Abstract
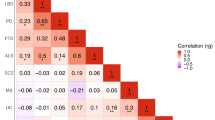
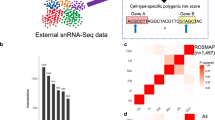
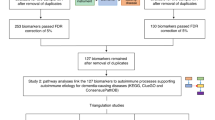
The occurrence of immune disease comorbidities in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has been observed in both epidemiological and molecular studies, suggesting a neuroinflammatory basis in AD. However, their shared genetic components have not been systematically studied. Here, we composed an atlas of the shared genetic associations between 11 immune-mediated diseases and AD by analyzing genome-wide association studies (GWAS) summary statistics. Our results unveiled a significant genetic overlap between AD and 11 individual immune-mediated diseases despite negligible genetic correlations, suggesting a complex shared genetic architecture distributed across the genome. The shared loci between AD and immune-mediated diseases implicated several genes, including GRAMD1B, FUT2, ADAMTS4, HBEGF, WNT3, TSPAN14, DHODH, ABCB9, and TNIP1, all of which are protein-coding genes and thus potential drug targets. Top biological pathways enriched with these identified shared genes were related to the immune system and cell adhesion. In addition, in silico single-cell analyses showed enrichment of immune and brain cells, including neurons and microglia. In summary, our results suggest a genetic relationship between AD and the 11 immune-mediated diseases, pinpointing the existence of a shared however non-causal genetic basis. These identified protein-coding genes have the potential to serve as a novel path to therapeutic interventions for both AD and immune-mediated diseases and their comorbidities.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the GWAS summary statistics data used in this study are publicly available to download from https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/home and https://atlas.ctglab.nl/.
References
Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2021;17:327–406.
Gatz M, Reynolds CA, Fratiglioni L, Johansson B, Mortimer JA, Berg S, et al. Role of genes and environments for explaining Alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63:168–74.
Heneka MT, Carson MJ, El Khoury J, Landreth GE, Brosseron F, Feinstein DL, et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14:388–405.
Jorfi M, Maaser-Hecker A, Tanzi RE. The neuroimmune axis of Alzheimer’s disease. Genome Med. 2023;15:6.
Podlesny-Drabiniok A, Marcora E, Goate AM. Microglial phagocytosis: a disease-associated process emerging from Alzheimer’s disease genetics. Trends Neurosci. 2020;43:965–79.
Olah M, Menon V, Habib N, Taga MF, Ma Y, Yung CJ, et al. Single cell RNA sequencing of human microglia uncovers a subset associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Commun. 2020;11:6129.
Bettcher BM, Tansey MG, Dorothee G, Heneka MT. Peripheral and central immune system crosstalk in Alzheimer disease - a research prospectus. Nat Rev Neurol. 2021;17:689–701.
Stephenson J, Nutma E, van der Valk P, Amor S. Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology. 2018;154:204–19.
Huang J, Su B, Karhunen V, Gill D, Zuber V, Ahola-Olli A, et al. Inflammatory diseases, inflammatory biomarkers, and Alzheimer disease: an observational analysis and Mendelian randomization. Neurology. 2023;100:e568–81.
Liu L, Chen ST, Li HJ, Qiang Y, Sun XY, Zhou YQ, et al. Association between Psoriasis and Dementia: current evidence. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020;12:570992.
Zhang B, Wang HE, Bai YM, Tsai SJ, Su TP, Chen TJ, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with higher dementia risk: a nationwide longitudinal study. Gut. 2021;70:85–91.
Yokoyama JS, Wang Y, Schork AJ, Thompson WK, Karch CM, Cruchaga C, et al. Association between genetic traits for immune-mediated diseases and Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol. 2016;73:691–7.
Wightman DP, Jansen IE, Savage JE, Shadrin AA, Bahrami S, Holland D, et al. A genome-wide association study with 1,126,563 individuals identifies new risk loci for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet. 2021;53:1276–82.
Watanabe K, Stringer S, Frei O, Umicevic Mirkov M, de Leeuw C, Polderman TJC, et al. A global overview of pleiotropy and genetic architecture in complex traits. Nat Genet. 2019;51:1339–48.
