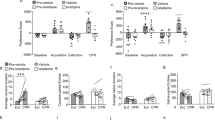
Abstract
Remote memory usually decreases over time, whereas remote drug-cue associated memory exhibits enhancement, increasing the risk of relapse during abstinence. Memory system consolidation is a prerequisite for remote memory formation, but neurobiological underpinnings of the role of consolidation in the enhancement of remote drug memory are unclear. Here, we found that remote cocaine-cue associated memory was enhanced in rats that underwent self-administration training, together with a progressive increase in the response of prelimbic cortex (PrL) CaMKII neurons to cues. System consolidation was required for the enhancement of remote cocaine memory through PrL CaMKII neurons during the early period post-training. Furthermore, dendritic spine maturation in the PrL relied on the basolateral amygdala (BLA) input during the early period of consolidation, contributing to remote memory enhancement. These findings indicate that memory consolidation drives the enhancement of remote cocaine memory through a time-dependent increase in activity and maturation of PrL CaMKII neurons receiving a sustained BLA input.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ryan TJ, Frankland PW. Forgetting as a form of adaptive engram cell plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022;23:173–86.
Xue YX, Deng JH, Chen YY, Zhang LB, Wu P, Huang GD, et al. Effect of selective inhibition of reactivated nicotine-associated memories with propranolol on nicotine craving. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:224–32.
Wright WJ, Graziane NM, Neumann PA, Hamilton PJ, Cates HM, Fuerst L, et al. Silent synapses dictate cocaine memory destabilization and reconsolidation. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23:32–46.
Shin CB, Templeton TJ, Chiu AS, Kim J, Gable ES, Vieira PA, et al. Endogenous glutamate within the prelimbic and infralimbic cortices regulates the incubation of cocaine-seeking in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2018;128:293–300.
Ma YY, Lee BR, Wang X, Guo C, Liu L, Cui R, et al. Bidirectional modulation of incubation of cocaine craving by silent synapse-based remodeling of prefrontal cortex to accumbens projections. Neuron. 2014;83:1453–67.
Parvaz MA, Moeller SJ, Goldstein RZ. Incubation of cue-induced craving in adults addicted to cocaine measured by electroencephalography. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73:1127–34.
Frankland PW, Bontempi B. The organization of recent and remote memories. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:119–30.
Fukushima H, Zhang Y, Archbold G, Ishikawa R, Nader K, Kida S. Enhancement of fear memory by retrieval through reconsolidation. Elife. 2014;3:e02736.
Kitamura T, Ogawa SK, Roy DS, Okuyama T, Morrissey MD, Smith LM, et al. Engrams and circuits crucial for systems consolidation of a memory. Science. 2017;356:73–78.
Lee JH, Kim WB, Park EH, Cho JH. Neocortical synaptic engrams for remote contextual memories. Nat Neurosci. 2023;26:259–73.
Dixsaut L, Graff J. Brain-wide screen of prelimbic cortex inputs reveals a functional shift during early fear memory consolidation. Elife. 2022;11:e78542.
Kol A, Adamsky A, Groysman M, Kreisel T, London M, Goshen I. Astrocytes contribute to remote memory formation by modulating hippocampal-cortical communication during learning. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23:1229–39.
Rich MT, Huang YH, Torregrossa MM. Plasticity at thalamo-amygdala synapses regulates cocaine-cue memory formation and extinction. Cell Rep. 2019;26:1010–20.
Hsiang HL, Epp JR, van den Oever MC, Yan C, Rashid AJ, Insel N, et al. Manipulating a “cocaine engram” in mice. J Neurosci. 2014;34:14115–27.
Xue YX, Luo YX, Wu P, Shi HS, Xue LF, Chen C, et al. A memory retrieval-extinction procedure to prevent drug craving and relapse. Science. 2012;336:241–5.
Luo YX, Xue YX, Liu JF, Shi HS, Jian M, Han Y, et al. A novel UCS memory retrieval-extinction procedure to inhibit relapse to drug seeking. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7675–89.
Bruno CA, O’Brien C, Bryant S, Mejaes JI, Estrin DJ, Pizzano C, et al. pMAT: An open-source software suite for the analysis of fiber photometry data. Pharm Biochem Behav. 2021;201:173093.
