Abstract
Alcohol misuse and alcohol use disorder (AlUD) have neurobiological consequences. This meta-analysis of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) studies aimed to assess the differences in brain metabolite levels in alcohol misuse and AUD relative to controls (PROSPERO registration: CRD42020209890). Hedge’s g with random-effects modeling was used. Sub-group and meta-regression techniques explored potential sources of demographic and MRS parameter heterogeneity. A comprehensive literature review identified 43 studies, resulting in 69 models across gray and white matter (GM, WM). Lower N-acetylaspartate levels were found in frontal, anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), hippocampal, and cerebellar GM, and frontal and parietal WM, suggesting decreased neuronal and axonal viability. Lower choline-containing metabolite levels (all metabolites contributing to choline peak) were found in frontal, temporal, thalamic, and cerebellar GM, and frontal and parietal WM, suggesting membrane alterations related to alcohol misuse. Lower creatine-containing metabolite levels (Cr; all metabolites contributing to Cr peak) were found in temporal and occipital cortical GM, while higher levels were noted in midbrain/brainstem GM; this finding may have implications for using Cr as an internal reference. The lack of significant group differences in glutamate-related levels is possibly related to biological and methodological complexities. The few studies reporting on GABA found lower levels restricted to the ACC. Confounding variables were age, abstinence duration, treatment status, and MRS parameters (echo time, quantification type, data quality). This first meta-analysis of proton MRS studies consolidates the numerous individual studies to identify neurometabolite alterations within alcohol misuse and AUD. Future studies can leverage this new formalized information to investigate treatments that might effectively target the observed disturbances.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Esser MB, Hedden SL, Kanny D, Brewer RD, Gfroerer JC, Naimi TS. Prevalence of alcohol dependence among US adult drinkers, 2009–2011. Prev Chronic Dis. 2014;11:E206.
U.S. Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020–2025. 9th Edition. December 2020. Available at DietaryGuidelines.gov.
Global status report on alcohol and health 2018. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0IGO.
Grant BF, Goldstein RB, Saha TD, Chou SP, Jung J, Zhang H, et al. Epidemiology of DSM-5 alcohol use disorder: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions III. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72:757–66.
Witkiewitz K, Litten R, Leggio L. Advances in the science and treatment of alcohol use disorder. Sci Adv. 2019;5:eaax4043.
Jenson C, Cushing C, Aylward B, Craig J, Sorell D, Steele R. Effectiveness of motivational interviewing for adolescent substance use behavior change: a meta-analytic review. J Consulting Clin Psychol. 2011;79:433–40.
Blodgett JC, Del ReA, Maisel NC, Finney JW. A meta‐analysis of topiramate’s effects for individuals with alcohol use disorders. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2014;38:1481–8.
Maisel NC, Blodgett JC, Wilbourne PL, Humphreys K, Finney JW. Meta‐analysis of naltrexone and acamprosate for treating alcohol use disorders: when are these medications most helpful? Addiction 2013;108:275–93.
Gilpin NW, Koob GF. Neurobiology of alcohol dependence: focus on motivational mechanisms. Alcohol Res Health. 2008;31:185.
Robbins TW, Everitt B. Limbic-striatal memory systems and drug addiction. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2002;78:625–36.
Hellem T, Shi X, Latendresse G, Renshaw PF. The utility of magnetic resonance spectroscopy for understanding substance use disorders: a systematic review of the literature. J Am Psychiatr Nurses Assoc. 2015;21:244–75.
Soares D, Law M. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain: review of metabolites and clinical applications. Clin Radiol. 2009;64:12–21.
Meyerhoff DJ, Durazzo TC, Ende G. Chronic Alcohol Consumption, Abstinence and Relapse: Brain Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Studies in Animals and Humans. In: Sommer W, Spanagel R, editors. Behavioral Neurobiology of Alcohol Addiction. Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences, vol 13. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-28720-6_131.
Meyerhoff DJ, Durazzo TC. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in alcohol use disorders: a potential new endophenotype? Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2008;32:1146–58.
Rae CD. A guide to the metabolic pathways and function of metabolites observed in human brain 1 H magnetic resonance spectra. Neurochem Res. 2014;39:1–36.
Meyerhoff DJ. Brain proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of alcohol use disorders. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;125:313–37.
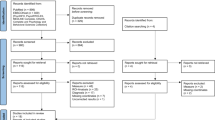
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n160.
Downes MJ, Brennan ML, Williams HC, Dean RS. Development of a critical appraisal tool to assess the quality of cross-sectional studies (AXIS). BMJ Open. 2016;6:e011458.
