Abstract
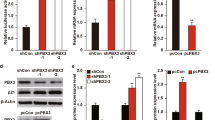
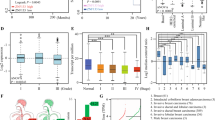
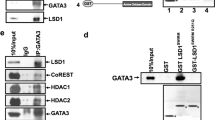
Liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1, NR5A2) is an orphan nuclear receptor that has an essential role in cancer progression, notably in breast cancer. Although its role in promoting cancer cell proliferation and migration is well documented, the molecular basis is not completely established. Here, we report that LRH-1 inhibition affects two- and three-dimensional cell proliferation of different types of breast cancer cells, including estrogen receptor α (ERα)-positive and triple-negative cells. This phenotype is accompanied by the upregulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CDKN1A (aka p21CIP1/WAF1) in a p53-independent manner. Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis shows that LRH-1 cooperates with FOXA1 and binds directly to CDKN1A promoter and a distal regulatory region found at −62 kb from its transcriptional start sites, allowing repression of CDKN1A transcription. LRH-1 or FOXA1 depletion induces CDKN1A upregulation by removing histone deacetylase 2 from the promoter and distal regulatory elements and permitting histone acetylation in these regions. Analysis of breast cancer samples reveals that a high LRH-1 level is inversely correlated with CDKN1A expression in breast cancer patients and is associated with poor prognosis. This study reveals a novel mechanism of control of cell proliferation by LRH-1 regulating CDKN1A transcription in breast cancer cells, independent of ERα and p53 status. Targeting LRH-1 may provide an attractive prospect for treatment of tumors that are resistant to hormonal and targeted therapy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lam SW, Jimenez CR, Boven E . Breast cancer classification by proteomic technologies: current state of knowledge. Cancer Treat Rev 2014; 40: 129–138.
Bianco S, Gevry N . Endocrine resistance in breast cancer: from cellular signaling pathways to epigenetic mechanisms. Transcription 2012; 3: 4165–70.
Atkin SD, Owen BM, Bookout AL, Cravo RM, Lee C, Elias CF et al. Nuclear receptor LRH-1 induces the reproductive neuropeptide kisspeptin in the hypothalamus. Mol Endocrinol 2013; 27: 598–605.
Duggavathi R, Volle DH, Mataki C, Antal MC, Messaddeq N, Auwerx J et al. Liver receptor homolog 1 is essential for ovulation. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 1871–1876.
Zhang C, Large MJ, Duggavathi R, Demayo FJ, Lydon JP, Schoonjans K et al. Liver receptor homolog-1 is essential for pregnancy. Nat Med 2013; 19: 1061–1066.
Benod C, Vinogradova MV, Jouravel N, Kim GE, Fletterick RJ, Sablin EP . Nuclear receptor liver receptor homologue 1 (LRH-1) regulates pancreatic cancer cell growth and proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 16927–16931.
Botrugno OA, Fayard E, Annicotte JS, Haby C, Brennan T, Wendling O et al. Synergy between LRH-1 and beta-catenin induces G1 cyclin-mediated cell proliferation. Mol Cell 2004; 15: 499–509.
Holmstrom SR, Deering T, Swift GH, Poelwijk FJ, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA et al. LRH-1 and PTF1-L coregulate an exocrine pancreas-specific transcriptional network for digestive function. Genes Dev 2011; 25: 1674–1679.
Sidler D, Renzulli P, Schnoz C, Berger B, Schneider-Jakob S, Fluck C et al. Colon cancer cells produce immunoregulatory glucocorticoids. Oncoimmunology 2012; 1: 529–530.
Lazarus KA, Wijayakumara D, Chand AL, Simpson ER, Clyne CD . Therapeutic potential of Liver Receptor Homolog-1 modulators. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2012; 130: 138–146.
Oosterveer MH, Mataki C, Yamamoto H, Harach T, Moullan N, van Dijk TH et al. LRH-1-dependent glucose sensing determines intermediary metabolism in liver. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 2817–2826.
Schoonjans K, Dubuquoy L, Mebis J, Fayard E, Wendling O, Haby C et al. Liver receptor homolog 1 contributes to intestinal tumor formation through effects on cell cycle and inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 2058–2062.
Wang SL, Zheng DZ, Lan FH, Deng XJ, Zeng J, Li CJ et al. Increased expression of hLRH-1 in human gastric cancer and its implication in tumorigenesis. Mol Cell Biochem 2008; 308: 93–100.
