Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the correlation between total serum and transcutaneous bilirubin and to determine the reliability of transcutaneous bilirubinometry for screening and monitoring of neonatal jaundice among preterms.
Study Design
Ninety nine infants with gestational ages ≤34 weeks were prospectively enrolled. Babies were classified into three groups as; 24–28, 29–31, and 32–34 weeks. Total serum bilirubin and simultaneous transcutaneous bilirubin were measured before the onset of phototheraphy, during and at 24 h after discontinuing phototherapy.
Results
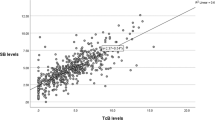
Total serum bilirubin significantly correlated with transcutaneous bilirubin in the whole cohort (r = 0.867, p < 0.001) and in each group before, during and after phototheraphy. Hypotension was the only variable which effects the difference between two methods at postnatal first day of life (p = 0.039).
Conclusion
Transcutaneous bilirubin levels were highly correlated with total serum bilirubin levels even in 24–28 GW babies. Transcutaneous bilirubin may be useful for screening and monitoring of jaundice in very preterm newborns.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Neonatal Jaundice. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, 2010, www.nice.org.uk.
Bhutani VK, Stark AR, Lazzeroni LC, Poland R, Gourley GR, Kazmierczak S, et al. Predischarge screening for severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia identifies infants who need phototherapy. J Pediatr. 2013;162:477–82.
Maisels MJ, Kring E. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry decreases the need for serum bilirubin measurements and saves money. Pediatrics. 1997;99:599–601.
De Luca D, Zecca E, de Turris P, Barbato G, Marras M, Romagnoli C. Using BiliCheck for preterm neonates in a subintensive unit: diagnostic usefulness and suitability. Early Hum Dev. 2007;83:313–7.
Bhutani VK, Gourley GR, Adler S, Kreamer B, Dalin C, Johnson LH. Noninvasive measurement of total serum bilirubin in a multiracial predischarge newborn population to assess the risk of severe hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics. 2000;106:17.
American Academy of Pediatrics, Subcommittee on Hyperbilirubinemia. Clinical guideline: management of hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant 35 or more weeks of gestation. Pediatrics. 2004;114:297–316.
Schmidt ET, Wheeler CA, Jackson GL, Engle WD. Evaluation of transcutaneous bilirubinometry in preterm neonates. J Perinatol. 2009;29:564–9.
Rubaltelli FF, Gourley GR, Loskamp N, Modi N, Roth-Kleiner M, Sender A, et al. Transcutaneous bilirubin measurement: a multicenter evaluation of a new device. Pediatrics. 2001;107:1264–71.
Fonseca R, Kyralessa R, Malloy M, Richardson J, Jain SK. Covered skin transcutaneous bilirubin estimation is comparable with serum bilirubin during and after phototherapy. J Perinatol. 2012;32:129–31.
Tan KL, Dong F. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry during and after phototherapy. Acta Paediatr. 2003;92:327–31.
Ozkan H, Oren H, Duman N, Duman M. Dermal bilirubin kinetics during phototherapy in term neonates. Acta Paediatr. 2003;92:577–81.
Hegyi T, Hiatt IM, Gertner IM, Zanni R, Tolentino T. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry II. Dermal bilirubin kinetics during phototherapy. Pediatr Res. 1983;17:888–91.
Nanjundaswamy S, Petrova A, Mehta R, Hegyi T. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry in preterm infants receiving phototherapy. Am J Perinatol. 2005;22:127–31.
Knupfer M, Pulzer F, Braun L, Heilmann A, Robel-Tillig E, Vogtmann C. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr. 2001;90:899–903.
Tan KL, Mylvaganam A. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry in preterm very low birthweight infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1988;77:796–801.
Nagar G, Vandermeer B, Campbell S, Kumar M. Reliability of transcutaneous bilirubin devices in preterm infants: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2013;132:871–81.
Rubio A, Epiard C, Gebus M, Deiber M, Samperiz S, Genty C, et al. Diagnosis accuracy of transcutaneous bilirubinometry in very preterm newborns. Neonatology. 2017;111:1–7.
Maisels MJ. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry. Neo Rev. 2006;7:217–25.
Pendse A, Jasani B, Nanavati R, Kabra N. Comparison of transcutaneous bilirubin measurement with total serum bilirubin levels in preterm neonates receiving phototherapy. Indian Pediatr. 2017;54:641–3.
Jangaard KA, Curtis H, Goldbloom RB. Estimation of bilirubin using BiliChek, a transcutaneous bilirubin measurement device: effects of gestational age and use of phototherapy. Paediatr Child Health. 2006;11:79–83.
Zecca E, Barone G, De Luca D, Marra R, Tiberi E, Romagnoli C. Skin bilirubin measurement during phototherapy in preterm and term newborn infants. Early Hum Dev. 2009;85:537–40.
Maisels MJ, Coffey MP, Kring E. Transcutaneous bilirubin levels in newborns <35 weeks’ gestation. J Perinatol. 2015;35:739–44.
Willems WA, van den Berg LM, de Wit H, Molendijk A. Transcutaneous bilirubinometry with the BiliCheck in very premature newborns. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2004;16:209–14.
Bosschaart N, Kok JH, Newsum AM, Ouweneel DM, Mentink R, van Leeuwen TG, et al. Limitations and opportunities of transcutaneous bilirubin measurements. Pediatrics. 2012;129:689–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arman, D., Topcuoğlu, S., Gürsoy, T. et al. The accuracy of transcutaneous bilirubinometry in preterm infants. J Perinatol 40, 212–218 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-019-0445-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-019-0445-3
This article is cited by
-
Transcutaneous bilirubin reliability during and after phototherapy depending on skin color
European Journal of Pediatrics (2024)
-
Transcutaneous bilirubin levels in extremely preterm infants less than 30 weeks gestation
Journal of Perinatology (2023)
-
Screening methods for neonatal hyperbilirubinemia: benefits, limitations, requirements, and novel developments
Pediatric Research (2021)
-
Reliability of transcutaneous bilirubin determination based on skin color determined by a neonatal skin color scale of our own
European Journal of Pediatrics (2021)
-
TcB, FFR, phototherapy and the persistent occurrence of kernicterus spectrum disorder
Journal of Perinatology (2020)