Abstract
Depression and anxiety are common comorbidities in breast cancer patients. Whether depression and anxiety are associated with breast cancer progression or mortality is unclear. Herein, based on a systematic literature search, 17 eligible studies involving 282,203 breast cancer patients were included. The results showed that depression was associated with cancer recurrence [1.24 (1.07, 1.43)], all-cause mortality [1.30 (1.23, 1.36)], and cancer-specific mortality [1.29 (1.11, 1.49)]. However, anxiety was associated with recurrence [1.17 (1.02, 1.34)] and all-cause mortality [1.13 (1.07, 1.19)] but not with cancer-specific mortality [1.05 (0.82, 1.35)]. Comorbidity of depression and anxiety is associated with all-cause mortality [1.34 (1.24, 1.45)] and cancer-specific mortality [1.45 (1.11, 1.90)]. Subgroup analyses demonstrated that clinically diagnosed depression and anxiety, being female and of younger age (<60 years), and shorter follow-up duration (≤5 years) were related to a poorer prognosis. Our study highlights the critical role of depression/anxiety as an independent factor in predicting breast cancer recurrence and survival. Further research should focus on a favorable strategy that works best to improve outcomes among breast cancer patients with mental disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Breast cancer is one of the most prevalent cancers as well as the leading cause of death among women. According to the WHO statistics from 2018, breast cancer has an incidence of 11.6% among all types of cancer, accounting for 6.5% of mortalities worldwide [1]. The survival rate of breast cancer patients in developed countries has improved in recent decades due to the advances in early screening and treatment [2]. However, the mortality rate of breast cancer patients in some developing countries remains high due to inefficient screening and treatment, leaving an overall high death toll worldwide [3]. Recurrence and metastasis are the main causes of death in breast cancer. In addition, cardiovascular complications in breast cancer survivors were identified as another important cause of death among these women [4, 5]. Therefore, in order to improve the prognosis and overall survival, it is important to identify the risk factors influencing breast cancer-related death.
A number of factors can affect breast cancer progression and mortality. Recent studies have shown that the status of lymph nodes, tumor size, and histological subtypes are important risk factors determining its clinical outcomes [6,7,8]. In addition, clinical studies have demonstrated that demographic characteristics and lifestyle factors, such as age, obesity, smoking, and estrogen application, are also significantly related to breast cancer onset and development [9,10,11,12,13]. Importantly, with the transformation from the traditional medical system to a biopsychosocial medical network, much more attention has been paid to the role of psychological factors in the etiology and prognosis of breast cancer.
The diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer are frequently accompanied by changes in physical status and function, unpleasant side effects, decline in quality of life, and impaired social relationships [14, 15]. Therefore, breast cancer patients always suffer from negative emotions under chronic psychological stress. Clinical studies have also suggested that patients with breast cancer suffer a much higher prevalence of mental disorders compared with the general population. Depression and anxiety are the two most common psychiatric symptoms. Results from previous meta-analyses revealed that the prevalence of depression and anxiety among breast cancer patients was up to 32.2% and 41.9%, respectively [16, 17]. Depression and anxiety can affect the physiological function, treatment compliance, psychological function, and quality of life of patients with breast cancer and may even be an important factor affecting the mortality of breast cancer patients. Although whether psychological factors predict breast cancer mortality has been widely investigated, the findings are not consistent. Seven studies reported that depression was associated with an increase in the risk of mortality [18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Another six studies found no association between depression and mortality [25,26,27,28,29,30]. Previous meta-analyses presented evidence that depression was related to mortality [31, 32] but not to progression in cancer patients [32]. However, these meta-analyses were constrained by high heterogeneity based on mixed types of cancers. Furthermore, as breast cancer is a hormone-dependent neoplasm, its response to mental illness may be distinct from that of other cancers. Meanwhile, several studies have assessed whether improvements in depression are associated with survival benefits. Giese-Davis et al. [33] found that a decrease in depression under supportive-expressive group therapy (SEGT) predicted longer survival for women with breast cancer. A recent meta-analysis also found that SEGT and other supportive psychotherapeutic interventions did improve overall cancer survival [34], while Kissane et al. [35] found no evidence that SEGT prolongs survival. With regard to anxiety, its influence on breast cancer prognosis is still under dispute. Shim et al. [24] found that anxiety is predictive of all-cause mortality for breast cancer patients. Groenvold et al. [27] demonstrated that anxiety was associated with relapse-free survival, but not with overall survival. However, several studies indicated that no association was found between anxiety and mortality in breast cancer patients [21, 23, 25, 28, 36]. Notably, animal models have clearly shown that chronic psychological stress can promote tumor growth and lung metastasis [37, 38]. Thaker et al. [39] found that chronic stress promotes ovarian tumor growth and angiogenesis in a murine model, and that adrenergic blockade reverses the effect. Hence, it is necessary to conduct comprehensive and rigorous studies to determine the relationship between depression and anxiety and breast cancer survival and progression.
