Abstract
Background/objectives
During obesity, hypertrophic enlargement of white adipose tissue (WAT) promotes ectopic lipid deposition and development of insulin resistance. In contrast, WAT hyperplasia is associated with preservation of insulin sensitivity. The complex network of factors that regulates white adipogenesis is not fully understood. Bone morphogenic protein 7 (BMP7) can induce brown adipogenesis, but its role on white adipogenesis remains to be elucidated. Here, we assessed BMP7-mediated effects on white adipogenesis in ob/ob mice.
Methods
BMP7 was overexpressed in either WAT or liver of ob/ob mice using adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors. Analysis of gene expression, histological and morphometric alterations, and metabolites and hormones concentrations were carried out.
Results
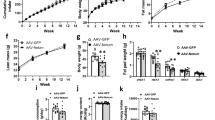
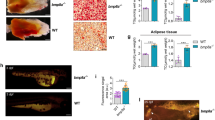
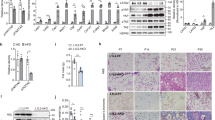
Overexpression of BMP7 in adipocytes of subcutaneous and visceral WAT increased fat mass, the proportion of small-size adipocytes and the expression of adipogenic and mature adipocyte genes, suggesting induction of adipogenesis irrespective of fat depot. These changes were associated with reduced hepatic steatosis and improved insulin sensitivity. In contrast, liver-specific overproduction of BMP7 did not promote WAT hyperplasia despite BMP7 circulating levels were similar to those achieved after genetic engineering of WAT.
Conclusions
This study unravels a new autocrine/paracrine role of BMP7 on white adipogenesis and highlights that BMP7 may modulate WAT plasticity and increase insulin sensitivity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang QA, Tao C, Gupta RK, Scherer PE. Tracking adipogenesis during white adipose tissue development, expansion and regeneration. Nat Med. 2013;19:1338–44.
Spalding KL, Arner E, Westermark PO, Bernard S, Buchholz BA, Bergmann O, et al. Dynamics of fat cell turnover in humans. Nature. 2008;453:783–7.
Arner P, Andersson DP, Thörne A, Wirén M, Hoffstedt J, Näslund E, et al. Variations in the size of the major omentum are primarily determined by fat cell number. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98:E897–901.
Hammarstedt A, Gogg S, Hedjazifar S, Nerstedt A, Smith U. Impaired adipogenesis and dysfunctional adipose tissue in human hypertrophic obesity. Physiol Rev. 2018;98:1911–41.
Acosta JR, Douagi I, Andersson DP, Bäckdahl J, Rydén M, Arner P, et al. Increased fat cell size: a major phenotype of subcutaneous white adipose tissue in non-obese individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2016;59:560–70.
Hoffstedt J, Arner E, Wahrenberg H, Andersson DP, Qvisth V, Löfgren P, et al. Regional impact of adipose tissue morphology on the metabolic profile in morbid obesity. Diabetologia. 2010;53:2496–503.
McLaughlin TM, Liu T, Yee G, Abbasi F, Lamendola C, Reaven GM, et al. Pioglitazone increases the proportion of small cells in human abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue. Obesity. 2010;18:926–31.
Li H, Wu G, Fang Q, Zhang M, Hui X, Sheng B, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 increases insulin sensitivity through specific expansion of subcutaneous fat. Nat Commun. 2018;9:272.
Fried SK, Lee M-J, Karastergiou K. Shaping fat distribution: new insights into the molecular determinants of depot- and sex-dependent adipose biology. Obesity. 2015;23:1345–52.
Carobbio S, Pellegrinelli V, Vidal-Puig A. Adipose tissue function and expandability as determinants of lipotoxicity and the metabolic syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:161–96.
Kim SM, Lun M, Wang M, Senyo SE, Guillermier C, Patwari P, et al. Loss of white adipose hyperplastic potential is associated with enhanced susceptibility to insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2014;20:1049–58.