Peek AL, Rebbeck T, Puts NA, Watson J, Aguila M-ER, Leaver AM. Brain GABA and glutamate levels across pain conditions: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis of 1H-MRS studies using the MRS-Q quality assessment tool. Neuroimage 2020;210:116532.
Borenstein M, Hedges L, Rothstein H. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Version 3. 3 ed. Englewood, NJ: Biostat; 2013.
Hedges L, Olkin I. Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis. San Diego, CA: Academic; 1985.
Borenstein M, Higgins JP. Meta-analysis and subgroups. Prev Sci. 2013;14:134–43.
Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel‐plot–based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta‐analysis. Biometrics 2000;56:455–63.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Bmj 1997;315:629–34.
Richardson M, Garner P, Donegan S. Interpretation of subgroup analyses in systematic reviews: a tutorial. Clin Epidemiol Glob Health. 2019;7:192–8.
Borenstein M, Cooper H, Hedges L, Valentine J. Effect sizes for continuous data. Handb Res Synth Meta-Anal. 2009;2:221–35.
Fein G, Landman B. Treated and treatment-naive alcoholics come from different populations. Alcohol 2005;35:19–26.
Ray LA, Bujarski S, Yardley MM, Roche DJ, Hartwell EE. Differences between treatment-seeking and non-treatment-seeking participants in medication studies for alcoholism: do they matter? Am J Drug Alcohol Abus. 2017;43:703–10.
Haass‐Koffler CL, Piacentino D, Li X, Long VM, Lee MR, Swift RM, et al. Differences in Sociodemographic and Alcohol‐Related Clinical Characteristics Between Treatment Seekers and Nontreatment Seekers and Their Role in Predicting Outcomes in the COMBINE Study for Alcohol Use Disorder. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2020;44:2097–108.
Rohn MC, Lee MR, Kleuter SB, Schwandt ML, Falk DE, Leggio L. Differences between treatment‐seeking and nontreatment‐seeking alcohol‐dependent research participants: an exploratory analysis. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2017;41:414–20.
Prisciandaro JJ, Schacht JP, Prescot AP, Brenner HM, Renshaw PF, Brown TR, et al. Intraindividual changes in brain GABA, glutamate, and glutamine during monitored abstinence from alcohol in treatment‐naive individuals with alcohol use disorder. Addiction Biol. 2020;25:e12810.
Prisciandaro JJ, Schacht JP, Prescot AP, Renshaw PF, Brown TR, Anton RF. Brain glutamate, GABA, and glutamine levels and associations with recent drinking in treatment‐naive individuals with alcohol use disorder versus light drinkers. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2019;43:221–6.
Meyerhoff D, Blumenfeld R, Truran D, Lindgren J, Flenniken D, Cardenas V, et al. Effects of heavy drinking, binge drinking, and family history of alcoholism on regional brain metabolites. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2004;28:650–61.
Barantin L, Pape AL, Akoka S. A new method for absolute quantitation MRS metabolites. Magn Reson Med. 1997;38:179–82.
Li BS, Wang H, Gonen O. Metabolite ratios to assumed stable creatine level may confound the quantification of proton brain MR spectroscopy. Magn Reson imaging. 2003;21:923–8.
Öz G, Deelchand DK, Wijnen JP, Mlynárik V, Xin L, Mekle R, et al. Advanced single voxel 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy techniques in humans: experts’ consensus recommendations. NMR Biomed. 2021;34:e4236.
Wilson M, Andronesi O, Barker PB, Bartha R, Bizzi A, Bolan PJ, et al. Methodological consensus on clinical proton MRS of the brain: Review and recommendations. Magn Reson Med. 2019;82:527–50.
Zucker I, Prendergast BJ. Sex differences in pharmacokinetics predict adverse drug reactions in women. Biol Sex Differ. 2020;11:1–14.
Agabio R, Pani PP, Preti A, Gessa GL, Franconi F. Efficacy of medications approved for the treatment of alcohol dependence and alcohol withdrawal syndrome in female patients: a descriptive review. Eur Addict Res. 2016;22:1–16.
Agabio R, Pisanu C, Luigi Gessa G, Franconi F. Sex differences in alcohol use disorder. Curr Med Chem. 2017;24:2661–70.
Endres D, Tebartz van Elst L, Maier SJ, Feige B, Goll P, Meyer SA, et al. Neurochemical sex differences in adult ADHD patients: an MRS study. Biol Sex Differ. 2019;10:1–11.