Paternoster L, Standl M, Waage J, Baurecht H, Hotze M, Strachan DP, et al. Multi-ancestry genome-wide association study of 21,000 cases and 95,000 controls identifies new risk loci for atopic dermatitis. Nat Genet. 2015;47:1449–56.
Dubois PC, Trynka G, Franke L, Hunt KA, Romanos J, Curtotti A, et al. Multiple common variants for celiac disease influencing immune gene expression. Nat Genet. 2010;42:295–302.
de Lange KM, Moutsianas L, Lee JC, Lamb CA, Luo Y, Kennedy NA, et al. Genome-wide association study implicates immune activation of multiple integrin genes in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Genet. 2017;49:256–61.
Ji SG, Juran BD, Mucha S, Folseraas T, Jostins L, Melum E, et al. Genome-wide association study of primary sclerosing cholangitis identifies new risk loci and quantifies the genetic relationship with inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Genet. 2017;49:269–73.
Okada Y, Wu D, Trynka G, Raj T, Terao C, Ikari K, et al. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis contributes to biology and drug discovery. Nature. 2014;506:376–81.
Bentham J, Morris DL, Graham DSC, Pinder CL, Tombleson P, Behrens TW, et al. Genetic association analyses implicate aberrant regulation of innate and adaptive immunity genes in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 2015;47:1457–64.
Jin Y, Andersen G, Yorgov D, Ferrara TM, Ben S, Brownson KM, et al. Genome-wide association studies of autoimmune vitiligo identify 23 new risk loci and highlight key pathways and regulatory variants. Nat Genet. 2016;48:1418–24.
Kurki MI, Karjalainen J, Palta P, Sipilä TP, Kristiansson K, Donner K, et al. FinnGen: unique genetic insights from combining isolated population and national health register data. MedRxiv 2022:2022.2003. 2003.22271360.
Bulik-Sullivan BK, Loh PR, Finucane HK, Ripke S, Yang J, Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics C, et al. LD Score regression distinguishes confounding from polygenicity in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet. 2015;47:291–5.
Frei O, Holland D, Smeland OB, Shadrin AA, Fan CC, Maeland S, et al. Bivariate causal mixture model quantifies polygenic overlap between complex traits beyond genetic correlation. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2417.
Andreassen OA, Desikan RS, Wang Y, Thompson WK, Schork AJ, Zuber V, et al. Abundant genetic overlap between blood lipids and immune-mediated diseases indicates shared molecular genetic mechanisms. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0123057.
Andreassen OA, Djurovic S, Thompson WK, Schork AJ, Kendler KS, O’Donovan MC, et al. Improved detection of common variants associated with schizophrenia by leveraging pleiotropy with cardiovascular-disease risk factors. Am J Hum Genet. 2013;92:197–209.
Bedre R. reneshbedre/bioinfokit: Bioinformatics data analysis and visualization toolkit. Zenodo March 2020;5 (10.5281).
Smeland OB, Frei O, Shadrin A, O’Connell K, Fan CC, Bahrami S, et al. Discovery of shared genomic loci using the conditional false discovery rate approach. Hum Genet. 2020;139:85–94.
Schwartzman A, Lin X. The effect of correlation in false discovery rate estimation. Biometrika. 2011;98:199–214.
Werme J, van der Sluis S, Posthuma D, de Leeuw CA. An integrated framework for local genetic correlation analysis. Nat Genet. 2022;54:274–82.
Lambert JC, Grenier-Boley B, Chouraki V, Heath S, Zelenika D, Fievet N, et al. Implication of the immune system in Alzheimer’s disease: evidence from genome-wide pathway analysis. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;20:1107–18.
Scheltens P, Blennow K, Breteler MM, de Strooper B, Frisoni GB, Salloway S, et al. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 2016;388:505–17.
de Bakker PI, Raychaudhuri S. Interrogating the major histocompatibility complex with high-throughput genomics. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:R29–36.
Jia P, Wang L, Fanous AH, Chen X, Kendler KS, International Schizophrenia C. et al. A bias-reducing pathway enrichment analysis of genome-wide association data confirmed association of the MHC region with schizophrenia. J Med Genet. 2012;49:96–103.
Buniello A, MacArthur JAL, Cerezo M, Harris LW, Hayhurst J, Malangone C, et al. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog of published genome-wide association studies, targeted arrays and summary statistics 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:D1005–12.