Lu L, Uejima JL, Gray SM, Bossert JM, Shaham Y. Systemic and central amygdala injections of the mGluR(2/3) agonist LY379268 attenuate the expression of incubation of cocaine craving. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;61:591–8.
Lu L, Wang X, Wu P, Xu C, Zhao M, Morales M, et al. Role of ventral tegmental area glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in incubation of cocaine craving. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;66:137–45.
Wang C, Yue H, Hu Z, Shen Y, Ma J, Li J, et al. Microglia mediate forgetting via complement-dependent synaptic elimination. Science. 2020;367:688–94.
Sebastian V, Estil JB, Chen D, Schrott LM, Serrano PA. Acute physiological stress promotes clustering of synaptic markers and alters spine morphology in the hippocampus. PLoS One. 2013;8:e79077.
Muller CP, Quednow BB, Lourdusamy A, Kornhuber J, Schumann G, Giese KP. CaM Kinases: From memories to addiction. Trends Pharm Sci. 2016;37:153–66.
DeNardo LA, Liu CD, Allen WE, Adams EL, Friedmann D, Fu L, et al. Temporal evolution of cortical ensembles promoting remote memory retrieval. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:460–9.
Xia F, Richards BA, Tran MM, Josselyn SA, Takehara-Nishiuchi K, Frankland PW. Parvalbumin-positive interneurons mediate neocortical-hippocampal interactions that are necessary for memory consolidation. Elife. 2017;6:1–25.
Gomez JL, Bonaventura J, Lesniak W, Mathews WB, Sysa-Shah P, Rodriguez LA, et al. Chemogenetics revealed: DREADD occupancy and activation via converted clozapine. Science. 2017;357:503–7.
Tye KM, Janak PH. Amygdala neurons differentially encode motivation and reinforcement. J Neurosci. 2007;27:3937–45.
Klavir O, Prigge M, Sarel A, Paz R, Yizhar O. Manipulating fear associations via optogenetic modulation of amygdala inputs to prefrontal cortex. Nat Neurosci. 2017;20:836–44.
Carelli RM, Williams JG, Hollander JA. Basolateral amygdala neurons encode cocaine self-administration and cocaine-associated cues. J Neurosci. 2003;23:8204–11.
Josselyn SA, Tonegawa S. Memory engrams: Recalling the past and imagining the future. Science. 2020;367:eaaw4325.
Ebrahimi S, Okabe S. Structural dynamics of dendritic spines: Molecular composition, geometry and functional regulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1838:2391–8.
Gawin FHKH. Abstinence symptomatology and psychiatric diagnosis in cocaine abusers. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1986;43:107–13.
Grimm JW, Hope BT, Wise RA, Shaham Y. Incubation of cocaine craving after withdrawal. Nature. 2001;412:141–2.
Liu X, Yuan K, Lu T, Lin X, Zheng W, Xue Y, et al. Preventing incubation of drug craving to treat drug relapse: From bench to bedside. Mol Psychiatry. 2023;28:1415–29.
Venniro M, Reverte I, Ramsey LA, Papastrat KM, D’Ottavio G, Milella MS, et al. Factors modulating the incubation of drug and non-drug craving and their clinical implications. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;131:847–64.
Bedi G, Preston KL, Epstein DH, Heishman SJ, Marrone GF, Shaham Y, et al. Incubation of cue-induced cigarette craving during abstinence in human smokers. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;69:708–11.
Wang G, Shi J, Chen N, Xu L, Li J, Li P, et al. Effects of length of abstinence on decision-making and craving in methamphetamine abusers. PLoS One. 2013;8:1–7.
Li P, Wu P, Xin X, Fan YL, Wang GB, Wang F, et al. Incubation of alcohol craving during abstinence in patients with alcohol dependence. Addict Biol. 2015;20:513–22.
Grant S, London ED, Newlin DB, Villemagne VL, Liu X, Contoreggi C, et al. Activation of memory circuits during cue-elicited cocaine craving. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:12040–5.
Yue JL, Yuan K, Bao YP, Meng SQ, Shi L, Fang Q, et al. The effect of a methadone-initiated memory reconsolidation updating procedure in opioid use disorder: A translational study. EBioMedicine. 2022;85:104283.
Tronson NC, Taylor JR. Addiction: A drug-induced disorder of memory reconsolidation. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013;23:573–80.
