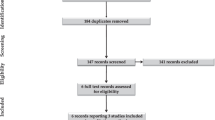
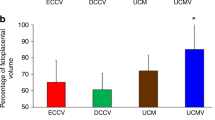
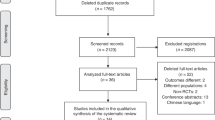
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the feasibility and safety of umbilical cord milking (UCM) in neonates who are depressed at birth.
Study design
This is a quasi-randomized, non-blinded, controlled trial on infants (≥35 weeks) who were depressed at birth. UCM (cord milked three times) was performed during the even months and the neonates born during the odd months were in the control group. Primary outcome was feasibility and safety.
Results
A total of 101 infants were enrolled (50 UCM group and 51 control group) between January 2015 and October 2016. UCM was performed in 95% of infants (59/62) who qualified to receive UCM. There were no significant differences in resuscitation delay, resuscitation efforts, and short-term outcomes between the two groups.
Conclusions
UCM is feasible for term and late preterm infants who are depressed at birth. A larger clinical trial is needed to evaluate long-term benefits of UCM in neonates with HIE.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fogarty M, Osborn DA, Askie L, Seidler AL, Hunter K, Lui K, et al. Delayed vs early umbilical cord clamping for preterm infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218:1–18.
Kc A, Rana N, Malqvist M, Jarawka Ranneberg L, Subedi K, Andersson O. Effects of delayed umbilical cord clamping vs early clamping on anemia in infants at 8 and 12 months: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171:264–70.
WHO. Guideline: delayed umbilical cord clamping for improved maternal and infant health and nutrition outcomes. WHO: Geneva; 2014.
Committee on Obstetric Practice. Committee opinion no. 684 summary: delayed umbilical cord clamping after birth. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;129:232–3.
Rabe H, Jewison A, Alvarez RF, Crook D, Stilton D, Bradley R, et al. Milking compared with delayed cord clamping to increase placental transfusion in preterm neonates: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;117(2 Pt 1):205–11.
Katheria A, Garey D, Truong G, Akshoomoff N, Steen J, Maldonado M, et al. A randomized clinical trial of umbilical cord milking vs delayed cord clamping in preterm infants: neurodevelopmental outcomes at 22-26 months of corrected age. J Pediatr. 2017;194:76–80.
Tagin MA, Woolcott CG, Vincer MJ, Whyte RK, Stinson DA. Hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2012;166:558–66.
Yang Z, You Y, Levison SW. Neonatal hypoxic/ischemic brain injury induces production of calretinin-expressing interneurons in the striatum. J Comp Neurol. 2008;511:19–33.
Liao Y, Cotten M, Tan S, Kurtzberg J, Cairo MS. Rescuing the neonatal brain from hypoxic injury with autologous cord blood. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48:890–900.
Pimentel-Coelho PM, Rosado-de-Castro PH, da Fonseca LM, Mendez-Otero R. Umbilical cord blood mononuclear cell transplantation for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Res. 2012;71(4 Pt 2):464–73.
Upadhyay A, Gothwal S, Parihar R, Garg A, Gupta A, Chawla D, et al. Effect of umbilical cord milking in term and near term infants: randomized control trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013;208:120 e121–126.
Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Ehrenkranz RA, Tyson JE, McDonald SA, Donovan EF, et al. Whole-body hypothermia for neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1574–84.
Pauliah SS, Shankaran S, Wade A, Cady EB, Thayyil S. Therapeutic hypothermia for neonatal encephalopathy in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e58834.
Sarnat HB, Sarnat MS. Neonatal encephalopathy following fetal distress. A clinical and electroencephalographic study. Arch Neurol. 1976;33:696–705.
Shankaran S, Woldt E, Koepke T, Bedard MP, Nandyal R. Acute neonatal morbidity and long-term central nervous system sequelae of perinatal asphyxia in term infants. Early Hum Dev. 1991;25:135–48.
de Vries LS, Jongmans MJ. Long-term outcome after neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2010;95:F220–224.
