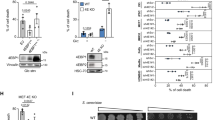
Abstract
Mutations of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway has essential roles in development and cancer. Although β-catenin and adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene mutations are well established and are known to drive tumorigenesis, discoveries of mutations in other components of the pathway lagged, which hinders the understanding of cancer mechanisms. Here we report that δ-catenin (gene designation: CTNND2), a primarily neural member of the β-catenin superfamily that promotes canonical Wnt/β-catenin/LEF-1-mediated transcription, displays exonic mutations in human prostate cancer and promotes cancer cell survival adaptation and metabolic reprogramming. When overexpressed in cells derived from prostate tumor xenografts, δ-catenin gene invariably gives rise to mutations, leading to sequence disruptions predicting functional alterations. Ectopic δ-catenin gene integrating into host chromosomes is locus nonselective. δ-Catenin mutations promote tumor development in mouse prostate with probasin promoter (ARR2PB)-driven, prostate-specific expression of Myc oncogene, whereas mutant cells empower survival advantage upon overgrowth and glucose deprivation. Reprogramming energy utilization accompanies the downregulation of glucose transporter-1 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage while preserving tumor type 2 pyruvate kinase expression. δ-Catenin mutations increase β-catenin translocation to the nucleus and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) expression. Therefore, introducing δ-catenin mutations is an important milestone in prostate cancer metabolic adaptation by modulating β-catenin and HIF-1α signaling under glucose shortage to amplify its tumor-promoting potential.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW . Cancer genes and the pathways they control. Nat Med 2004; 10: 789–799.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
Paffenholz R, Franke WW . Identification and localization of a neurally expressed member of the plakoglobin/armadillo multigene family. Differentiation 1997; 61: 293–304.
Zhou J, Liyanage U, Medina M, Ho C, Simmons AD, Lovett M et al. Presenilin 1 interaction in the brain with a novel member of the Armadillo family. NeuroReport 1997; 8: 2085–2090.
Lu Q, Paredes M, Medina M, Zhou J, Cavallo R, Peifer M et al. δ-Catenin, an adhesive junction-associated protein which promotes cell scattering. J Cell Biol 1999; 144: 519–532.
Burger MJ, Tebay MA, Keith PA, Samaratunga HM, Clements J, Lavin MF et al. Expression analysis of δ-catenin and prostate-specific membrane antigen: their potential as diagnostic markers for prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 2002; 100: 228–237.
Lu Q, Dobbs LJ, Gregory CW, Lanford GW, Revelo MP, Shappell S et al. Increased expression of delta-catenin/neural plakophilin-related armadillo protein is associated with the down-regulation and redistribution of E-cadherin and p120ctn in human prostate cancer. Hum Pathol 2005; 36: 1037–1048.
Fang Y, Li Z, Wang X, Zhang S . Expression and biological role of δ-catenin in human ovarian cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2004; 138: 1769–1776.
Zhang JY, Wang Y, Zhang D, Yang ZQ, Dong XJ, Jiang GY et al. δ-Catenin promotes malignant phenotype of non-small cell lung cancer by non-competitive binding to E-cadherin with p120ctn in cytoplasm. J Pathol 2010; 222: 76–88.
Kim H, He Y, Yang I, Zeng Y, Kim Y, Seo YW et al. δ-Catenin promotes E-cadherin processing and activates β-catenin-mediated signaling: implications on human prostate cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012; 1822: 509–521.
Lu B, Jiang D, Wang P, Gao Y, Sun W, Xiao X et al. Replication study supports CTNND2 as a susceptibility gene for high myopia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis ScI 2011; 252: 8258–8261.
Jun G, Moncaster JA, Koutras C, Seshadri S, Buros J, McKee AC et al. δ-Catenin is genetically and biologically associated with cortical cataract and future Alzheimer-related structural and functional brain changes. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e43728.
Hirsch D, Kemmerling R, Davis S, Camps J, Meltzer PS, Ried T et al. Chromothripsis and focal copy number alterations determine poor outcome in malignant melanoma. Cancer Res 2012; 73: 1454–1460.
Zeng Y, Abdallah A, Lu JP, Wang T, Chen YH, Terrian DM et al. δ-Catenin promotes prostate cancer cell growth and progression by altering cell cycle and survival gene profiles. Mol Cancer 2009; 8: 8–19.
