Abstract
Background
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is strictly associated with the epidemic of obesity and is becoming the most prevalent liver disease worldwide. In severe obesity, bariatric surgery (BS) is the most effective treatment not only for obesity but also for the associated metabolic co-morbidities, NAFLD, among others. To date, noninvasive diagnostic/prognostic methods cannot evaluate hepatic improvements following surgery.
Objectives
We aimed to measure plasma level of insulin-growth factor-2 protein (IGF2) and epithermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and to assess their relationship with clinical and biochemical parameters during the 12 months follow-up.
Methods
Demographic, clinical–biochemical data, and plasma IGF2 and EGFR were measured in 69 patients preoperatively (T0) and 6 and 12 months (T6M and T12M, respectively) after BS. Liver biopsy was performed at T0. Relationships between IGF2, EGFR, and several biochemical parameters were performed using Pearson or Spearman correlation analysis.
Results
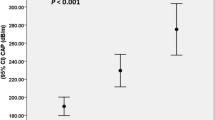
IGF2 plasma level increases during follow-up, passing from 2.5 (1.8–15.5) at baseline to 13.3 (8.6–19.1) at T12M, p < 0.001. Conversely, EGFR showed a not significant reduction. At T12M, the plasma level of both markers was comparable to those of lean subjects. The clinical–biochemical parameters (BMI, glycated hemoglobin, HOMA-IR) also return to the normal range at T12M. Correlation analysis demonstrated that IGF2 was significantly associated with total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, and albumin at T0 while with blood glucose, ALT, GGT, and AST/ALT ratio at T6M and T12M.
Conclusions
IGF2 plasma levels increase after bariatric surgery, and these changes are associated with the modification of hepatic biochemical parameters, even if other clinic or metabolic improvements cannot be excluded.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy T, Henry L, Eslam M, et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.109.
Araújo AR, Rosso N, Bedogni G, Tiribelli C, Bellentani S. Global epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: what we need in the future. Liver Int. 2018;38:47–51.
Schwimmer JB, Deutsch R, Kahen T, Lavine JE, Stanley C, Behling C. Prevalence of fatty liver in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2006;118:1388–93.
Anderson EL, Howe LD, Jones HE, Higgins JPT, Lawlor DA, Fraser A. The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0140908.
McPherson S, Hardy T, Henderson E, Burt AD, Day CP, Anstee QM. Evidence of NAFLD progression from steatosis to fibrosing-steatohepatitis using paired biopsies: implications for prognosis and clinical management. J Hepatol. 2015;62:1148–55.
Singh S, Allen AM, Wang Z, Prokop LJ, Murad MH, Loomba R. Fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver vs nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of paired-biopsy studies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:643–54.e1–9.
Angulo P, Kleiner DE, Dam-Larsen S, Adams LA, Bjornsson ES, Charatcharoenwitthaya P, et al. Liver fibrosis, but no other histologic features, is associated with long-term outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:389–97.e10.
Younossi ZM, Loomba R, Anstee QM, Rinella ME, Bugianesi E, Marchesini G, et al. Diagnostic modalities for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and associated fibrosis. Hepatology. 2018;68:349–60.
Drescher HK, Weiskirchen S, Weiskirchen R. Current status in testing for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Cells. 2019;8. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080845.
Dixon JB, Bhathal PS, O’Brien PE. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: predictors of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in the severely obese. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:91–100.
Gupta R, Bhangoo A, Matthews NAV, Anhalt H, Matta Y, Lamichhane B, et al. The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome in obese children. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2011;24:907–11.
WHO. Facts and figures on childhood obesity. WHO. http://www.who.int/end-childhood-obesity/facts/en/. Accessed 1 Jul 2020.
MLRP Lima, SCO Mourão, MTC Diniz, VHR Leite. Hepatic histopathology of patients with morbid obesity submitted to gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2005;15:661–9.
Bower G, Toma T, Harling L, Jiao LR, Efthimiou E, Darzi A, et al. Bariatric surgery and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review of liver biochemistry and histology. Obes Surg. 2015;25:2280–9.