Herein, we conducted a meta-analysis of depression and anxiety in relation to mortality and progression in patients with breast cancer. We collected and quantitatively integrated the data regarding the association between recurrence, all-cause mortality and cancer-specific mortality with depression and anxiety, respectively. The results demonstrate that depression and anxiety are both associated with recurrence and all-cause mortality. Furthermore, depression and comorbid depression and anxiety are related to cancer-specific mortality, while anxiety alone is not. Our findings highlight the importance of depression and anxiety in predicting breast cancer prognosis and suggest that careful consideration should be given to routine screening for mental distress in breast cancer patients.
Methods
Protocol and guidance
This study was performed in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis. The protocol for this review has been registered at PROSPERO (CRD42020162466).
Search strategy
Following recommendations of the Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology group [40], we searched the following electronic databases for studies written in English from their inception until December 15, 2019: PubMed, Embase, The Cochrane Library, and PsycINFO. The search strategy was implemented using combined index terms (Medical Subject Headings, Emtree) and free-text keywords. Keywords included (“breast cancer” OR “breast neoplasm”) AND (“depression” OR “anxiety”) AND (“survival” OR “mortality” OR “metastasis” OR “recurrence”). Tables S1–S4 in the supplementary show the detailed methods used for searching all of the databases. Additional studies were searched by examining the reference lists of reviews and eligible publications for potentially eligible studies.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The retrieved studies were eligible for qualitative and quantitative analysis if they (1) were cohort studies, (2) investigated patients with breast cancer, (3) assessed depression or anxiety by standard diagnostic criteria or self-report scales, and (4) provided HRs or risk ratios (RRs) and their 95% CIs for all-cause mortality or cancer-specific mortality.
The studies were excluded if they (1) had participants with malignancy other than breast cancer, (2) only recruited patients with breast cancer but without depression or anxiety, and (3) lacked measurement of cancer recurrence or mortality. In addition, if duplicate articles were derived from an identical or overlapping patient population, only the latest and/or complete one was used in the meta-analysis. When there were multiple groups of useful data in the same article, only the data derived from the group with the largest sample size were selected for the analysis.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two reviewers independently extracted the data from the included studies. The following details are presented in this review: first author’s name, year of publication, country, participant number, age, time of assessment of depression, follow-up duration, depression/anxiety measurement, and adjusted major confounders.
All of the selected articles were examined in terms of quality based on the Newcastle–Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale for cohort studies [41]. This semiquantitative scale uses a star system to assess the quality for eight items across three domains: selection (four items, one star each), comparability (one item, up to two stars), and exposure (three items, one star each). In this meta-analysis, we graded quality as good (≥7 stars), fair (4–6 stars), or poor (<4 stars). Any discrepancy between the two reviewers was resolved by discussion with the third reviewer.
Statistical analysis
The outcomes were recurrence-free survival (the time until breast cancer recurrence, other malignant disease, or death), all-cause mortality (death from any cause), and breast cancer-specific mortality (death resulting from breast cancer) in patients with breast cancer based on the effects of depression and anxiety. The method was based on the HRs with 95% CIs obtained from each study. The relative risk (RR) was deemed approximatively equivalent to the HR if the HR was not reported. Most HRs were adjusted by different variables, such as age or tumor stage. If there were unadjusted HRs (or RRs) and adjusted ones, the adjusted were preferred. Subgroup analyses were conducted according to age (average ≤60 vs. >60 years), follow-up duration (<5 vs. ≥5 years), time of assessment of depression (before cancer diagnoses vs. after cancer diagnoses), and measure of mental status (clinical diagnose vs. symptom scale).
The Cochrane Q test and I2 statistic were employed to evaluate heterogeneity between studies, and an I2 > 50% was considered statistically significant [42]. If the I2 value was 50% or greater, we pooled the results using a random-effects model. Otherwise, a fixed-effect model was applied. The funnel plots and Egger test were used to detect potential publication bias [43, 44]. To assess the stability of the results, a leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was carried out. Analyses were performed with Stata 15.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA).
Results
Eligible studies and study characteristics
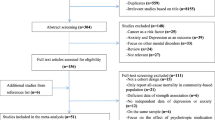
After identifying 7884 references, 1127 duplicate publications, and 6708 irrelevant studies were excluded, leaving 49 potentially eligible studies (Fig. 1). Finally, 17 cohort studies conducted between 2002 and 2019 were included in the meta-analysis.
The general characteristics of the included studies are listed in Table 1. A total of 282,203 patients with breast cancer were involved, and trials ranged in size from 34 to 124,381 participants. The duration of follow-up ranged from 2 to 25 years. Among these studies, nine studies were from Europe, five were from the US, two were from Asia, and one was from Australia. Mental symptoms were assessed by various tools, such as the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D), Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), and 12-item General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12), while clinical mental disorders were diagnosed based on the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) or the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-MD). Most studies were adjusted for variables that affect the risk of cancer mortality, such as age, tumor stage, and comorbidities.
According to quality assessment criteria, 15 studies were graded as good quality and two studies as fair quality. Detailed information is listed in Supplementary Table S5.
