Abstract
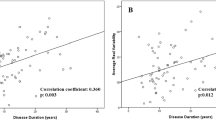
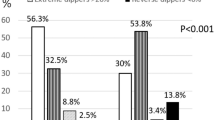
Predictors of adverse cardiovascular outcomes include elevated nighttime systolic blood pressure (SBP) and a non-dipping pattern. We investigated whether these factors correlate with systemic inflammation, cardiovascular risk, and markers of central and peripheral vascular damage in rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a disease characterized by excess cardiovascular risk. Twenty-four-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring was applied in patients and controls. Vascular assessments included measurement of arterial stiffness (pulse wave velocity) and carotid atherosclerosis (carotid intima-media thickness). Peripheral vascular resistance was estimated from impedance cardiography. Cardiovascular risk was calculated from the Framingham Heart Study. RA patients exhibited a higher prevalence of non-dipping pattern, elevated nighttime SBP and blunted dipping, compared to controls without cardiovascular comorbidities. Among RA patients, dipping levels correlated with arterial stiffness, and nighttime SBP with all vascular markers and cardiovascular risk. After adjustment for inflammation, the above associations with vascular measures were no longer significant. Plain categorization to dippers and non-dippers did not reveal any differences regarding inflammation, vascular measurements, and cardiovascular risk. However, the combination of a non-dipping profile with high nighttime SBP was accompanied by significantly higher levels of arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk, compared to non-dippers with normal nighttime SBP; these parameters were similar between the latter group and dippers. Inflammation appears to mediate the observed associations of nighttime SBP and dipping levels with markers of subclinical vascular damage in RA patients. In these patients, the combination of a non-dipping profile with elevated nighttime SBP is accompanied by prominent subclinical vascular impairment and confers the highest cardiovascular risk.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Halm VP, Peters MJL, Voskuyl AE, Boers M, Lems WF, Visser M, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis versus diabetes as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease: a cross-sectional study, the CARRE Investigation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:1395–1400.
Van Doornum S, McColl G, Wicks IP. Accelerated atherosclerosis: an extraarticular feature of rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:862–73.
Krakoff LR. Ambulatory blood pressure improves prediction of cardiovascular risk: implications for better antihypertensive management. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2013;15:317.
O’Brien E. Twenty-four-hour ambulatory blood pressure measurement in clinical practice and research: a critical review of a technique in need of implementation. J Intern Med. 2011;269:478–95.
Cicek Y, Durakoglugil ME, Kocaman SA, Cetin M, Erdogan T, Dogan S, et al. Non-dipping pattern in untreated hypertensive patients is related to increased pulse wave velocity independent of raised nocturnal blood pressure. Blood Press. 2013;22:34–8.
Cuspidi C, Sala C, Tadic M, Gherbesi E, Grassi G, Mancia G. Nondipping pattern and carotid atherosclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hypertens. 2016;34:382–5.
Fan H-Q, Li Y, Thijs L, Hansen TW, Boggia J, Kikuya M, et al. Prognostic value of isolated nocturnal hypertension on ambulatory measurement in 8711 individuals from 10 populations. J Hypertens. 2010;28:2036–45.
Ohkubo T, Hozawa A, Yamaguchi J, Kikuya M, Ohmori K, Michimata M, et al. Prognostic significance of the nocturnal decline in blood pressure in individuals with and without high 24-h blood pressure: the Ohasama study. J Hypertens. 2002;20:2183–9.
Salles GF, Reboldi G, Fagard RH, Cardoso CRL, Pierdomenico SD, Verdecchia P, et al. Prognostic effect of the nocturnal blood pressure fall in hypertensive patients: The ambulatory blood pressure collaboration in patients with hypertension (ABC-H) meta-analysis. Hypertension. 2016;67:693–700.
Mancia G, Verdecchia P. Clinical value of ambulatory blood pressure: evidence and limits. Circ Res. 2015;116:1034–45.
Kaya MG, Yarlioglues M, Gunebakmaz O, Gunturk E, Inanc T, Dogan A, et al. Platelet activation and inflammatory response in patients with non-dipper hypertension. Atherosclerosis. 2010;209:278–82.
Tsioufis C, Syrseloudis D, Dimitriadis K, Thomopoulos C, Tsiachris D, Pavlidis P, et al. Disturbed circadian blood pressure rhythm and C-reactive protein in essential hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2008;22:501–8.
Hamamoto K, Yamada S, Yasumoto M, Yoda M, Yoda K, Tsuda A, et al. Association of nocturnal hypertension with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Hypertens. 2016;29:340–7.
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NSHLA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS, et al. the American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:315–24.
Celik G, Yilmaz S, Ergulu Esmen S. Non-dipping blood pressure patterns and arterial stiffness parameters in patients with Behcet’s disease. Hypertens Res. 2015;38:856–61.
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redón J, Zanchetti A, Böhm M, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2013;31:1281–357.
Prevoo M, van’t Hof M, Kuper H, van Leeuwen M, van de Putte L, van Riel P. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight - joint counts. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:44–48.