Billeter AT, de la Garza Herrera JR, Scheurlen KM, Nickel F, Billmann F, Müller-Stich BP. Management of endocrine disease: which metabolic procedure? Comparing outcomes in sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en Y gastric bypass. Eur J Endocrinol. 2018;179:R77–93.
Caiazzo R, Lassailly G, Leteurtre E, Baud G, Verkindt H, Raverdy V, et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass versus adjustable gastric banding to reduce nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 5-year controlled longitudinal study. Ann Surg. 2014;260:893–8.
Kalinowski P, Paluszkiewicz R, Ziarkiewicz-Wróblewska B, Wróblewski T, Remiszewski P, Grodzicki M, et al. Liver function in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease randomized to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass versus sleeve gastrectomy: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg. 2017;266:738–45.
Esquivel CM, Garcia M, Armando L, Ortiz G, Lascano FM, Foscarini JM. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy resolves NAFLD: another formal indication for bariatric surgery? Obes Surg. 2018;28:4022–33.
Adamek A, Kasprzak A. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) system in liver diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051308.
Kessler SM, Laggai S, Van Wonterg E, Gemperlein K, Müller R, Haybaeck J, et al. Transient hepatic overexpression of insulin-like growth factor 2 induces free cholesterol and lipid droplet formation. Front Physiol. 2016;7:147.
Komposch K, Sibilia M. EGFR signaling in liver diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17010030.
Bhushan B, Michalopoulos GK. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in liver injury and lipid metabolism: Emerging new roles for an old receptor. Chem Biol Interact. 2020;324:109090.
Divella R, Daniele A, Gadaleta C, Tufaro A, Venneri MT, Paradiso A, et al. Circulating transforming growth factor-β and epidermal growth factor receptor as related to virus infection in liver carcinogenesis. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:141–5.
Giraudi PJ, Gambaro SE, Ornelas Arroyo S, Chackelevicius CM, Giuricin M, Silvestri M, et al. A simple in silico strategy identifies candidate biomarkers for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis in morbidly obese subjects. Liver Int. 2018;38:155–63.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28:412–9.
Authors/Task Force Members, Rydén L, Grant PJ, Anker SD, Berne C, Cosentino F, et al. ESC guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD: the Task Force on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and developed in collaboration with the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur Heart J. 2013;34:3035–87.
Palmisano S, Giacomel G, Silvestri M, Giuricin M, Kulla A, Giudici F, et al. Outcome of laparoscopic gastric bypass in obese and diabetic patients: when surgery fails. Minerva Chir. 2017;72:279–88.
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41:1313–21.
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathologic patterns and biopsy evaluation in clinical research. Semin Liver Dis. 2012;32:3–13.
Cianfarani S, Inzaghi E, Alisi A, Germani D, Puglianiello A, Nobili V. Insulin-like growth factor-I and -II levels are associated with the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children. J Pediatr. 2014;165:92–8.
Ajmera V, Perito ER, Bass NM, Terrault NA, Yates KP, Gill R, et al. Novel plasma biomarkers associated with liver disease severity in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2017;65:65–77.
GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators, Afshin A, Forouzanfar MH, Reitsma MB, Sur P, Estep K, et al. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:13–27.
Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1221–31.
Kelly T, Yang W, Chen C-S, Reynolds K, He J. Global burden of obesity in 2005 and projections to 2030. Int J Obes. 2008;32:1431–7.
Estes C, Razavi H, Loomba R, Younossi Z, Sanyal AJ. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology. 2018;67:123–33.
Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, Perumpail RB, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2015;148:547–55.
Aguilar-Olivos NE, Almeda-Valdes P, Aguilar-Salinas CA, Uribe M, Méndez-Sánchez N. The role of bariatric surgery in the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome. Metab Clin Exp. 2016;65:1196–207.
RNAMA Rehem, WMHM El-Shikh. Serum IGF-1, IGF-2 and IGFBP-3 as parameters in the assessment of liver dysfunction in patients with hepatic cirrhosis and in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 2011;58:949–54.
Liu J, Hu X, Chen J, Li X, Wang L, Wang B, et al. Pericentral hepatocytes produce insulin-like growth factor-2 to promote liver regeneration during selected injuries in mice. Hepatology. 2017;66:2002–15.