Effect of depression on recurrence and mortality in breast cancer patients
As shown in Fig. 2, seven studies [25, 27,28,29,30, 36, 45] yielded a pooled HR of 1.24 (1.07, 1.43) for the association between depression and recurrence based on fixed-effects model analyses. Low heterogeneity was observed, with I2 = 30.1% and P = 0.198. Furthermore, 12 studies [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30] yielded a pooled HR of 1.30 (1.23, 1.36) for the association between depression and all-cause mortality. Low heterogeneity was observed, with I2 = 0.0% and P = 0.57. Finally, four studies [18, 19, 21, 22] yielded a pooled HR of 1.29 (1.11, 1.49) for the association between depression and breast cancer-specific mortality. Low heterogeneity was observed, with I2 = 3.2% and P = 0.376.
Recurrence
The results showed that depression was associated with a 24% increase in the risk of cancer recurrence. In seven studies, the mean age of patients was <60 years. Two studies assessed depression before the breast cancer diagnosis, and five studies assessed it after the breast cancer diagnosis. Five studies assessed the effect of psychological symptoms using self-report scales, and two studies assessed it through clinical standardized interviews. There were two studies with a follow-up duration shorter than or equal to 5 years postdiagnosis and five studies with a follow-up duration longer than 5 years. Subgroup analysis, according to the assessment time of depression, mental status measurement tool, and follow-up duration, was performed (Fig. 3). The results showed that the prognostic impact of the depression was significant when depression was assessed after the breast cancer diagnosis [1.22 (1.05, 1.41)]. In addition, clinically diagnosed depression disorders were associated with recurrence [1.37 (1.10, 1.70)], while mental distress assessed by the symptom scale was not [1.15 (0.95, 1.38)]. In addition, studies with short-term follow-up (≤5 years) tended to report a higher recurrence risk [1.37 (1.10, 1.70)] compared with studies with longer follow-up of more than 5 years [1.15 (0.95, 1.38)].
All-cause mortality
The results showed that depression was associated with a 30% increase in the risk of all-cause mortality. The mean age of patients was <60 years in seven studies and over 60 years in three studies. Five studies assessed depression before breast cancer diagnosis, and eight studies assessed it after breast cancer diagnosis. Six studies assessed the effect of psychological symptoms using self-report scales, and six studies assessed it through clinical standardized interviews. There were four studies with follow-up duration ≤5 years postdiagnosis, and eight studies with follow-up duration longer than 5 years. Subgroup analysis was performed according to age, the assessment time of depression, the mental status measurement tool, and follow-up duration (Fig. 4). The results showed that the association was significant in both patients aged <60 years and those aged ≥60 years [1.25 (1.18, 1.34) and 1.38 (1.23, 1.55), respectively]. The significant prognostic impact of depression did not differ depending on whether it was assessed before [1.33 (1.22, 1.45)] or after [1.28 (1.21, 1.36)] the breast cancer diagnosis. Furthermore, there was no significant difference in risk between studies with a follow-up duration ≤5 years [1.30 (1.22, 1.38)] and those with a follow-up duration >5 years [1.30 (1.19, 1.41)]. However, clinically diagnosed depression disorders were associated with increased all-cause mortality [1.31 (1.24, 1.38)], while self-reported psychological symptoms were not [1.18 (1.00, 1.39)].
Breast cancer-specific mortality
Likewise, the results showed that depression was associated with a 29% increase in the risk of breast cancer-specific mortality. The mean age of patients was <60 years in one study and over 60 years in three studies. Three studies assessed depression before the breast cancer diagnosis, and one study assessed it after the breast cancer diagnosis. One study assessed the effect of depressive symptoms using self-report scales, and three studies assessed it through clinical standardized interviews. There were two studies with a follow-up duration shorter than or equal to 5 years postdiagnosis and two studies with a follow-up duration longer than 5 years.
Effect of anxiety on recurrence and mortality in breast cancer patients
As shown in Fig. 5, four studies [25, 27, 28, 36] yielded a pooled HR of 1.17 (1.02, 1.34) for the association between anxiety and recurrence based on fixed-effects model analyses. Low heterogeneity was observed, with I2 = 0.0% and P = 0.744. Furthermore, six studies [21, 23,24,25, 27, 28] yielded a pooled HR of 1.13 (1.07, 1.19) for the association between anxiety and all-cause mortality. Low heterogeneity was observed, with I2 = 0.0% and P = 0.789. However, there was no association between anxiety and breast cancer-specific mortality in two studies [1.05 (0.82, 1.35)] [21, 22]. Low heterogeneity was observed, with I2 = 48.7% and P = 0.163.
Recurrence
The results showed that depression was associated with a 17% increase in the risk of cancer recurrence. In four studies, the mean age of patients was <60 years. All included studies measured anxious symptoms using the HAD scale after the breast cancer diagnosis, and four studies had a follow-up duration longer than 5 years. Thus, subgroup analysis could not be carried out.
