Abstract
Objective
The present study evaluated the pain perception in preterm neonates during insertion of orogastric (OG) vs. nasogastric (NG) tube by measuring the cerebral regional oxygen saturation (crSO2) and premature infant pain profile-revised (PIPP-R) score.
Study design
Randomized controlled cross-over trial.
Results
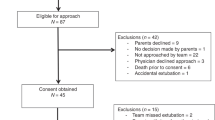
Fifty infants of mean (SD) gestational age of 31.54(2) and 31.64(2.2) weeks, birth weight of 1362(354) and 1507(365) grams were randomized into OG/NG (n = 25) and NG/OG (n = 25) sequences. Mean post-menstrual age at assessment was 33(2.8) and 33(1.5) weeks, and the difference between two interventions was 1.08(0.5) and 1.12(0.5) days in OG-NG and NG-OG, respectively. Mean crSO2(%) during insertion was significantly lower with NG compared to OG route. Mean PIPP-R score, heart rate variability, time to normalize crSO2, and the duration of cry were also significantly higher with NG insertion.
Conclusions
Compared to OG, NG route of feeding tube insertion was associated with higher fluctuations in crSO2 and higher PIPP-R scores.
Clinical Trial Registry of India (CTRI) Registration No
CTRI/2020/03/023728.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ong KK, Kennedy K, Castañeda-Gutiérrez E, Forsyth S, Godfrey KM, Koletzko B, et al. Postnatal growth in preterm infants and later health outcomes: a systematic review. Acta Paediatr. 2015;104:974–86.
Lau C. Development of Suck and Swallow mechanisms in infants. Ann Nutr Metab. 2015;66:7–14.
Watson J, McGuire W. Nasal versus oral route for placing feeding tubes in preterm or low birth weight infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2013:CD003952.
Greenspan JS, Wolfson MR, Holt WJ, Shaffer TH. Neonatal gastric intubation: differential respiratory effects between nasogastric and orogastric tubes. Ped Pulmonol. 1990;8:254–8.
Stocks J. Effect of nasogastric tubes on nasal resistance during infancy. Arch Dis Child. 1980;55:17–21.
van Someren V, Linnett SJ, Stothers JK, Sullivan PG. An investigation into the benefits of resiting nasoenteric feeding tubes. Pediatrics. 1984;74:379–83.
Finer NN, Higgins R, Kattwinkel J, Martin RJ. Summary proceedings from the apnea-of-prematurity group. Pediatrics. 2006;117:S47–51.
Metheny NA, Meert KL, Clouse RE. Complications related to feeding tube placement. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2007;23:178–82.
Pandey M, Datta V, Rehan HS. Role of sucrose in reducing painful response to orogastric tube insertion in preterm neonates. Indian J Pediatr. 2013;80:476–82.
Kristoffersen L, Skogvoll E, Hafström M. Pain reduction on insertion of a feeding tube in preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics. 2011;127:e1449–54.
Stevens BJ, Gibbins S, Yamada J, Dionne K, Lee G, Johnston C, et al. The premature infant pain profile-revised (PIPP-R): initial validation and feasibility. Clin J Pain. 2014;30:238–43.
Prince WL, Horns KM, Latta TM, Gerstmann DR. Treatment of neonatal pain without a gold standard: the case for caregiving interventions and sucrose administration. Neonatal Netw. 2004;23:33–45.
Benoit B, Martin-Misener R, Newman A, Latimer M, Campbell-Yeo M. Neurophysiological assessment of acute pain in infants: a scoping review of research methods. Acta Paediatr. 2017;106:1053–66.
Bartocci M, Bergqvist LL, Lagercrantz H, Anand KJ. Pain activates cortical areas in the preterm newborn brain. Pain. 2006;122:109–17.
Slater R, Cantarella A, Gallella S, Worley A, Boyd S, Meek J, et al. Cortical pain responses in human infants. J Neurosci. 2006;26:3662–6.
Slater R, Cantarella A, Franck L, Meek J, Fitzgerald M. How well do clinical pain assessment tools reflect pain in infants? PLoS Med. 2008;5:e129.
Olsson E, Ahlsén G, Eriksson M. Skin-to-skin contact reduces near-infrared spectroscopy pain responses in premature infants during blood sampling. Acta Paediatr. 2016;105:376–80.
Naulaers G, Meyns B, Miserez M, Leunens V, Van Huffel S, Casaer P, et al. Use of tissue oxygenation index and fractional tissue oxygen extraction as non-invasive parameters for cerebral oxygenation: a validation study in piglets. Neonatology. 2007;92:120–6.
Marulli A, Kamlin C, Dawson JA, Donath SM, Davis PG, Lorenz L. The effect of skin-to-skin care on cerebral oxygenation during nasogastric feeding of preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 2018;107:430–5.
El-Dib M, Soul JS. Monitoring and management of brain hemodynamics and oxygenation. Handb Clin Neurol. 2019;162:295–314.
Garvey AA, Kooi EMW, Smith A, Dempsey EM. Interpretation of cerebral oxygenation changes in the preterm infant. Children. 2018;5:94.
Dix LM, van Bel F, Lemmers PM. Monitoring cerebral oxygenation in neonates: an update. Front Pediatr. 2017;5:46.
Roche-Labarbe N, Carp SA, Surova A, Patel M, Boas DA, Grant PE, et al. Noninvasive optical measures of CBV, StO(2), CBF index, and rCMRO(2) in human premature neonates’ brains in the first six weeks of life. Hum Brain Mapp. 2010;31:341–52.
McNeill S, Gatenby JC, McElroy S, Engelhardt B. Normal cerebral, renal and abdominal regional oxygen saturations using near-infrared spectroscopy in preterm infants. J Perinatol. 2011;31:51–7.
Ravishankar A, Thawani R, Dewan P, Das S, Kashyap A, Batra P, et al. Oral dextrose for analgesia in neonates during nasogastric tube insertion: a randomised controlled trial. J Paediatr Child Health. 2014;50:141–5.
Bohnhorst B, Cech K, Peter C, Doerdelmann M. Oral versus nasal route for placing feeding tubes: no effect on hypoxemia and bradycardia in infants with apnea of prematurity. Neonatology. 2010;98:143–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SB, JU, SK, and PS conceptualized and designed the study, coordinated, and supervised data collection, drafted the initial manuscript, and reviewed and revised the manuscript. JU and SK collected all the data. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Upadhyay, J., Kumar, S., Singh, P. et al. Cortical hemodynamic activity and pain perception during insertion of feeding tubes in preterm neonates: a randomized controlled cross-over trial. J Perinatol 42, 121–125 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-021-01166-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-021-01166-8
This article is cited by
-
Nasogastric or Orogastric Feeding in Stable Preterm Neonates?
Indian Pediatrics (2023)
-
Neonatal Pain Response to Various Heel Prick Devices: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Indian Pediatrics (2023)
-
Nasogastric vs Orogastric Feeding in Stable Preterm (≤32 Weeks) Neonates: A Randomized Open-Label Controlled Trial
Indian Pediatrics (2023)