Abstract
Objective
To compare clonidine versus phenobarbital as adjunctive therapy in infants who failed monotherapy with morphine for neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS).
Study design
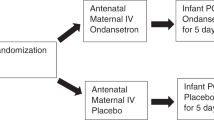
Prospective, randomized, open-label study of infants ≥ 35 weeks’ gestation. Infants received clonidine or phenobarbital per protocol. Primary outcome was morphine treatment days. Secondary outcomes were inpatient adjunctive days, length of stay (LOS), triple therapy, safety, and readmission rates.
Results
A total of 25 infants were treated with clonidine (n = 14) or phenobarbital (n = 11). Mean morphine treatment duration was significantly longer with clonidine (34.4 days, SD = 10.6) compared with phenobarbital (25.5 days, SD = 7.3, p = 0.026). The clonidine group also had higher inpatient adjunctive days (mean: 33.8 days [SD = 14.3] vs. 22 days [SD = 12.6], p = 0.042) and LOS (mean: 41.8 days [SD = 10.9] vs. 31 days [SD = 10]; p = 0.018) compared with phenobarbital.
Conclusions
Phenobarbital, as adjunctive therapy, led to significantly shorter duration of morphine therapy, inpatient adjunctive days, and length of stay compared with clonidine.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kocherlokata P. Neonatal abstinence syndrome. Pediatrics. 2014;134:540–60.
Hudak ML, Tan RC. The Committee on Drugs, Committee on Fetus and Newborn, American Academy of Pediatrics. Neonatal drug withdrawal. Pediatrics. 2012;129:e540–60.
McQueen K, Murphy-Oikonen J. Neonatal abstinence syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2468–79.
American Academy of Pediatrics on Drugs. Neonatal drug withdrawal. Pediatrics. 1998;101:1079–88.
Bio LL, Siu A, Poon CY. Update on the pharmacologic management of neonatal abstinence syndrome. J Perinatol. 2011;31:692–701.
Farwell JR, Lee YJ, Hirtz DG, Sulzbacher SI, Ellenberg JH, Nelson KB. Phenobarbital for febrile seizures—effects on intelligence and on seizure recurrence. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:364–9.
Sulzbacher S, Farwell JR, Temkin N, Lu AS, Hirtz DG. Late cognitive effects of early treatment with phenobarbital. Clin Pediatr. 1999;38:387–94.
Maitre NL, Smolinsky C, Slaughter JC, Stark AR. Adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes after exposure to phenobarbital and levetiracetam for the treatment of neonatal seizures. J Perinatol. 2013;33:841–6.
Surran B, Visintainer P, Chamberlain S, Kopcza K, Shah B, Singh R. Efficacy of clonidine versus phenobarbital in reducing neonatal morphine sulfate therapy days for neonatal abstinence syndrome. A prospective randomized clinical trial. J Perinatol. 2013;33:954–9.
Agthe AG, Kim GR, Mathias KB, Hendrix CW, Chavez-Valdez R, Jansson L, et al. Clonidine as an adjunct therapy to opioids for neonatal abstinence syndrome: a randomized. Pediatrics. 2009;123:849–56.
Bada H, Sithisarn T, Gibson J, Garlitz K, Caldwell R, Capilouto G, et al. Morphine versus clonidine for neonatal abstinence syndrome. Pediatrics. 2015;135:383–91.
Leikin JB, Mackendrick WP, Maloney GE, Rhee JW, Farrell E, Wahl M, et al. Use of clonidine in the prevention and management of neonatal abstinence syndrome. Clin Toxicol. 2007;47:551–5.
Meddock RP, Bloemer D. Evaluation of the cardiovascular effects of clonidine in neonates treated for neonatal abstinence syndrome. J Pediatr Pharm Ther. 2018;23:473–8.
Devlin LA, Lau T, Radmacher PG. Decreasing total medication exposure and length of stay while completing withdrawal for neonatal abstinence syndrome during the neonatal hospital stay. Front Pediatr. 2017;5:216.
Jansson LM, Valez M, Harrow C. The opioid exposed newborn: assessment and pharmacologic management. J Opioid Manag. 2009;5:47–55.
Burnette T, Chernicky L, Towers CV. The effect of standardizing treatment when managing neonatal abstinence syndrome. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;32:3415–9.
Ma C, Decarie D, Ensom MH. Stability of clonidine oral suspension in oral plastic syringes. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2014;71:657–61.
Coyle MG, Ferguson A, Lagasse L, Oh W, Lester B. Diluted tincture of opium (DTO) and phenobarbital versus DTO alone for neonatal opiate withdrawal in term infants. J Pediatr. 2002;140:561–4.
Wachman EM, Schiff DM, Silverstein M. Neonatal abstinence syndrome. JAMA. 2018;319:1362–74.
Forcelli PA, Kim J, Kondratyev A, Gale K. Pattern of antiepileptic drug-induced cell death in limbic regions of the neonatal rat brain. Epilepsia. 2011;52:e207–e211.
Chen J, Cai F, Cao J, Zhang X, Li S. Long-term antiepileptic drug administration during early life inhibits hippocampal neurogenesis in the developing brain. J Neurosci Res. 2009;87:2898–907.
Stefovska V, Uckermann O, Czuczwar M, Smitka M, Czuczwar P, Kis J, et al. Sedative and anticonvulsant drugs suppress postnatal neurogenesis. Ann Neurol. 2008;64:434–45.
Bhardwaj S, Forcelli P, Palchik G, Gale K, Srivastava L, Kondratyev A. Neonatal exposure to phenobarbital potentiates schizophrenia-like behavioral outcomes in the rat. Neuropharmacology. 2012;62:2337–45.
Forcelli PA, Kozlowski R, Snyder C, Kondratyev A, Gale K. Effects of neonatal antiepileptic drug exposure on cognitive, emotional, and motor function in adult rats. J Pharm Exp Ther. 2012;340:558–66.
Streetz VN, Gildon BL, Thompson DF. Role of clonidine in neonatal abstinence syndrome: a systemic review. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50:301–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CB was responsible for the study concept, design, data collection and interpretation, and preparation of the manuscript. TB was responsible for the study concept, design, data collection and interpretation, and critical review of the manuscript. REH was responsible for study design, data interpretation, and critical review of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brusseau, C., Burnette, T. & Heidel, R.E. Clonidine versus phenobarbital as adjunctive therapy for neonatal abstinence syndrome. J Perinatol 40, 1050–1055 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-020-0685-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-020-0685-2