All-cause mortality
The results showed that anxiety was associated with a 13% increase in the risk of all-cause mortality. The mean age of patients was <60 years in four studies and over 60 years in one study. Two studies measured anxiety before the breast cancer diagnosis, and four studies measured it after the breast cancer diagnosis. Three studies assessed the effect of anxiety symptoms using self-report scales, and three studies assessed it through clinical standardized interviews. There were three studies with a follow-up duration shorter than or equal to 5 years postdiagnosis and three studies with a follow-up duration longer than 5 years. Subgroup analysis according to age, the assessment time of anxiety, the mental status measurement tool, and follow-up duration was performed (Supplementary Fig. S1). The association was significant only in several subgroups: patients aged <60 years [1.13 (1.07, 1.20)], anxiety assessed after breast cancer diagnosis [1.13 (1.07, 1.20)], clinically diagnosed anxiety disorders [1.14 (1.08, 1.20)], and follow-up duration ≤5 years [1.14 (1.08, 1.20)].
Breast cancer-specific mortality
The results showed that anxiety was not related to the risk of breast cancer-specific mortality. The mean age of patients was over 60 years in two studies. Both studies measured depression before breast cancer diagnosis. One study assessed the effect of depressive symptoms using self-report scales, and the other study assessed it through clinical standardized interviews. One study had a follow-up duration ≤5 years postdiagnosis, and the other study had a follow-up duration longer than 5 years. Considering the limited studies included, subgroup analysis was not performed.
Effect of depression and anxiety on mortality in breast cancer patients
As shown in Supplementary Fig. S2, four studies [21, 23, 24, 46] yielded a pooled HR of 1.34 (1.24, 1.45) for the association between depression and anxiety and all-cause mortality based on fixed-effects model analyses. Low heterogeneity was observed, with I2 = 0.0% and P = 0.755. Furthermore, two studies [21, 47] yielded a pooled HR of 1.45 (1.11, 1.90) for the association between depression and anxiety and breast cancer-specific mortality. Low heterogeneity was observed, with I2 = 49.3% and P = 0.160.
Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
Due to the small number of studies for both depression and anxiety, funnel plots and Egger’s tests were only created/computed for the primary outcome of depression or anxiety. There was no evidence of publication bias based on visual inspection of funnel plots (Supplementary Fig. S3) or according to Egger’s tests (P > 0.1). Sensitivity analysis was performed to assess the stability of the results, and a single study from the meta-analysis was omitted each time. The results showed that the corresponding pooled estimates were not significantly altered, indicating that no individual study influences the results (Supplementary Fig. S4).
Discussion
The meta-analysis confirms that depression, anxiety, and the combination of both are associated with increased recurrence and all-cause mortality in patients with breast cancer. In our study, depression predicted a 30% increase in mortality risk among cancer patients, which is more severe than the increased risk of 18% found by a study carried out in 2010 [31]. This may indicate an increasing tendency in the mortality risk in recent years. Importantly, in contrast to previous depression-focused meta-analyses, our findings show that anxiety can also predict recurrence and all-cause mortality in breast cancer patients. The all-cause mortality risk is the highest in patients with combined depression and anxiety, followed by those with depression alone. In addition, depression predicts a slightly higher risk of recurrence than anxiety. Depression and comorbid depression and anxiety can also increase the risk of cancer-specific mortality, while anxiety does not. Our results suggest that depression is a stronger risk factor for cancer progression and mortality than anxiety, and comorbid depression and anxiety are most closely related to mortality. Considering that depression and anxiety often co-occur clinically, more attention should be paid to them during the treatment of cancer patients.
There are several factors that may explain the increased mortality rate of breast cancer patients with depression and anxiety, such as lifestyle, behavioral factors, and biological factors. First, patients with mental disorders may be more prone to unhealthy lifestyle factors, such as smoking, drinking, obesity, and insomnia, which may increase the risk of mortality and cardiovascular disease [48]. Second, treatment nonadherence is also a severe problem. For instance, breast cancer patients may have difficulties adhering to chemotherapy and other complementary treatments [49], which could lead to poor prognosis. Furthermore, mortality could also be caused by nonnatural causes of death, especially suicide [50]. Depression and anxiety are also related to biological mechanisms such as abnormal activation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis and high norepinephrine and cortisol levels in patients [51, 52]. Thaker et al. [39] validated that chronic stress could lead to higher levels of tissue catecholamines, greater tumor burden, and more invasive growth of ovarian carcinoma. Bai et al. [53] reported that stress-induced epinephrine enhances lactate dehydrogenase A and promotes breast cancer stem-like cells. Kamiya et al. [54] found that chronic stress accelerates cancer growth and progression via stimulation of sympathetic neural nerves in tumor. It is interesting to investigate the expression profiles of neuroendocrine-related receptors in breast cancer and to develop novel targeting strategies in the future.
The different effects of depression and anxiety on breast cancer may indicate their distinct mechanisms. Anxiety is characterized by prominent tension, worry, and feelings of apprehension. Depression is indicated by depressive mood, slow thinking, and loss of interest. Patients with depression are more prone to committing suicide than those with anxiety, which may contribute to the higher all-cause mortality. Both depression and anxiety can lead to insomnia. However, anxiety is characterized by difficulty in falling asleep, and depression is characterized by waking up early. Different manifestations reflect different mechanisms of neuroendocrine disorders. More research is still needed to explore the distinct mechanisms between depression and anxiety.