Jung RE, Haier RJ, Yeo RA, Rowland LM, Petropoulos H, Levine AS, et al. Sex differences in N-acetylaspartate correlates of general intelligence: an 1H-MRS study of normal human brain. Neuroimage 2005;26:965–72.
Prisciandaro JJ, Mikkelsen M, Saleh MG, Edden RA. An evaluation of the reproducibility of 1H-MRS GABA and GSH levels acquired in healthy volunteers with J-difference editing sequences at varying echo times. Magn Reson Imaging. 2020;65:109–13.
Smucny J, Carter CS, Maddock RJ. Medial Prefrontal Cortex Glutamate is Reduced in Schizophrenia and Moderated by Measurement Quality: a Meta-analysis of 1H-MRS Studies. Biol Psychiatry. 2021;90:643–51.
Abé C, Mon A, Durazzo TC, Pennington DL, Schmidt TP, Meyerhoff DJ. Polysubstance and alcohol dependence: unique abnormalities of magnetic resonance-derived brain metabolite levels. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013;130:30–7.
Bauer J, Pedersen A, Scherbaum N, Bening J, Patschke J, Kugel H, et al. Craving in alcohol-dependent patients after detoxification is related to glutamatergic dysfunction in the nucleus accumbens and the anterior cingulate cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013;38:1401–8.
Durazzo TC, Pathak V, Gazdzinski S, Mon A, Meyerhoff DJ. Metabolite levels in the brain reward pathway discriminate those who remain abstinent from those who resume hazardous alcohol consumption after treatment for alcohol dependence. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2010;71:278–89.
Hermann D, Weber-Fahr W, Sartorius A, Hoerst M, Frischknecht U, Tunc-Skarka N, et al. Translational magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals excessive central glutamate levels during alcohol withdrawal in humans and rats. Biol Psychiatry. 2012;71:1015–21.
Lee E, Jang D-P, Kim J-J, An SK, Park S, Kim I-Y, et al. Alteration of brain metabolites in young alcoholics without structural changes. Neuroreport 2007;18:1511–4.
Mon A, Durazzo TC, Meyerhoff DJ. Glutamate, GABA, and other cortical metabolite concentrations during early abstinence from alcohol and their associations with neurocognitive changes. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012;125:27–36.
Schweinsburg BC, Taylor MJ, Videen JS, Alhassoon OM, Patterson TL, Grant I. Elevated myo‐inositol in gray matter of recently detoxified but not long‐term abstinent alcoholics: a preliminary MR spectroscopy study. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2000;24:699–705.
Thoma R, Mullins P, Ruhl D, Monnig M, Yeo RA, Caprihan A, et al. Perturbation of the glutamate–glutamine system in alcohol dependence and remission. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011;36:1359–65.
Yeo RA, Thoma RJ, Gasparovic C, Monnig M, Harlaar N, Calhoun VD, et al. Neurometabolite concentration and clinical features of chronic alcohol use: a proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Psychiatry Res: Neuroimaging. 2013;211:141–7.
Abé C, Mon A, Hoefer ME, Durazzo TC, Pennington DL, Schmidt TP, et al. Metabolic abnormalities in lobar and subcortical brain regions of abstinent polysubstance users: magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Alcohol Alcohol. 2013;48:543–51.
Durazzo TC, Gazdzinski S, Banys P, Meyerhoff DJ. Cigarette smoking exacerbates chronic alcohol‐induced brain damage: a preliminary metabolite imaging study. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2004;28:1849–60.
Bendszus M, Weijers H-G, Wiesbeck G, Warmuth-Metz M, Bartsch AJ, Engels S, et al. Sequential MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopy in patients who underwent recent detoxification for chronic alcoholism: correlation with clinical and neuropsychological data. Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22:1926–32.
Ende G, Welzel H, Walter S, Weber-Fahr W, Diehl A, Hermann D, et al. Monitoring the effects of chronic alcohol consumption and abstinence on brain metabolism: a longitudinal proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;58:974–80.
Fein G, Meyerhoff D, Di Sclafani V, Ezekiel F, Poole N, MacKay S, et al. 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging separates neuronal from glial changes in alcohol-related brain atrophy. Chapter NIAAA Res Monogr No. 1994;27:227–41.
Jagannathan N, Desai N, Raghunathan P. Brain metabolite changes in alcoholism: an in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) study. Magn Reson Imaging. 1996;14:553–7.