Ichikawa T, Nakao K, Hamasaki K, Furukawa R, Tsuruta S, Ueda Y, et al. Role of growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor 1 and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 in development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Int. 2007;1:287–94.
Sumida Y, Yonei Y, Tanaka S, Mori K, Kanemasa K, Imai S, et al. Lower levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 standard deviation score are associated with histological severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Res. 2015;45:771–81.
Dichtel LE, Corey KE, Misdraji J, Bredella MA, Schorr M, Osganian SA, et al. The association between IGF-1 levels and the histologic severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2017;8:e217.
Hagström H, Stål P, Hultcrantz R, Brismar K, Ansurudeen I. IGFBP-1 and IGF-I as markers for advanced fibrosis in NAFLD—a pilot study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2017;52:1427–34.
Petäjä EM, Zhou Y, Havana M, Hakkarainen A, Lundbom N, Ihalainen J, et al. Phosphorylated IGFBP-1 as a non-invasive predictor of liver fat in NAFLD. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24740.
Chishima S, Kogiso T, Matsushita N, Hashimoto E, Tokushige K. The relationship between the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor system and the histological features of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Intern Med. 2017;56:473–80.
Brynskov T, Laugesen CS, Floyd AK, Frystyk J, Sørensen TL. The IGF-axis and diabetic retinopathy before and after gastric bypass surgery. Obes Surg. 2017;27:408–15.
Street ME, Smerieri A, Montanini L, Predieri B, Iughetti L, Valenzise M, et al. Interactions among pro-inflammatory cytokines, IGF system and thyroid function in pre-pubertal obese subjects. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2013;27:259–66.
Heald AH, Kärvestedt L, Anderson SG, McLaughlin J, Knowles A, Wong L, et al. Low insulin-like growth factor-II levels predict weight gain in normal weight subjects with type 2 diabetes. Am J Med. 2006;119:167.e9–15.
Sandhu MS, Gibson JM, Heald AH, Dunger DB, Wareham NJ. Low circulating IGF-II concentrations predict weight gain and obesity in humans. Diabetes. 2003;52:1403–8.
Chaim FDM, Pascoal LB, Chaim FHM, Palma BB, Damázio TA, da Costa LBE, et al. Histological grading evaluation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease after bariatric surgery: a retrospective and longitudinal observational cohort study. Sci Rep. 2020;10:8496.
Baldwin D, Chennakesavalu M, Gangemi A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass against laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for amelioration of NAFLD using four criteria. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2019;15:2123–30.
Sinclair P, Brennan DJ, le Roux CW. Gut adaptation after metabolic surgery and its influences on the brain, liver and cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15:606–24.
Seeley RJ, Chambers AP, Sandoval DA. The role of gut adaptation in the potent effects of multiple bariatric surgeries on obesity and diabetes. Cell Metab. 2015;21:369–78.
Taqi E, Wallace LE, de Heuvel E, Chelikani PK, Zheng H, Berthoud H-R, et al. The influence of nutrients, biliary-pancreatic secretions, and systemic trophic hormones on intestinal adaptation in a Roux-en-Y bypass model. J Pediatr Surg. 2010;45:987–95.
Ceccarini G, Pelosini C, Ferrari F, Magno S, Vitti J, Salvetti G, et al. Serum IGF-binding protein 2 (IGFBP-2) concentrations change early after gastric bypass bariatric surgery revealing a possible marker of leptin sensitivity in obese subjects. Endocrine. 2019;65:86–93.
Yan J, Charles JF. Gut microbiota and IGF-1. Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;102:406–14.
Acknowledgements
Finanziamento Ricerca di Ateneo—U05SPFRA14—FRA 2014 (CdA dd. 19.12.2014) and Fondazione Italiana Fegato. PJG by Fondazione Umberto Veronesi (Grants 2015-2017). NR is funded by Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Trieste (CRTrieste) and by Fondazione Italiana Fegato ONLUS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giraudi, P.J., Giuricin, M., Bonazza, D. et al. Modifications of IGF2 and EGFR plasma protein concentrations in NAFLD patients after bariatric surgery. Int J Obes 45, 374–382 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-020-00687-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-020-00687-0