The associations between depression/anxiety and mortality vary by age, assessment tools and time, and follow-up duration. Pinquart et al. [31] observed a stronger association between depression and mortality in older patients than in younger patients on the basis of the association between depression and various types of cancers. However, our study showed different results, namely that younger patients had a higher mortality risk compared with the elderly. Considering that our research is breast cancer-oriented and more representative for breast cancer, the inconsistent results may suggest that the mechanisms for mortality may differ across different types of cancer. It is believed that the severity of depression and anxiety is negatively correlated with age [55, 56]. In addition, younger patients with depression may have more difficulty in coping with cancer and may be more distressed due to their multiple social roles and heavier family burdens [19]. Therefore, younger women with breast cancer on average have a poorer prognosis than older ones.
Furthermore, we found that mental disorders diagnosed by a clinical interview were linked to a higher recurrence risk and poorer cancer survival than those assessed by self-rating scales. As patients with more severe depressive symptoms tend to be evaluated by clinical diagnostic interviews, whereas those with mild and moderate depressive symptoms are usually assessed by self-rating scales [57], this finding reflects the dose–response relationship to some extent—that is, the more severe the depression is, the higher the mortality becomes. In addition, depression assessment after cancer diagnosis was more strongly associated with worse survival than a prior diagnosis of depression. A prior diagnosis of depression may represent early detection, diagnosis, and treatment, which are key to improving the survival rate. This finding suggests that we should pay more attention to the early detection of patients’ psychological state and strive to enhance their mental health.
Moreover, the length of follow-up was related to different mortality risks. Studies with short-term follow-up tended to report higher mortality compared with studies with a longer follow-up of more than 5 years, consistent with the finding of Watson et al. [25, 58], that there is a significant association between depression and mortality at 5 years’ follow-up but not at 10 years. Another meta-analysis also showed that the association was the strongest in studies with intervals of ≤2 years [31]. This could be explained by the severity of depression and anxiety weakening over time [59], resulting in a decrease in the strength of the correlation between mental distress and mortality over time. Hence, more attention should be paid to the early period after cancer diagnosis. Interestingly, there is evidence that the symptom-management approach of cognitive-behavioral therapy may have more profound effects among recently diagnosed patients, while the emotionally expressive existential focus of SEGT may be more helpful in the later stages of progressive cancer. Thus, when choosing the psychosocial interventions, the phase of the disease should be considered [34].
Interestingly, most reported associations were adjusted by demographic and tumor-related variables, such as tumor stage, positive lymph nodes, and tumor size. Mental distress was still associated with poorer prognosis after adjustment for the variables, which suggests that it is an independent risk factor for cancer mortality. However, the strength of the correlation between mental distress and mortality was gradually attenuated after adjustment (Supplementary Table S6). This variation was also found in previous similar meta-analyses of the association between depression in cardiac patients and prognosis [57, 60]. One plausible explanation is that the association between breast cancer and mental distress is bidirectional—that is, the severity of the cancer in turn leads to a poorer prognosis and mental disorders.
Nevertheless, there are several limitations to the current meta-analysis. First, as previously discussed, histological subtypes, tumor stage, and the status of hormone receptors may affect the association between mental distress and cancer progression and mortality. However, because each study adjusted for a different set of variables, a pooled association consistently adjusted for the same variables across the studies could not be reached. Furthermore, as the majority of cases in this study had mixed pathological subtypes, tumor stages, and hormone receptors, subgroup analysis for further comparison based on these factors also could not be carried out. Second, we could not accurately compare the different levels of depression/anxiety in the included trials due to the various tools for assessing depression/anxiety used in the included trials. This is one of the reasons this study did not examine the dose–response associations between depression/anxiety and mortality. Third, misclassification could have occurred, as depression and anxiety were usually evaluated only at one time, while these mental disorders are not fixed and prone to fluctuations over time.
Implications
Our findings strongly support the role of depression and anxiety in breast cancer progression and mortality, and they have important public health implications. First, more attention should be paid to psychosocial distress in breast cancer patients. Given the high prevalence of psychosocial distress and the resulting adverse effects on cancer recurrence and mortality, more health education should be carried out to make doctors, patients, and their families aware of the importance of psychological factors. Second, routine screening and early detection is recommended. As depression and anxiety may change across the trajectory of cancer care, screening at regular intervals can help effectively monitor psychological changes in the early period and allow for timely intervention to prevent it from getting worse. Furthermore, our study indirectly highlights the significance of treatment for depression and anxiety in breast cancer patients. It is believed that psychotherapy and mind–body therapies may relieve depressive symptoms in patients with breast cancer [61]. However, doctors should be careful when prescribing antidepressants. Several studies have reported that antidepressant use is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease mortality and all-cause mortality [62, 63], while others did not observe an association between antidepressant use and the risk of recurrence and mortality [64, 65]. Therefore, physicians, oncologists, and psychiatrists should work together to develop better options in the coordination of care and treatment for these patients.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that depression and anxiety both have adverse effects on recurrence and all-cause mortality in patients with breast cancer, and depression can predict cancer-specific mortality, while anxiety cannot. Comorbidity of depression and anxiety is associated with all-cause mortality and cancer-specific mortality. The findings indirectly support the need for early and regular detection and timely treatment of mental disorders in patients with breast cancer, especially in the early period after cancer diagnosis. Furthermore, physicians should work more closely with psychiatrists and oncologists on the coordination of care and treatment for these patients. However, further research is required to identify the intervention strategies and coordination models that work best to improve outcomes among cancer patients with mental disorders and to further clarify the causal pathways between mental illness and worse survival.