Schweinsburg BC, Alhassoon OM, Taylor MJ, Gonzalez R, Videen JS, Brown GG, et al. Effects of alcoholism and gender on brain metabolism. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:1180–3.
Xia Y, Ma D, Hu J, Tang C, Wu Z, Liu L, et al. Effect of metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 genotype on N-acetylaspartate levels and neurocognition in non-smoking, active alcoholics. Behav Brain Funct. 2012;8:1–11.
Parks MH, Dawant BM, Riddle WR, Hartmann SL, Dietrich MS, Nickel MK, et al. Longitudinal brain metabolic characterization of chronic alcoholics with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2002;26:1368–80.
Seitz D, Widmann U, Seeger U, Nägele T, Klose U, Mann K, et al. Localized proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the cerebellum in detoxifying alcoholics. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 1999;23:158–63.
Martin PR, Gibbs SJ, Nimmerrichter AA, Riddle WR, Welch LW, Willcott MR. Brain proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies in recently abstinent alcoholics. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 1995;19:1078–82.
Frischknecht U, Hermann D, Tunc‐Skarka N, Wang GY, Sack M, van Eijk J, et al. Negative association between MR‐spectroscopic glutamate markers and gray matter volume after alcohol withdrawal in the hippocampus: a translational study in humans and rats. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2017;41:323–33.
Gazdzinski S, Durazzo TC, Yeh P-H, Hardin D, Banys P, Meyerhoff DJ. Chronic cigarette smoking modulates injury and short-term recovery of the medial temporal lobe in alcoholics. Psychiatry Res: Neuroimaging. 2008;162:133–45.
de Souza RSM, Rosa M Jr, Rodrigues TM, Escobar TDC, Gasparetto EL, Nakamura-Palacios EM. Lower choline rate in the left prefrontal cortex is associated with higher amount of alcohol use in alcohol use disorder. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:563.
Wang JJ, Durazzo TC, Gazdzinski S, Yeh PH, Mon A, Meyerhoff DJ. MRSI and DTI: a multimodal approach for improved detection of white matter abnormalities in alcohol and nicotine dependence. NMR Biomed: Int J Devoted Dev Appl Magn Resonance In vivo. 2009;22:516–22.
Ende G, Hermann D, Demirakca T, Hoerst M, Tunc‐Skarka N, Weber‐Fahr W, et al. Loss of control of alcohol use and severity of alcohol dependence in non‐treatment‐seeking heavy drinkers are related to lower glutamate in frontal white matter. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2013;37:1643–9.
Gazdzinski S, Durazzo TC, Mon A, Yeh P-H, Meyerhoff DJ. Cerebral white matter recovery in abstinent alcoholics—a multimodality magnetic resonance study. Brain 2010;133:1043–53.
Schweinsburg BC, Taylor MJ, Alhassoon OM, Videen JS, Brown GG, Patterson TL, et al. Chemical pathology in brain white matter of recently detoxified alcoholics: a 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy investigation of alcohol‐associated frontal lobe injury. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2001;25:924–34.
Zahr NM, Carr RA, Rohlfing T, Mayer D, Sullivan EV, Colrain IM, et al. Brain metabolite levels in recently sober individuals with alcohol use disorder: Relation to drinking variables and relapse. Psychiatry Res: Neuroimaging. 2016;250:42–9.
Durazzo TC, Gazdzinski S, Rothlind JC, Banys P, Meyerhoff DJ. Brain metabolite concentrations and neurocognition during short‐term recovery from alcohol dependence: preliminary evidence of the effects of concurrent chronic cigarette smoking. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2006;30:539–51.
Mason GF, Petrakis IL, de Graaf RA, Gueorguieva R, Guidone E, Coric V, et al. Cortical gamma-aminobutyric acid levels and the recovery from ethanol dependence: preliminary evidence of modification by cigarette smoking. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;59:85–93.
Bloomer CW, Langleben DD, Meyerhoff DJ. Magnetic resonance detects brainstem changes in chronic, active heavy drinkers. Psychiatry Res: Neuroimaging. 2004;132:209–18.
Prisciandaro J, Tolliver B, Prescot A, Brenner H, Renshaw P, Brown T, et al. Unique prefrontal GABA and glutamate disturbances in co-occurring bipolar disorder and alcohol dependence. Transl Psychiatry 2017;7:e1163–e.
Silveri MM, Cohen‐Gilbert J, Crowley DJ, Rosso IM, Jensen JE, Sneider JT. Altered anterior cingulate neurochemistry in emerging adult binge drinkers with a history of alcohol‐induced blackouts. Alcohol: Clin Exp Res. 2014;38:969–79.