Rajzer MW, Wojciechowska W, Klocek M, Palka I, Brzozowska-Kiszka MM, Kawecka-Jaszcz K. Comparison of aortic pulse wave velocity measured by three techniques: complior, SphygmoCor and arteriograph. J Hypertens. 2008;26:2001–7.
Stein JH, Korcarz CE, Hurst RT, Lonn E, Kendall CB, Mohler ER, et al. Use of carotid ultrasound to identify subclinical vascular disease and evaluate cardiovascular disease risk: a consensus statement from the American Society of Echocardiography Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Task Force Endorsed by the Society for Vascular. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008;21:93–111.
Van De Water JM, Miller TW, Vogel RL, Mount BE, Dalton ML. Impedance cardiography the next vital sign technology? Chest. 2003;123:2028–33.
Ventura HO, Taler SJ, Strobeck JE. Hypertension as a hemodynamic disease: the role of impedance cardiography in diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic decision making. Am J Hypertens. 2005;18:26S–43S.
Crowson CS, Gabriel SE, Semb AG, van Riel PLCM, Karpouzas G, Dessein PH, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-specific cardiovascular risk scores are not superior to general risk scores: a validation analysis of patients from seven countries. Rheumatology. 2017;56:1102–10.
D’Agostino RB, Vasan RS, Pencina MJ, Wolf PA, Cobain M, Massaro JM, et al. General cardiovascular risk profile for use in primary care: the Framingham heart study. Circulation. 2008;117:743–53.
Bacaksiz A, Akif Vatankulu M, Sonmez O, Erdogan E, Tasal A, Turfan M, et al. Non-dipping nocturnal blood pressure in psoriasis vulgaris. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2012;124:822–9.
Pourafkari L, Masnadi-Shirazi K, Taban M, Mohammadi S, Parizad R, Ghaffari S, et al. Higher frequency of nocturnal blood pressure dipping but not heart rate dipping in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2017;62:2863–9.
Karakulak UN, Sahiner L, Maharjan N, Okutucu S, Evranos B, Aladag E, et al. Evaluation of the ambulatory arterial stiffness index in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Blood Press Monit. 2015;20:254–9.
Belt NK, Kronholm E, Kauppi MJ. Sleep problems in fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis compared with the general population. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009;27:35–41.
Taylor-Gjevre RM, Gjevre JA, Nair B, Skomro R, Lim HJ. Components of sleep quality and sleep fragmentation in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Musculoskelet Care. 2011;9:152–9.
Ulus Y, Akyol Y, Tander B, Durmus D, Bilgici A, Kuru O. Sleep quality in fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis: associations with pain, fatigue, depression, and disease activity. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29:S92–6.
Irwin MR, Olmstead R, Carrillo C, Sadeghi N, FitzGerald JD, Ranganath VK, et al. Sleep loss exacerbates fatigue, depression, and pain in rheumatoid arthritis. Sleep. 2012;35:537–43.
Mousa T, El-Sayed MA, Motawea AK, Salama MA, Elhendy A. Association of blunted nighttime blood pressure dipping with coronary artery stenosis in men. Am J Hypertens. 2004;17:977–80.
Cicconetti P. Blunted nocturnal fall in blood pressure and left ventricular mass in elderly individuals with recently diagnosed isolated systolic hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2003;16:900–5.
Hoshide S, Kario K, Hoshide Y, Umeda Y, Hashimoto T, Kunii O, et al. Associations between nondipping of nocturnal blood pressure decrease and cardiovascular target organ damage in strictly selected community-dwelling normotensives. Am J Hypertens. 2003;16:434–8.
Cavelaars M, Tulen JHM, van Bemmel JH, van den Meiracker AH. Physical activity, dipping and haemodynamics. J Hypertens. 2004;22:2303–9.
Hermida RC, Ayala DE, Mojón A, Fernández JR. Influence of circadian time of hypertension treatment on cardiovascular risk: results of the Mapec study. Chronobiol Int. 2010;27:1629–51.
Manning G, Rushton L, Donnelly R, Millar-Craig MW. Variability of diurnal changes in ambulatory blood pressure and nocturnal dipping status in untreated hypertensive and normotensive subjects. Am J Hypertens. 2000;13:1035–8.
Cuspidi C, Meani S, Salerno M, Valerio C, Fusi V, Severgnini B, et al. Reproducibility of nocturnal blood pressure fall in early phases of untreated essential hypertension: a prospective observational study. J Hum Hypertens. 2004;18:503–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gkaliagkousi, E., Anyfanti, P., Chatzimichailidou, S. et al. Association of nocturnal blood pressure patterns with inflammation and central and peripheral estimates of vascular health in rheumatoid arthritis. J Hum Hypertens 32, 259–267 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0047-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-018-0047-0
This article is cited by
-
Clinical Significance of Nocturnal Hypertension and Nighttime Blood Pressure Dipping in Hypertension
Current Hypertension Reports (2024)
-
Association between ambulatory blood pressure monitoring patterns with cognitive function and risk of dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research (2023)