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Plevritis SK, Munoz D, Kurian AW, Stout NK, Alagoz O, Near AM, et al. Association of screening and treatment with breast cancer mortality by molecular subtype in US Women, 2000–2012. JAMA. 2018;319:154–64.
DeSantis CE, Bray F, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Anderson BO, Jemal A. International variation in female breast cancer incidence and mortality rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2015;24:1495–506.
Gulati M, Mulvagh SL. The connection between the breast and heart in a woman: breast cancer and cardiovascular disease. Clin Cardiol. 2018;41:253–7.
Abdel-Qadir H, Austin PC, Lee DS, Amir E, Tu JV, Thavendiranathan P, et al. A population-based study of cardiovascular mortality following early-stage breast cancer. JAMA Cardiol. 2017;2:88–93.
Carter CL, Allen C, Henson DE. Relation of tumor size, lymph node status, and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer. 1989;63:181–7.
Schwartz AM, Henson DE, Chen D, Rajamarthandan S. Histologic grade remains a prognostic factor for breast cancer regardless of the number of positive lymph nodes and tumor size: a study of 161708 cases of breast cancer from the SEER Program. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014;138:1048–52.
Solak M, Turkoz FP, Keskin O, Aksoy S, Babacan T, Sarici F, et al. The lymph node ratio as an independent prognostic factor for non-metastatic node-positive breast cancer recurrence and mortality. J BUON. 2015;20:737–45.
Weiss SE, Tartter PI, Ahmed S, Brower ST, Brusco C, Bossolt K, et al. Ethnic differences in risk and prognostic factors for breast cancer. Cancer. 1995;76:268–74.
Adami HO, Malker B, Meirik O, Persson I, Bergkvist L, Stone B. Age as a prognostic factor in breast cancer. Cancer. 1985;56:898–902.
Arce-Salinas C, Aguilar-Ponce JL, Villarreal-Garza C, Lara-Medina FU, Olvera-Caraza D, Alvarado Miranda A, et al. Overweight and obesity as poor prognostic factors in locally advanced breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;146:183–8.
Lafourcade A, His M, Baglietto L, Boutron-Ruault MC, Dossus L, Rondeau V. Factors associated with breast cancer recurrences or mortality and dynamic prediction of death using history of cancer recurrences: the French E3N cohort. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:171–80.
Alburo AF, Dubon E, Aguirre I, Pérez V, Hernandez-Rodriguez NA. Estrogen receptor β expression in high-grade breast cancer patients may predict metastases and mortality. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:671.
Caruso R, Nanni M, Riba M, Sabato S, Grassi L. The burden of psychosocial morbidity related to cancer: patient and family issues. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2017;29:1–14.
Hodgkinson K, Butow P, Hunt G, Pendlebury S, Hobbs K, Wain G. Breast cancer survivors’ supportive care needs 2–10 years after diagnosis. Support Care Cancer. 2007;15:515–23.
Balouchi A, Hashemi S-M, Rafiemanesh H, Amirshahi M, Afsargharehbagh R. Global prevalence of depression among breast cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019;176:519–33.
Hashemi S-M, Rafiemanesh H, Aghamohammadi T, Badakhsh M, Amirshahi M, Sari M, et al. Prevalence of anxiety among breast cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer. 2019;27:166–78.
Goodwin JS, Zhang DD, Ostir GV. Effect of depression on diagnosis, treatment, and survival of older women with breast cancer. J Am Geriatrics Soc. 2004;52:106–11.
Vodermaier A, Linden W, Rnic K, Young SN, Ng A, Ditsch N, et al. Prospective associations of depression with survival: a population-based cohort study in patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014;143:373–84.
Kanani R, Davies EA, Hanchett N, Jack RH. The association of mood disorders with breast cancer survival: an investigation of linked cancer registration and hospital admission data for South East England. Psycho-oncology. 2016;25:19–27.
Iglay K, Santorelli ML, Hirshfield KM, Williams JM, Rhoads GG, Lin Y, et al. Impact of preexisting mental illness on all-cause and breast cancer-specific mortality in elderly patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:4012–8.
Liang X, Margolis KL, Hendryx M, Reeves K, Wassertheil-Smoller S, Weitlauf J, et al. Effect of depression before breast cancer diagnosis on mortality among postmenopausal women. Cancer. 2017;123:3107–15.
Desai R, Camacho F, Tan X, LeBaron V, Blackhall L, Balkrishnan R. Mental health comorbidities and elevated risk of opioid use in elderly breast cancer survivors using adjuvant endocrine treatments. J Oncol Pract. 2019;15:e777–86.