Westbrook TF, Martin ES, Schlabach MR, Leng Y, Liang AC, Feng B et al. A genetic screen for candidate tumor suppressors identifies REST. Cell 2005; 121: 837–848.
Yuan H, Perry CN, Huang C, Iwai-Kanai E, Carreira RS, Glembotski CC et al. LPS-induced autophagy is mediated by oxidative signaling in cardiomyocytes and is associated with cytoprotection. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2009; 296: H470–H479.
Rios-Doria J, Day KC, Kuefer R, Rashid MG, Chinnaiyan AM, Rubin MA et al. The role of calpain in the proteolytic cleavage of E-cadherin in prostate and mammary epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 1372–1379.
Davis MA, Ireton RC, Reynolds AB . A core function for p120-catenin in cadherin turnover. J Cell Biol 2003; 163: 525–534.
Papadopoulos N, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . The role of companion diagnostics in the development and use of mutation-targeted cancer therapies. Nat Biotechnol 2006; 24: 985–995.
Ding L, Getz G, Wheeler DA, Mardis ER, McLellan MD, Cibulskis K et al. Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2008; 455: 1069–1075.
Baum C, von Kalle C, Staal FJ, Li Z, Fehse B, Schmidt M et al. Chance or necessity? Insertional mutagenesis in gene therapy and its consequences. Mol Ther 2004; 9: 5–13.
Yun J, Rago C, Cheong I, Pagliarini R, Angenendt P, Rajagopalan H et al. Glucose deprivation contributes to the development of KRAS pathway mutations in tumor cells. Science 2009; 325: 1555–1559.
Israely I, Costa RM, Xie CW, Silva AJ, Kosik KS, Liu X et al. Deletion of the neuron-specific protein delta-catenin leads to severe cognitive and synaptic dysfunction. Curr Biol 2004; 14: 1657–1663.
Ellwood-Yen K, Graeber TG, Wongvipat J, Iruela-Arispe ML, Zhang J, Matusik R et al. Myc-driven murine prostate cancer shares molecular features with human prostate tumors. Cancer Cell 2003; 4: 223–238.
Warburg O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956; 123: 309–314.
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB . Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009; 324: 1029–1033.
Mathupala SP, Ko YH, Pedersen PL . Hexokinase II Cancer’s double-edged sword acting as both facilitator and gatekeeper of malignancy when bound to mitochondria. Oncogene 2006; 25: 4777–4786.
Wu M, Neilson A, Swift AL, Moran R, Tamagnine J, Parslow D et al. Multiparameter metabolic analysis reveals a close link between attenuated mitochondrial bioenergetic function and enhanced glycolysis dependency in human tumor cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2007; 292: C125–C136.
Lu Q . δ-Catenin dysregulation in cancer: interactions with E-cadherin and beyond. J Pathol 2010; 222: 119–123.
Kouchi Z, Barthet G, Serban G, Georgakopoulos A, Shioi J, Robakis NK . P120 catenin recruits cadherins to gamma-secretase and inhibits production of Abeta peptide. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 1954–1961.
Kim JS, Bareiss S, Kim KK, Tatum R, Han JR, Jin YH et al. Presenilin-1 inhibits delta-catenin-induced cellular branching and promotes delta-catenin processing and turnover. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 351: 903–908.
Bareiss S, Kim K, Lu Q . Delta-catenin/NPRAP: a new member of the glycogen synthase kinase-3beta signaling complex that promotes beta-catenin turnover in neurons. J Neurosci Res 2010; 88: 2350–2363.
Oh M, Kim H, Yang I, Park JH, Cong WT, Baek MC et al. GSK-3 phosphorylates delta-catenin and negatively regulates its stability via ubiquitination/proteosome-mediated proteolysis. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 28579–28589.
Dai SD, Wang Y, Zhang JY, Zhang D, Zhang PX, Jiang GY et al. Upregulation of δ-catenin is associated with poor prognosis and enhances transcriptional activity through Kaiso in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci 2011; 102: 95–103.
Kim SW, Park JI, Spring CM, Sater AK, Ji H, Otchere AA et al. Non-canonical Wnt signals are modulated by the Kaiso transcriptional repressor and p120-catenin. Nat Cell Biol 2004; 6: 1212–1220.