Shankaran S. Therapeutic hypothermia for neonatal encephalopathy. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2012;14:608–19.
Cotten CM, Murtha AP, Goldberg RN, Grotegut CA, Smith PB, Goldstein RF, et al. Feasibility of autologous cord blood cells for infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 2014;164:973–979 e971.
Linderkamp O, Nelle M, Kraus M, Zilow EP. The effect of early and late cord-clamping on blood viscosity and other hemorheological parameters in full-term neonates. Acta Paediatr. 1992;81:745–50.
Bora R, Akhtar SS, Venkatasubramaniam A, Wolfson J, Rao R. Effect of 40-cm segment umbilical cord milking on hemoglobin and serum ferritin at 6 months of age in full-term infants of anemic and non-anemic mothers. J Perinatol. 2015;35:832–6.
Schwarting S, Litwak S, Hao W, Bahr M, Weise J, Neumann H. Hematopoietic stem cells reduce postischemic inflammation and ameliorate ischemic brain injury. Stroke. 2008;39:2867–75.
Liesz A, Suri-Payer E, Veltkamp C, Doerr H, Sommer C, Rivest S, et al. Regulatory T cells are key cerebroprotective immunomodulators in acute experimental stroke. Nat Med. 2009;15:192–9.
Fan CG, Zhang QJ, Tang FW, Han ZB, Wang GS, Han ZC. Human umbilical cord blood cells express neurotrophic factors. Neurosci Lett. 2005;380:322–5.
Ikeda T, Xia XY, Xia YX, Ikenoue T, Han B, Choi BH. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor protects against ischemia/hypoxia-induced brain injury in neonatal rat. Acta Neuropathol. 2000;100:161–7.
Holtzman DM, Sheldon RA, Jaffe W, Cheng Y, Ferriero DM. Nerve growth factor protects the neonatal brain against hypoxic-ischemic injury. Ann Neurol. 1996;39:114–22.
Feng Y, Rhodes PG, Bhatt AJ. Neuroprotective effects of vascular endothelial growth factor following hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Pediatr Res. 2008;64:370–4.
Cao X, Shoichet MS. Investigating the synergistic effect of combined neurotrophic factor concentration gradients to guide axonal growth. Neuroscience. 2003;122:381–9.
Aly H, Khashaba MT, El-Ayouty M, El-Sayed O, Hasanein BMIL-1beta. IL-6 and TNF-alpha and outcomes of neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Brain Dev. 2006;28:178–82.
Silveira RC, Procianoy RS. Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of term newborn infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Pediatr. 2003;143:625–9.
Shang Y, Mu L, Guo X, Li Y, Wang L, Yang W, et al. Clinical significance of interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8:1259–62.
Neuhoff S, Moers J, Rieks M, Grunwald T, Jensen A, Dermietzel R, et al. Proliferation, differentiation, and cytokine secretion of human umbilical cord blood-derived mononuclear cells in vitro. Exp Hematol. 2007;35:1119–31.
Newman MB, Willing AE, Manresa JJ, Sanberg CD, Sanberg PR. Cytokines produced by cultured human umbilical cord blood (HUCB) cells: implications for brain repair. Exp Neurol. 2006;199:201–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girish, M., Jain, V., Dhokane, R. et al. Umbilical cord milking for neonates who are depressed at birth: a randomized trial of feasibility. J Perinatol 38, 1190–1196 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-018-0161-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41372-018-0161-4
This article is cited by
-
Umbilical cord milking versus delayed cord clamping in term infants: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Journal of Perinatology (2021)
-
Short-term efficacy of umbilical cord milking in preterm infants: systematic review and meta-analysis
Pediatric Research (2021)
-
Umbilical cord milking in asphyxiated neonates: ethical dilemmas
Journal of Perinatology (2019)
-
Umbilical cord milking in preterm infants: time to act
Journal of Perinatology (2019)
-
Optimal Timing and Methodology of Umbilical Cord Clamping in Preterm Infants: a Review
Current Pediatrics Reports (2019)