Shim EJ, Lee JW, Cho J, Jung HK, Kim NH, Lee JE, et al. Association of depression and anxiety disorder with the risk of mortality in breast cancer: a National Health Insurance Service study in Korea. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019;179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-10019-05479-10543.
Watson M, Homewood J, Haviland J, Bliss JM. Influence of psychological response on breast cancer survival: 10-year follow-up of a population-based cohort. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:1710–4.
Onitilo AA, Nietert PJ, Egede LE. Effect of depression on all-cause mortality in adults with cancer and differential effects by cancer site. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2006;28:396–402.
Groenvold M, Petersen MA, Idler E, Bjorner JB, Fayers PM, Mouridsen HT. Psychological distress and fatigue predicted recurrence and survival in primary breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007;105:209–19.
Phillips KA, Osborne RH, Giles GG, Dite GS, Apicella C, Hopper JL, et al. Psychosocial factors and survival of young women with breast cancer: A population-based prospective cohort study. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4666–71.
Chen S, Chang C, Chen K, Liu C. Association between depressive disorders and risk of breast cancer recurrence after curative surgery. Medicine. 2016;95:1–6.
Eskelinen M, Korhonen R, Selander T, Ollonen P. Beck depression inventory as a predictor of long-term outcome among patients admitted to the breast cancer diagnosis unit: a 25-year cohort study in Finland. Anticancer Res. 2017;37:819–24.
Pinquart M, Duberstein PR. Depression and cancer mortality: a meta-analysis. Psychol Med. 2010;40:1797–810.
Satin JR, Wolfgang L, Phillips MJ. Depression as a predictor of disease progression and mortality in cancer patients: a meta-analysis. Cancer. 2009;115:5349–61.
Giese-Davis J, Collie K, Rancourt KM, Neri E, Kraemer HC, Spiegel D. Decrease in depression symptoms is associated with longer survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer: a secondary analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:413–420.
Mirosevic S, Jo B, Kraemer HC, Ershadi M, Neri E, Spiegel D. “Not just another meta-analysis”: sources of heterogeneity in psychosocial treatment effect on cancer survival. Cancer Med. 2019;8:363–73.
Kissane DW, Grabsch B, Clarke DM, Smith GC, Love AW, Bloch S, et al. Supportive-expressive group therapy for women with metastatic breast cancer: survival and psychosocial outcome from a randomized controlled trial. Psycho-oncology. 2010;16:277–86.
Bredal IS, Sandvik L, Karesen R, Ekeberg O. Prognostic value of health-related quality-of-life parameters in early-stage breast cancer: an 8-year follow-up study. Psycho-oncology. 2011;20:1102–7.
Chen H, Liu D, Guo L, Cheng X, Guo N, Shi M. Chronic psychological stress promotes lung metastatic colonization of circulating breast cancer cells by decorating a pre-metastatic niche through activating β-adrenergic signaling: chronic psychological stress promotes lung metastatic colonization. J Pathol. 2017;244:49–60.
Qin JF, Jin FJ, Li N, Guan HT, Lan L, Ni H, et al. Adrenergic receptor beta2 activation by stress promotes breast cancer progression through macrophages M2 polarization in tumor microenvironment. BMB Rep. 2015;48:295–300.
Thaker PH, Han LY, Kamat AA, Arevalo JM, Takahashi R, Lu C, et al. Chronic stress promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in a mouse model of ovarian carcinoma. Nat Med. 2006;12:939–44.
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. JAMA. 2000;283:2008–12.
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25:603–5.
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Decks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327:557–60.
Egger M. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;316:469–77.
Dahl Aarvik M, Sandven I, Dondo TB, Gale CP, Ruddox V, Munkhaugen J, et al. Effect of oral β-blocker treatment on mortality in contemporary post-myocardial infarction patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2019;5:12–20.
Graham J, Ramirez A, Love S, Richards M, Burgess C. Stressful life experiences and risk of relapse of breast cancer: observational cohort study. Bmj. 2002;324:1420–2.
Hjerl K, Andersen EW, Keiding N, Mouridsen HT, Mortensen PB, Jørgensen T. Depression as a prognostic factor for breast cancer mortality. Psychosomatics. 2003;44:24–30.
Batty GD, Russ TC, Stamatakis E, Kivimaki M. Psychological distress in relation to site specific cancer mortality: pooling of unpublished data from 16 prospective cohort studies. BMJ. 2017;356:1–11.
Strine TW, Mokdad AH, Dube SR, Balluz LS, Gonzalez O, Berry JT, et al. The association of depression and anxiety with obesity and unhealthy behaviors among community-dwelling US adults. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2008;30:127–37.
Souza BFD, Moraes JAD, Inocenti A, Santos MAND, Silva AEBDC, Miasso AI. Women with breast cancer taking chemotherapy: depression symptoms and treatment adherence. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2014;22:866–73.
Kim JM, Jang J-E, Stewart R, Kim S-Y, Kim S-W, Kang H-J, et al. Determinants of suicidal ideation in patients with breast cancer. Psycho-oncology. 2013;22:2848–56.