Gonzales RA, Jaworski JN. Alcohol and glutamate. Alcohol Health Res World. 1997;21:120.
Brousse G, Arnaud B, Vorspan F, Richard D, Dissard A, Dubois M, et al. Alteration of glutamate/GABA balance during acute alcohol withdrawal in emergency department: a prospective analysis. Alcohol Alcohol. 2012;47:501–8.
Spanagel R. The role of the glutamatergic system in alcohol addiction. Fortschr der Neurologie-Psychiatr. 2003;71:S33–5.
Ramadan S, Lin A, Stanwell P. Glutamate and glutamine: a review of in vivo MRS in the human brain. NMR Biomed. 2013;26:1630–46.
Choi IY, Andronesi OC, Barker P, Bogner W, Edden RA, Kaiser LG, et al. Spectral editing in 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy: Experts’ consensus recommendations. NMR Biomed. 2021;34:e4411.
Cai K, Haris M, Singh A, Kogan F, Greenberg JH, Hariharan H, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of glutamate. Nat Med. 2012;18:302–6.
Cai K, Singh A, Roalf DR, Nanga RPR, Haris M, Hariharan H, et al. Mapping glutamate in subcortical brain structures using high‐resolution GluCEST MRI. NMR Biomed. 2013;26:1278–84.
Harris AD, Saleh MG, Edden RA. Edited 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo: Methods and metabolites. Magn Reson Med. 2017;77:1377–89.
Tuithof M, Ten Have M, Van Den Brink W, Vollebergh W, De Graaf R. Treatment seeking for alcohol use disorders: treatment gap or adequate self-selection? Eur Addict Res. 2016;22:277–85.
Bartsch AJ, Homola G, Biller A, Smith SM, Weijers H-G, Wiesbeck GA, et al. Manifestations of early brain recovery associated with abstinence from alcoholism. Brain 2007;130:36–47.
Jansen JF, Backes WH, Nicolay K, Kooi ME. 1H MR spectroscopy of the brain: absolute quantification of metabolites. Radiology 2006;240:318–32.
Ernst T, Kreis R, Ross B. Absolute quantitation of water and metabolites in the human brain. I. Compartments and water. J Magn Reson Ser B. 1993;102:1–8.
Gasparovic C, Song T, Devier D, Bockholt HJ, Caprihan A, Mullins PG, et al. Use of tissue water as a concentration reference for proton spectroscopic imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official. J Int Soc Magn Reson Med. 2006;55:1219–26.
Zöllner HJ, Považan M, Hui SC, Tapper S, Edden RA, Oeltzschner G. Comparison of different linear‐combination modeling algorithms for short‐TE proton spectra. NMR Biomed. 2021;34:e4482.
Zöllner HJ, Tapper S, Hui SC, Barker PB, Edden RA, Oeltzschner G. Comparison of linear combination modeling strategies for edited magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 3 T. NMR Biomed. 2022;35:e4618.
Craven AR, Bhattacharyya PK, Clarke WT, Dydak U, Edden RA, Ersland L, et al. Comparison of seven modelling algorithms for γ‐aminobutyric acid–edited proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. NMR Biomed. 2022:e4702. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.4702. Online ahead of print.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Teri Lynn Herbert (MUSC) for her invaluable help with setting up the literature searches for this meta-analysis. Dr Anna Kirkland is currently funded through the NIDA T32 at MUSC (DA007288-30), Brittney Browning is funded through the NIAAA T32 (AA007474-34), and Dr Lindsay Squeglia is funded through an NIAAA K23 (AA025399) and R01 (AA027399).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AEK, BDB, LMS. Methodology: AEK, BDB, LL, DJM, LMS. Software: AEK, BDB. Formal Analysis: AEK. Data Curation: AEK, BDB. Writing—Original Draft: AEK, BDB, LMS. Writing—Review & Editing: All authors. Visualization: AEK, BDB, RG. Supervision: LMS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
LL is a U.S. federal employee at the National Institutes of Health, and his work is funded by the NIDA and NIAAA intramural research program. Outside his federal employment, he receives an honorarium from the UK Medical Council on Alcoholism (Editor-in-Chief for Alcohol and Alcoholism) and royalties from Routledge for a textbook. All other authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirkland, A.E., Browning, B.D., Green, R. et al. Brain metabolite alterations related to alcohol use: a meta-analysis of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies. Mol Psychiatry 27, 3223–3236 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01594-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01594-8