Drange OK, Smeland OB, Shadrin AA, Finseth PI, Witoelar A, Frei O, et al. Genetic overlap between Alzheimer’s disease and bipolar disorder implicates the MARK2 and VAC14 genes. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:220.
Monereo-Sanchez J, Schram MT, Frei O, O’Connell K, Shadrin AA, Smeland OB, et al. Genetic overlap between Alzheimer’s disease and depression mapped onto the brain. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:653130.
Fominykh V, Shadrin AA, Jaholkowski PP, Bahrami S, Athanasiu L, Wightman DP, et al. Shared genetic loci between Alzheimer’s disease and multiple sclerosis: crossroads between neurodegeneration and immune system. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;183:106174.
Watanabe K, Taskesen E, van Bochoven A, Posthuma D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1826.
Clarke L, Fairley S, Zheng-Bradley X, Streeter I, Perry E, Lowy E, et al. The International Genome sample resource (IGSR): a worldwide collection of genome variation incorporating the 1000 Genomes Project data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45:D854–9.
Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H. ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:e164.
Rentzsch P, Witten D, Cooper GM, Shendure J, Kircher M. CADD: predicting the deleteriousness of variants throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:D886–94.
Boyle AP, Hong EL, Hariharan M, Cheng Y, Schaub MA, Kasowski M, et al. Annotation of functional variation in personal genomes using RegulomeDB. Genome Res. 2012;22:1790–7.
Pei G, Hu R, Jia P, Zhao Z. DeepFun: a deep learning sequence-based model to decipher non-coding variant effect in a tissue- and cell type-specific manner. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:W131–9.
Dai Y, Hu R, Liu A, Cho KS, Manuel AM, Li X, et al. WebCSEA: web-based cell-type-specific enrichment analysis of genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:W782–90.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B (Methodol). 2018;57:289–300.
Davies NM, Holmes MV, Davey Smith G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ. 2018;362:k601.
Hemani G, Zheng J, Elsworth B, Wade KH, Haberland V, Baird D, et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife. 2018;7.
Yeung CHC, Au Yeung SL, Schooling CM. Association of autoimmune diseases with Alzheimer’s disease: a Mendelian randomization study. J Psychiatr Res. 2022;155:550–8.
Andersen JP, Zhang J, Sun H, Liu X, Liu J, Nie J, et al. Aster-B coordinates with Arf1 to regulate mitochondrial cholesterol transport. Mol Metab. 2020;42:101055.
Rausch P, Rehman A, Kunzel S, Hasler R, Ott SJ, Schreiber S, et al. Colonic mucosa-associated microbiota is influenced by an interaction of Crohn disease and FUT2 (Secretor) genotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:19030–5.
Wacklin P, Makivuokko H, Alakulppi N, Nikkila J, Tenkanen H, Rabina J, et al. Secretor genotype (FUT2 gene) is strongly associated with the composition of Bifidobacteria in the human intestine. PLoS One. 2011;6:e20113.
Wacklin P, Tuimala J, Nikkila J, Sebastian T, Makivuokko H, Alakulppi N, et al. Faecal microbiota composition in adults is associated with the FUT2 gene determining the secretor status. PLoS One. 2014;9:e94863.
Wu S, Liu X, Jiang R, Yan X, Ling Z. Roles and mechanisms of gut microbiota in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:650047.
Bairamian D, Sha S, Rolhion N, Sokol H, Dorothee G, Lemere CA, et al. Microbiota in neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction: a focus on Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2022;17:19.
Matsuzaki M, Yokoyama M, Yoshizawa Y, Kaneko N, Naito H, Kobayashi H, et al. ADAMTS4 is involved in the production of the Alzheimer disease amyloid biomarker APP669-711. Mol Psychiatry. 2023;28:1802–12.
Walter S, Jumpertz T, Huttenrauch M, Ogorek I, Gerber H, Storck SE, et al. The metalloprotease ADAMTS4 generates N-truncated Abeta4-x species and marks oligodendrocytes as a source of amyloidogenic peptides in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;137:239–57.