Jeffery E, Church CD, Holtrup B, Colman L, Rodeheffer MS. Rapid depot-specific activation of adipocyte precursor cells at the onset of obesity. Nat Cell Biol. 2015;17:376–85.
Permana PA, Nair S, Lee Y-H, Luczy-Bachman G, Vozarova De Courten B, Tataranni PA. Subcutaneous abdominal preadipocyte differentiation in vitro inversely correlates with central obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004;286:E958–62.
Tchoukalova Y, Koutsari C, Jensen M. Committed subcutaneous preadipocytes are reduced in human obesity. Diabetologia. 2007;50:151–7.
Almuraikhy S, Kafienah W, Bashah M, Diboun I, Jaganjac M, Al-Khelaifi F, et al. Interleukin-6 induces impairment in human subcutaneous adipogenesis in obesity-associated insulin resistance. Diabetologia. 2016;59:2406–16.
Arner P, Arner E, Hammarstedt A, Smith U. Genetic predisposition for type 2 diabetes, but not for overweight/obesity, is associated with a restricted adipogenesis. PLoS One. 2011;6:e18284.
Carreira ACO, Zambuzzi WF, Rossi MC, Filho RA, Sogayar MC, Granjeiro JM. Bone morphogenetic proteins: promising molecules for bone healing, bioengineering, and regenerative medicine. In: Vitamins and hormones. Elsevier Inc., Oxford, UK, 2015;293–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2015.06.002.
Schulz TJ, Tseng YH. Emerging role of bone morphogenetic proteins in adipogenesis and energy metabolism. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20:523–31.
Blázquez-Medela AM, Jumabay M, Rajbhandari P, Sallam T, Guo Y, Yao J, et al. Noggin depletion in adipocytes promotes obesity in mice. Mol Metab. 2019;25:50–63.
Tseng Y-H, Kokkotou E, Schulz TJ, Huang TL, Winnay JN, Taniguchi CM, et al. New role of bone morphogenetic protein 7 in brown adipogenesis and energy expenditure. Nature. 2008;454:1000–4.
Salisbury EA, Lazard ZW, Ubogu EE, Davis AR, Olmsted-Davis EA. Transient brown adipocyte-like cells derive from peripheral nerve progenitors in response to bone morphogenetic protein 2. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1:874–85.
Qian S-W, Tang Y, Li X, Liu Y, Zhang Y-Y, Huang H-Y, et al. BMP4-mediated brown fat-like changes in white adipose tissue alter glucose and energy homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:E798–807.
Kim M, Kim JI, Kim JB, Choe S. The activin-βA/BMP-2 chimera AB204 is a strong stimulator of adipogenesis. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11:1524–31.
Gustafson B, Hedjazifar S, Gogg S, Hammarstedt A, Smith U. Insulin resistance and impaired adipogenesis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015;26:193–200.
Elsen M, Raschke S, Tennagels N, Schwahn U, Jelenik T, Roden M, et al. BMP4 and BMP7 induce the white-to-brown transition of primary human adipose stem cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014;306:C431–40.
Hinoi E, Nakamura Y, Takada S, Fujita H, Iezaki T, Hashizume S, et al. Growth differentiation factor-5 promotes brown adipogenesis in systemic energy expenditure. Diabetes. 2014;63:162–75.
Lord E, Bergeron E, Senta H, Park H, Faucheux N. Effect of BMP-9 and its derived peptide on the differentiation of human white preadipocytes. Growth Factors. 2010;28:149–56.
Pei Z, Yang Y, Kiess W, Sun C, Luo F. Dynamic profile and adipogenic role of growth differentiation factor 5 (GDF5) in the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014;560:27–35.
Kuo MM-C, Kim S, Tseng C-Y, Jeon Y-H, Choe S, Lee DK. BMP-9 as a potent brown adipogenic inducer with anti-obesity capacity. Biomaterials. 2014;35:3172–9.
Ayuso E, Mingozzi F, Montane J, Leon X, Anguela XM, Haurigot V, et al. High AAV vector purity results in serotype- and tissue-independent enhancement of transduction efficiency. Gene Ther. 2010;17:503–10.