Rodova M, Kelly KF, VanSaun M, Daniel JM, Werle MJ . Regulation of the rapsyn promoter by kaiso and delta-catenin. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 7188–7196.
Kim K, Sirota A, Chen Yh YH, Jones SB, Dudek R, Lanford GW et al. Dendrite-like process formation and cytoskeletal remodeling regulated by delta-catenin expression. Exp Cell Res 2002; 275: 171–184.
Kim H, Han JR, Park J, Oh M, James SE, Chang S et al. Delta-catenin-induced dendritic morphogenesis. An essential role of p190RhoGEF interaction through Akt1-mediated phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 977–987.
Kim H, Oh M, Lu Q, Kim K . E-Cadherin negatively modulates delta-catenin-induced morphological changes and RhoA activity reduction by competing with p190RhoGEF for delta-catenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 377: 636–641.
Zhang H, Dai SD, Zhang D, Liu D, Zhang FY, Zheng TY et al. Delta-catenin promotes the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by binding to E-cadherin in a competitive manner with p120 catenin. Target Oncol (e-pub ahead of print 20 February 2013; doi:10.1007/s11523-013-0269-6).
Wolf A, Keil R, Götzl O, Mun A, Schwarze K, Lederer M, Hüttelmaier S, Hatzfeld M . The armadillo protein p0071 regulates Rho signalling during cytokinesis. Nat Cell Biol 2006; 8: 1432–1440.
Wang T, Chen YH, Hong H, Zeng Y, Zhang J, Lu JP et al. Increased nucleotide polymorphic changes in the 5′-untranslated region of delta-catenin (CTNND2) gene in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2009; 28: 555–564.
Wilson KF, Erickson JW, Antonyak MA, Cerione RA . Rho GTPases and their roles in cancer metabolism. Trends Mol Med 2013; 19: 74–82.
Inoki K, Ouyang H, Zhu T, Lindvall C, Wang Y, Zhang X et al. TSC2 integrates Wnt and energy signals via a coordinated phosphorylation by AMPK and GSK3 to regulate cell growth. Cell 2006; 126: 955–968.
Gu D, Sater AK, Ji H, Cho K, Clark M, Stratton SA et al. Xenopus delta-catenin is essential in early embryogenesis and is functionally linked to cadherins and small GTPases. J Cell Sci 2009; 122 (Part 22): 4049–4061.
Martinez MC, Ochiishi T, Majewski M, Kosik KS . Dual regulation of neuronal morphogenesis by a delta-catenin-cortactin complex and Rho. J Cell Biol 2003; 162: 99–111.
Deng W, Tsao SW, Lucas JN, Leung CS, Cheung AL . A new method for improving metaphase chromosome spreading. Cytometry A 2003; 51: 46–51.
Huang X, Hu J, Hu X, Zhang C, Zhang L, Wang S et al. Cytogenetic characterization of the bay scallop, Argopecten irradians irradians, by multiple staining techniques and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genes Genet Syst 2007; 82: 257–263.
Acknowledgements
We thank Joani Zary Oswald for technical assistance. This work was supported, in part, by DOD Grant PC040569 (to QL), NIH Grants CA111891 and CA165202 (to QL), ES016888 (to Y-HC) and DK073488 and DK074825 (to PDN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
JN, JZ, J-PL, DZ, JF, HH and CB declare no conflict of interest. QL, Y-HC and PDN are funded by the NIH.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nopparat, J., Zhang, J., Lu, JP. et al. δ-Catenin, a Wnt/β-catenin modulator, reveals inducible mutagenesis promoting cancer cell survival adaptation and metabolic reprogramming. Oncogene 34, 1542–1552 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.89
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.89
This article is cited by
-
Intratumor δ-catenin heterogeneity driven by genomic rearrangement dictates growth factor dependent prostate cancer progression
Oncogene (2020)
-
The clinical value of the prostatic exosomal protein expression in the diagnosis of chronic prostatitis: a single-center study
International Urology and Nephrology (2020)
-
Overexpression of Suprabasin is Associated with Proliferation and Tumorigenicity of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Genetic alterations of δ-catenin/NPRAP/Neurojungin (CTNND2): functional implications in complex human diseases
Human Genetics (2016)
-
A non-tight junction function of claudin-7—Interaction with integrin signaling in suppressing lung cancer cell proliferation and detachment
Molecular Cancer (2015)