF in MAPK signaling. Cancer Cell. 2014;26:402–13.
Pratilas CA, Hanrahan AJ, Halilovic E, Persaud Y, Soh J, Chitale D, et al. Genetic predictors of MEK dependence in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 2008;68:9375–83.
Dahlman KB, Xia J, Hutchinson K, Ng C, Hucks D, Jia P, et al. BRAF(L597) mutations in melanoma are associated with sensitivity to MEK inhibitors. Cancer Discov 2012;2:791–7.
Joshi M, Rice SJ, Liu X, Miller B, Belani CP. Trametinib with or without vemurafenib in BRAF mutated non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One 2015;10:e0118210.
Noeparast A, Teugels E, Giron P, Verschelden G, De Brakeleer S, Decoster L, et al. Non-V600 BRAF mutations recurrently found in lung cancer predict sensitivity to the combination of Trametinib and Dabrafenib. Oncotarget 2016;8:60094-60108.
Little AS, Balmanno K, Sale MJ, Newman S, Dry JR, Hampson M, et al. Amplification of the driving oncogene, KRAS or BRAF, underpins acquired resistance to MEK1/2 inhibitors in colorectal cancer cells. Sci Signal 2011;4:ra17.
Duncan JS, Whittle MC, Nakamura K, Abell AN, Midland AA, Zawistowski JS, et al. Dynamic reprogramming of the kinome in response to targeted MEK inhibition in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell. 2012;149:307–21.
Caunt CJ, Sale MJ, Smith PD, Cook SJ. MEK1 and MEK2 inhibitors and cancer therapy: the long and winding road. Nat Rev Cancer 2015;15:577–92.
Kitai H, Ebi H, Tomida S, Floros KV, Kotani H, Adachi Y, et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition defines feedback activation of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling induced by MEK inhibition in KRAS-mutant lung cancer. Cancer Discov 2016;6:754–69.
Bollag G, Tsai J, Zhang J, Zhang C, Ibrahim P, Nolop K, et al. Vemurafenib: the first drug approved for BRAF-mutant cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2012;11:873–86.
Garnett MJ, Edelman EJ, Heidorn SJ, Greenman CD, Dastur A, Lau KW, et al. Systematic identification of genomic markers of drug sensitivity in cancer cells. Nature. 2012;483:570–5.
Corcoran RB, Ebi H, Turke AB, Coffee EM, Nishino M, Cogdill AP, et al. EGFR-mediated re-activation of MAPK signaling contributes to insensitivity of BRAF mutant colorectal cancers to RAF inhibition with vemurafenib. Cancer Discov 2012;2:227–35.
Prahallad A, Sun C, Huang S, Di Nicolantonio F, Salazar R, Zecchin D, et al. Unresponsiveness of colon cancer to BRAF(V600E) inhibition through feedback activation of EGFR. Nature. 2012;483:100–3.
Montero-Conde C, Ruiz-Llorente S, Dominguez JM, Knauf JA, Viale A, Sherman EJ, et al. Relief of feedback inhibition of HER3 transcription by RAF and MEK inhibitors attenuates their antitumor effects in BRAF-mutant thyroid carcinomas. Cancer Discov 2013;3:520–33.
Lito P, Pratilas CA, Joseph EW, Tadi M, Halilovic E, Zubrowski M, et al. Relief of profound feedback inhibition of mitogenic signaling by RAF inhibitors attenuates their activity in BRAFV600E melanomas. Cancer Cell 2012;22:668–82.
Yao Z, Yaeger R, Rodrik-Outmezguine VS, Tao A, Torres NM, Chang MT, et al. Tumours with class 3 BRAF mutants are sensitive to the inhibition of activated RAS. Nature. 2017;548:234–8.
Nieto P, Ambrogio C, Esteban-Burgos L, Gomez-Lopez G, Blasco MT, Yao Z, et al. A Braf kinase-inactive mutant induces lung adenocarcinoma. Nature. 2017;548:239–43.
Garnett MJ, Rana S, Paterson H, Barford D, Marais R. Wild-type and mutant B-RAF activate C-RAF through distinct mechanisms involving heterodimerization. Mol Cell 2005;20:963–9.
Tang Z, Yuan X, Du R, Cheung SH, Zhang G, Wei J, et al. BGB-283, a novel RAF kinase and EGFR inhibitor, displays potent antitumor activity in BRAF-mutated colorectal cancers. Mol Cancer Ther 2015;14:2187–97.