Pruessner M, Hellhammer DH, Pruessner JC, Lupien SJ. Self-reported depressive symptoms and stress levels in healthy young men: associations with the cortisol response to awakening. Psychosom Med. 2003;65:92–9.
Sephton S, Sapolsky R, Kraemer H, Spiegel D. Diurnal cortisol rhythm as a predictor of breast cancer survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:994–1000.
Cui B, Luo Y, Tian P, Peng F, Lu J, Yang Y, et al. Stress-induced epinephrine enhances lactate dehydrogenase A and promotes breast cancer stem-like cells. J Clin Investig. 2019;129:1030–46.
Kamiya A, Hayama Y, Kato S, Shimomura A, Shimomura T, Irie K, et al. Genetic manipulation of autonomic nerve fiber innervation and activity and its effect on breast cancer progression. Nat Neurosci. 2019;22:1289–305.
Haomin Yang JSB, Fang Fang, Chiesa Flaminia, Johansson AnnaLV, Hall Per, Czene Kamila. Time-dependent risk of depression, anxiety, and stress-related disorders in patients with invasive and in situ breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2016;140:841–52.
Fischer D, Wedel B. Anxiety and depression disorders in cancer patients: incidence, diagnosis and therapy. Mag Eur Med Oncol. 2012;5:52–4.
Meijer A, Conradi HJ, Bos EH, Thombs BD, van Melle JP, de Jonge P. Prognostic association of depression following myocardial infarction with mortality and cardiovascular events: a meta-analysis of 25 years of research. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2011;33:203–16.
Watson M, Haviland JS, Greer S, Davidson J, Bliss JM. Influence of psychological response on survival in breast cancer: a population-based cohort study. Lancet. 1999;354:1331–6.
Lovibond PF. Long-term stability of depression, anxiety, and stress syndromes. J Abnorm Psychol. 1998;107:520–6.
Nicholson A, Kuper H, Hemingway H. Depression as an aetiologic and prognostic factor in coronary heart disease: a meta-analysis of 6362 events among 146 538 participants in 54 observational studies. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:2763–74.
Liliana Coutiño-Escamilla, Maricela Piña-Pozas, Aurelio Tobías, et al. Non-pharmacological therapies for depressive symptoms in breast cancer patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Breast. 2019;44:135–43.
Wernli KJ, Hampton JM, Trentham-Dietz A, Newcomb PA. Use of antidepressants and NSAIDs in relation to mortality in long-term breast cancer survivors. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2011;20:131–7.
Busby J, Mills K, Zhang SD, Liberante FG, Cardwell CR. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use and breast cancer survival: a population-based cohort study. Breast Cancer Res BCR. 2018;20:4–13.
Baker Holly. Use of antidepressants and breast cancer recurrence. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:e11.
Chubak J, Buist DSM, Boudreau DM, Rossing MA, Lumley T, Weiss NS. Breast cancer recurrence risk in relation to antidepressant use after diagnosis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008;112:123–32.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant [81873306, 81573651, 81973526, 81703749, 81703764]; Guangdong Science and Technology Department under Grant [2016A030306025]; Guangdong High-level Personnel of Special Support Program under Grant [A1-3002-16-111-003]; Department of Education of Guangdong Province under Grant [2018KZDXM022, A1-2606-19-111-009]; Guangdong traditional Chinese medicine bureau project under Grant [20181132, 20182044, 20201132]; the Ph.D. Start-up Fund of Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province under Grant [2017A030310213, 2018A030310506]; Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province under Grant [2017B030314166]; Guangzhou science and technology project under Grant [201904010407]; The Specific Research Fund for TCM Science and Technology of Guangdong provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine under Grant [YN2018MJ07, YN2018QJ08], and the Foundation for Young Scholars of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine under Grant [QNYC20190101].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZYW and XW conceived and designed the study. XW, NW, and YFZ were responsible for the literature search and study selection. XW, SQW, and YFZ were responsible for the data extraction and quality assessment. XW, BWY, and JPZ performed the statistical analyses. XW and ZYW wrote the first draft of the article. LDZ and YL provided valuable feedback regarding interpretation of the results. All authors contributed in data interpreting, writing, and correcting the paper drafts and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, N., Zhong, L. et al. Prognostic value of depression and anxiety on breast cancer recurrence and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 282,203 patients. Mol Psychiatry 25, 3186–3197 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-00865-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-00865-6
This article is cited by
-
Suicidal ideation in Chinese patients with advanced breast cancer: a multi-center mediation model study
BMC Psychology (2024)
-
The effect of the Yara smartphone application on anxiety, sleep quality, and suicidal thoughts in patients with major depressive disorder in Iran: a randomized controlled trial
BMC Psychiatry (2024)
-
Age- and sex-specific associations of frailty with mortality and healthcare utilization in community-dwelling adults from Ontario, Canada
BMC Geriatrics (2024)
-
The cancer-immune dialogue in the context of stress
Nature Reviews Immunology (2024)
-
Association between malnutrition and anxiety in cancer patients—a retrospective study
Supportive Care in Cancer (2024)