Grimm JW, Harkness JH, Ratliff C, Barnes J, North K, Collins S. Effects of systemic or nucleus accumbens-directed dopamine D1 receptor antagonism on sucrose seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology. 2011;216:219–33.
Pickens CL, Golden SA, Adams-Deutsch T, Nair SG, Shaham Y. Long-lasting incubation of conditioned fear in rats. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;65:881–6.
Matos MR, Visser E, Kramvis I, van der Loo RJ, Gebuis T, Zalm R, et al. Memory strength gates the involvement of a CREB-dependent cortical fear engram in remote memory. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2315.
Galaj E, Ranaldi R. Neurobiology of reward-related learning. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021;124:224–34.
Gueye AB, Allain F, Samaha AN. Intermittent intake of rapid cocaine injections promotes the risk of relapse and increases mesocorticolimbic BDNF levels during abstinence. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019;44:1027–35.
Markou A, Li J, Tse K, Li X. Cue-induced nicotine-seeking behavior after withdrawal with or without extinction in rats. Addict Biol. 2018;23:111–9.
Hyman SE, Malenka RC. Addiction and the brain: The neurobiology of compulsion and its persistence. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:695–703.
Yehuda R, Hoge CW, McFarlane AC, Vermetten E, Lanius RA, Nievergelt CM, et al. Post-traumatic stress disorder. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2015;1:15057.
Lesburgueres E, Gobbo OL, Alaux-Cantin S, Hambucken A, Trifilieff P, Bontempi B. Early tagging of cortical networks is required for the formation of enduring associative memory. Science. 2011;331:924–8.
Squire LR, Genzel L, Wixted JT, Morris RG. Memory consolidation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7:a021766.
West EA, Saddoris MP, Kerfoot EC, Carelli RM. Prelimbic and infralimbic cortical regions differentially encode cocaine-associated stimuli and cocaine-seeking before and following abstinence. Eur J Neurosci. 2014;39:1891–902.
Nicolas C, Russell TI, Pierce AF, Maldera S, Holley A, You ZB, et al. Incubation of cocaine craving after intermittent-access self-administration: Sex differences and estrous cycle. Biol Psychiatry. 2019;85:915–24.
Ferreira R, Brandao ML, Nobre MJ. 5-HT1A receptors of the prelimbic cortex mediate the hormonal impact on learned fear expression in high-anxious female rats. Horm Behav. 2016;84:84–96.
Everitt BJ, Robbins TW. Neural systems of reinforcement for drug addiction: From actions to habits to compulsion. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:1481–9.
Janak PH, Tye KM. From circuits to behaviour in the amygdala. Nature. 2015;517:284–92.
Lu L, Hope BT, Dempsey J, Liu SY, Bossert JM, Shaham Y. Central amygdala ERK signaling pathway is critical to incubation of cocaine craving. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:212–9.
Tonegawa S, Morrissey MD, Kitamura T. The role of engram cells in the systems consolidation of memory. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018;19:485–98.
Barrientos C, Knowland D, Wu MMJ, Lilascharoen V, Huang KW, Malenka RC, et al. Cocaine-induced structural plasticity in input regions to distinct cell types in nucleus accumbens. Biol Psychiatry. 2018;84:893–904.
Mashhoon Y, Wells AM, Kantak KM. Interaction of the rostral basolateral amygdala and prelimbic prefrontal cortex in regulating reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior. Pharm Biochem Behav. 2010;96:347–53.
Ghazizadeh A, Hong S, Hikosaka O. Prefrontal cortex represents long-term memory of object values for months. Curr Biol. 2018;28:2206–17.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the STI2030-Major Projects (no. 2021ZD0200800), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 82288101 and no. 81901352). All schematic images were created with BioRender.com.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LL, YH, YX, XL, and TL designed the study. XL, TL, KY, XC, SH, and WZheng performed the experiments. XL, TL, YH, and YB analyzed the data. XL and TL prepared the first draft of the manuscript. WZhang, SM, WY, LS, JS, KY, YX, YH, and LL revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Lu, T., Chen, X. et al. Memory consolidation drives the enhancement of remote cocaine memory via prefrontal circuit. Mol Psychiatry (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-023-02364-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-023-02364-w