Hatzivassiliou G, Song K, Yen I, Brandhuber BJ, Anderson DJ, Alvarado R, et al. RAF inhibitors prime wild-type RAF to activate the MAPK pathway and enhance growth. Nature. 2010;464:431–5.
Poulikakos PI, Persaud Y, Janakiraman M, Kong X, Ng C, Moriceau G, et al. RAF inhibitor resistance is mediated by dimerization of aberrantly spliced BRAF(V600E). Nature. 2011;480:387–90.
Blasco RB, Francoz S, Santamaria D, Canamero M, Dubus P, Charron J, et al. c-Raf, but not B-Raf, is essential for development of K-Ras oncogene-driven non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2011;19:652–63.
Karreth FA, Frese KK, DeNicola GM, Baccarini M, Tuveson DA. C-Raf is required for the initiation of lung cancer by K-Ras(G12D). Cancer Discov 2011;1:128–36.
Lito P, Saborowski A, Yue J, Solomon M, Joseph E, Gadal S, et al. Disruption of CRAF-mediated MEK activation is required for effective MEK inhibition in KRAS mutant tumors. Cancer Cell 2014;25:697–710.
Lin L, Asthana S, Chan E, Bandyopadhyay S, Martins MM, Olivas V, et al. Mapping the molecular determinants of BRAF oncogene dependence in human lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci Usa 2014;111:E748–E757.
De Roock W, Claes B, Bernasconi D, De Schutter J, Biesmans B, Fountzilas G, et al. Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS, and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: a retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol 2010;11:753–62.
Heidorn SJ, Milagre C, Whittaker S, Nourry A, Niculescu-Duvas I, Dhomen N, et al. Kinase-dead BRAF and oncogenic RAS cooperate to drive tumor progression through CRAF. Cell. 2010;140:209–21.
Van Cutsem E, Atreya CE, Andre T, Bendell JC, Schellens J,Gordon M, et al. Updated Results of the MEK inhibitor trametinib (T), BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib (D), and anti-EGFR antibody panitumumab (P) in patients (pts) with BRAF V600E mutated (BRAFm) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Ann Oncol. 2015;26(4 Suppl):iv119.
Desai J, Gan H, Barrow C, Jameson MB, Solomon B, Atkinson V, et al. A Phase IB study of RAF dimer inhibitor BGB-283 in patients with B-RAF or K-RAS/N-RAS mutated solid tumors. AACR Annual Meeting; 2017. CT-002 2017.
Laquerre S, Arnone M, Moss K, Yang J, Fisher K, Kane-Carson LS, et al. A selective RAF kinase inhibitor induces cell death and tumor regression of human cancer cell lines encoding B-RAFV600E mutation Mol Cancer Ther 2009;8(12 Suppl):B88.
Okimoto RA, Lin L, Olivas V, Chan E, Markegard E, Rymar A, et al. Preclinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor that evades paradoxical MAPK pathway activation in protein kinase BRAF-mutant lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci Usa 2016;113:13456–61.
Team RC. A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2016.
Bates DM, Maechler M, Bolker B. lme4: linear mixed-effects models using S4 classes. R package version 0999999-0. 2012.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (H. Ebi, 26830105 and 16K07164; S. Yano, 21390256) from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and Grant-in-Aid to Project for Cancer Research and Therapeutics Evolution (P-CREATE) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (H. Ebi and S.Yano, 16cm0106513h0001). A.C.F. is a George and Lavinia Blick Scholar and a Harrison Endowed Scholar in Cancer Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotani, H., Adachi, Y., Kitai, H. et al. Distinct dependencies on receptor tyrosine kinases in the regulation of MAPK signaling between BRAF V600E and non-V600E mutant lung cancers. Oncogene 37, 1775–1787 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0035-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0035-9
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic landscape and future direction of metastatic colorectal cancer
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2023)
-
Clinical application of a lung cancer organoid (tumoroid) culture system
npj Precision Oncology (2021)
-
Inhibition of EGFR signaling with Spautin-1 represents a novel therapeutics for prostate cancer
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
Targeting EGFR and RAS/RAF Signaling in the Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: From Current Treatment Strategies to Future Perspectives
Drugs (2019)