Jimenez V, Muñoz S, Casana E, Mallol C, Elias I, Jambrina C, et al. In vivo AAV-mediated genetic engineering of white and brown adipose tissue in adult mice. Diabetes. 2013;62:1–12.
Jimenez V, Jambrina C, Casana E, Sacristan V, Muñoz S, Darriba S, et al. FGF21 gene therapy as treatment for obesity and insulin resistance. EMBO Mol Med. 2018;10. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201708791.
Muñoz S, Franckhauser S, Elias I, Ferré T, Hidalgo A, Monteys AM, et al. Chronically increased glucose uptake by adipose tissue leads to lactate production and improved insulin sensitivity rather than obesity in the mouse. Diabetologia. 2010;53:2417–30.
Carr TP, Andresen CJ, Rudel LL. Enzymatic determination of triglyceride, free cholesterol, and total cholesterol in tissue lipid extracts. Clin Biochem. 1993;26:39–42.
Lagarrigue S, Lopez-Mejia IC, Denechaud P-D, Escoté X, Castillo-Armengol J, Jimenez V, et al. CDK4 is an essential insulin effector in adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:335–48.
Kim JY, Van De Wall E, Laplante M, Azzara A, Trujillo ME, Hofmann SM, et al. Obesity-associated improvements in metabolic profile through expansion of adipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:2621–37.
Lindström P. The physiology of obese-hyperglycemic mice [ob/ob mice]. ScientificWorldJournal. 2007;7:666–85.
Gao G-P, Alvira MR, Wang L, Calcedo R, Johnston J, Wilson JM. Novel adeno-associated viruses from rhesus monkeys as vectors for human gene therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:11854–9.
Zincarelli C, Soltys S, Rengo G, Rabinowitz JE. Analysis of AAV serotypes 1-9 mediated gene expression and tropism in mice after systemic injection. Mol Ther. 2008;16:1073–80.
Wang L, Wang H, Bell P, McCarter RJ, He J, Calcedo R, et al. Systematic evaluation of AAV vectors for liver directed gene transfer in murine models. Mol Ther. 2010;18:118–25.
Mallol C, Casana E, Jimenez V, Casellas A, Haurigot V, Jambrina C, et al. AAV-mediated pancreatic overexpression of Igf1 counteracts progression to autoimmune diabetes in mice. Mol Metab. 2017;6:664–80.
Schulz TJ, Huang TL, Tran TT, Zhang H, Townsend KL, Shadrach JL, et al. Identification of inducible brown adipocyte progenitors residing in skeletal muscle and white fat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:143–8.
Townsend KL, Suzuki R, Huang TL, Jing E, Schulz TJ, Lee K, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP7) reverses obesity and regulates appetite through a central mTOR pathway. FASEB J. 2012;7:1–10.
Häring H-U. Novel phenotypes of prediabetes? Diabetologia. 2016;59:1806–18.
Stefan N, Kantartzis K, Machann J, Schick F, Thamer C, Rittig K, et al. Identification and characterization of metabolically benign obesity in humans. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168:1609–16.
Stefan N, Häring H-U, Schulze MB. Metabolically healthy obesity: the low-hanging fruit in obesity treatment? lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6:249–58.
Kusminski CM, Holland WL, Sun K, Park J, Spurgin SB, Lin Y, et al. MitoNEET-driven alterations in adipocyte mitochondrial activity reveal a crucial adaptive process that preserves insulin sensitivity in obesity. Nat Med. 2012;18:1539–49.
Lu Q, Li M, Zou Y, Cao T. Induction of adipocyte hyperplasia in subcutaneous fat depot alleviated type 2 diabetes symptoms in obese mice. Obesity. 2014;22:1623–31.
Shepherd PR, Gnudi L, Tozzo E, Yang H, Leach F, Kahn BB. Adipose cell hyperplasia and enhanced glucose disposal in transgenic mice overexpressing GLUT4 selectively in adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:22243–6.