Scialo F, Fernandez-Ayala DJ, Sanz A. Role of mitochondrial reverse electron transport in ROS signaling: potential roles in health and disease. Front Physiol. 2017;8:428.
da Rocha JF, Bastos L, Domingues SC, Bento AR, Konietzko U, da Cruz ESOAB, et al. APP binds to the EGFR ligands HB-EGF and EGF, acting synergistically with EGF to promote ERK signaling and neuritogenesis. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58:668–88.
Sasaki K, Omotuyi OI, Ueda M, Shinohara K, Ueda H. NMDA receptor agonists reverse impaired psychomotor and cognitive functions associated with hippocampal Hbegf-deficiency in mice. Mol Brain. 2015;8:83.
Jin K, Sun Y, Xie L, Batteur S, Mao XO, Smelick C, et al. Neurogenesis and aging: FGF-2 and HB-EGF restore neurogenesis in hippocampus and subventricular zone of aged mice. Aging Cell. 2003;2:175–83.
Oyagi A, Hara H. Essential roles of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor in the brain. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2012;18:803–10.
Adelaja A, Hoffmann A. Signaling crosstalk mechanisms that may fine-tune pathogen-responsive NFkappaB. Front Immunol. 2019;10:433.
Jones SV, Kounatidis I. Nuclear factor-Kappa B and Alzheimer disease, unifying genetic and environmental risk factors from cell to humans. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1805.
Sun Y, Zhu J, Zhou D, Canchi S, Wu C, Cox NJ, et al. A transcriptome-wide association study of Alzheimer’s disease using prediction models of relevant tissues identifies novel candidate susceptibility genes. Genome Med. 2021;13:141.
Wang XL, Li L. Cell type-specific potential pathogenic genes and functional pathways in Alzheimer’s Disease. BMC Neurol. 2021;21:381.
Nakajima T, Fujino S, Nakanishi G, Kim YS, Jetten AM. TIP27: a novel repressor of the nuclear orphan receptor TAK1/TR4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:4194–204.
Driedonks TAP. Nolte-‘t Hoen ENM. Circulating Y-RNAs in extracellular vesicles and ribonucleoprotein complexes; implications for the immune system. Front Immunol. 2018;9:3164.
Scheckel C, Drapeau E, Frias MA, Park CY, Fak J, Zucker-Scharff I et al. Regulatory consequences of neuronal ELAV-like protein binding to coding and non-coding RNAs in human brain. Elife. 2016;5.
Malik U, Javed A, Ali A, Asghar K. Structural and functional annotation of human FAM26F: a multifaceted protein having a critical role in the immune system. Gene. 2017;597:66–75.
Owen KA, Grammer AC, Lipsky PE. Deconvoluting the heterogeneity of SLE: The contribution of ancestry. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149:12–23.
Yin X, Kim K, Suetsugu H, Bang SY, Wen L, Koido M, et al. Meta-analysis of 208370 East Asians identifies 113 susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:632–40.
Hitomi Y, Nakamura M. The genetics of primary biliary cholangitis: a GWAS and Post-GWAS update. Genes (Basel). 2023;14.
Acknowledgements
We thank those investigators who generated and shared the genetic datasets used in the present study.
Funding
This research was partially supported by National Institutes of Health grants awarded to ZZ (R01LM012806, R01LM012806-07S1, R03AG077191, and U01AG079847). We thanked the resource support from Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT RP180734). OAA is supported by the Research Council of Norway (#324499, #324252, #223273), South-East Norway Health Authority (2022-073), KG Jebsen Stiftelsen, Norwegian Health Association (#22731), and EU Horizon 2020 (# 847776). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NE, BSF, YD, and ZZ designed the study and collected the data. NE, SB, and YD performed the analyses. NE, BSF, OAA, and SB contributed to the literature search. NE, BSF, YD, and ZZ drafted the initial manuscript and all the authors contributed to data interpretation and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
OAA is a consultant to Cortechs.ai, and has received speaker’s honoraria from Lundbeck, Janssen and Sunovion. NE, BSF, SB, YD, and ZZ have nothing to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Enduru, N., Fernandes, B.S., Bahrami, S. et al. Genetic overlap between Alzheimer’s disease and immune-mediated diseases: an atlas of shared genetic determinants and biological convergence. Mol Psychiatry (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-024-02510-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-024-02510-y