Beaven SW, Matveyenko A, Wroblewski K, Chao L, Wilpitz D, Hsu TW, et al. Reciprocal regulation of hepatic and adipose lipogenesis by liver X receptors in obesity and insulin resistance.Cell Metab. 2013;18:106–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2013.04.021.
Abreu-Vieira G, Fischer AW, Mattsson C, de Jong JMA, Shabalina IG, Rydén M, et al. Cidea improves the metabolic profile through expansion of adipose tissue. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7433.
Li P, Song Y, Zan W, Qin L, Han S, Jiang B, et al. Lack of CUL4B in adipocytes promotes PPARγ-mediated adipose tissue expansion and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes. 2017;66:300–13.
Grünberg JR, Hoffmann JM, Hedjazifar S, Nerstedt A, Jenndahl L, Elvin J, et al. Overexpressing the novel autocrine/endocrine adipokine WISP2 induces hyperplasia of the heart, white and brown adipose tissues and prevents insulin resistance. Sci Rep. 2017;7:43515.
Hammarstedt A, Sopasakis VR, Gogg S, Jansson P-A, Smith U. Improved insulin sensitivity and adipose tissue dysregulation after short-term treatment with pioglitazone in non-diabetic, insulin-resistant subjects. Diabetologia. 2005;48:96–104.
Long W, Hui JuZ, Fan Z, Jing W, Qiong L. The effect of recombinant adeno-associated virus-adiponectin (rAAV2/1-Acrp30) on glycolipid dysmetabolism and liver morphology in diabetic rats. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014;206:1–7.
Shklyaev S, Aslanidi G, Tennant M, Prima V, Kohlbrenner E, Kroutov V, et al. Sustained peripheral expression of transgene adiponectin offsets the development of diet-induced obesity in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:14217–22.
Cnop M, Havel PJ, Utzschneider KM, Carr DB, Sinha MK, Boyko EJ, et al. Relationship of adiponectin to body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and plasma lipoproteins: evidence for independent roles of age and sex. Diabetologia. 2003;46:459–69.
Ma H, Gomez V, Lu L, Yang X, Wu X, Xiao SY. Expression of adiponectin and its receptors in livers of morbidly obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:233–7.
Xu A, Wang Y, Keshaw H, Xu LY, Lam KSL, Cooper GJS. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin alleviates alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases in mice. J Clin Invest. 2003;112:91–100.
Ma H, Cui F, Dong J-J, You G-P, Yang X-J, Lu H-D, et al. Therapeutic effects of globular adiponectin in diabetic rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:14950–7.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (MINECO) and FEDER, Plan Nacional I+D+I (SAF2014-54866R and SAF2017-86266R), and Generalitat de Catalunya (2014 SGR 1669, 2017 SGR 1508, ICREA Academia Award to F.B.), Spain, and the European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes (EFSD/MSD European Research Programme on Novel Therapies for Type 2 Diabetes, 2013). VJ was recipient of a post-doctoral research fellowship from EFSD/Lilly. EC, VS, and CM received a predoctoral fellowship from Ministerio de Educación, Cultura y Deporte, JR from Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad, Spain. The authors thank Marta Moya, Sara Darriba, Tura Ferré, Maria Molas, Jennifer Barrero, and Lídia Hernández for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EC, VJ, and FB designed and supervised experiments and analyzed data. EC, VJ, VS, SM, CJ, JR, MG, and CM generated reagents and performed experiments. XL produced AAV vectors. EC, VJ, SF, and FB contributed to discussion and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casana, E., Jimenez, V., Sacristan, V. et al. BMP7 overexpression in adipose tissue induces white adipogenesis and improves insulin sensitivity in ob/ob mice. Int J Obes 45, 449–460 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-020-00700-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-020-00700-6
This article is cited by
-
Transcriptome study digs out BMP2 involved in adipogenesis in sheep tails
BMC Genomics (2022)
-
Treatment of skeletal and non-skeletal alterations of Mucopolysaccharidosis type IVA by AAV-mediated gene therapy
Nature Communications (2021)