Annicotte JS, Chavey C, Servant N, Teyssier J, Bardin A, Licznar A et al. The nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog-1 is an estrogen receptor target gene. Oncogene 2005; 24: 8167–8175.
Miki Y, Clyne CD, Suzuki T, Moriya T, Shibuya R, Nakamura Y et al. Immunolocalization of liver receptor homologue-1 (LRH-1) in human breast carcinoma: possible regulator of in situ steroidogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2006; 244: 24–33.
Bianco S, Brunelle M, Jangal M, Magnani L, Gevry N . LRH-1 governs vital transcriptional programs in endocrine-sensitive and -resistant breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 2014; 74: 2015–2025.
Chand AL, Herridge KA, Thompson EW, Clyne CD . The orphan nuclear receptor LRH-1 promotes breast cancer motility and invasion. Endocr Relat Cancer 2010; 17: 965–975.
Chand AL, Wijayakumara DD, Knower KC, Herridge KA, Howard TL, Lazarus KA et al. The orphan nuclear receptor LRH-1 and ERalpha activate GREB1 expression to induce breast cancer cell proliferation. PLoS One 2012; 7: e31593.
Lai CF, Flach KD, Alexi X, Fox SP, Ottaviani S, Thiruchelvam PT et al. Co-regulated gene expression by oestrogen receptor alpha and liver receptor homolog-1 is a feature of the oestrogen response in breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2013; 41: 10228–10240.
Thiruchelvam PT, Lai CF, Hua H, Thomas RS, Hurtado A, Hudson W et al. The liver receptor homolog-1 regulates estrogen receptor expression in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2011; 127: 385–396.
Chand AL, Herridge KA, Howard TL, Simpson ER, Clyne CD . Tissue-specific regulation of aromatase promoter II by the orphan nuclear receptor LRH-1 in breast adipose stromal fibroblasts. Steroids 2011; 76: 741–744.
Knower KC, Chand AL, Eriksson N, Takagi K, Miki Y, Sasano H et al. Distinct nuclear receptor expression in stroma adjacent to breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2013; 142: 211–223.
Lazarus KA, Zhao Z, Knower KC, To SQ, Chand AL, Clyne CD . Oestradiol reduces liver receptor homolog-1 mRNA transcript stability in breast cancer cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2013; 438: 533–539.
Brunner N, Boysen B, Jirus S, Skaar TC, Holst-Hansen C, Lippman J et al. MCF7/LCC9: an antiestrogen-resistant MCF-7 variant in which acquired resistance to the steroidal antiestrogen ICI 182,780 confers an early cross-resistance to the nonsteroidal antiestrogen tamoxifen. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 3486–3493.
De Santa F, Barozzi I, Mietton F, Ghisletti S, Polletti S, Tusi BK et al. A large fraction of extragenic RNA pol II transcription sites overlap enhancers. PLoS Biol 2010; 8: e1000384.
Wang D, Garcia-Bassets I, Benner C, Li W, Su X, Zhou Y et al. Reprogramming transcription by distinct classes of enhancers functionally defined by eRNA. Nature 2011; 474: 390–394.
Li G, Ruan X, Auerbach RK, Sandhu KS, Zheng M, Wang P et al. Extensive promoter-centered chromatin interactions provide a topological basis for transcription regulation. Cell 2012; 148: 84–98.
Robinson JL, Carroll JS . FoxA1 is a key mediator of hormonal response in breast and prostate cancer. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2012; 3: 68.
Hurtado A, Holmes KA, Ross-Innes CS, Schmidt D, Carroll JS . FOXA1 is a key determinant of estrogen receptor function and endocrine response. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 27–33.
Gomes NP, Bjerke G, Llorente B, Szostek SA, Emerson BM, Espinosa JM . Gene-specific requirement for P-TEFb activity and RNA polymerase II phosphorylation within the p53 transcriptional program. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 601–612.
Creyghton MP, Cheng AW, Welstead GG, Kooistra T, Carey BW, Steine EJ et al. Histone H3K27ac separates active from poised enhancers and predicts developmental state. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 21931–21936.
Heintzman ND, Hon GC, Hawkins RD, Kheradpour P, Stark A, Harp LF et al. Histone modifications at human enhancers reflect global cell-type-specific gene expression. Nature 2009; 459: 108–112.
Heintzman ND, Stuart RK, Hon G, Fu Y, Ching CW, Hawkins RD et al. Distinct and predictive chromatin signatures of transcriptional promoters and enhancers in the human genome. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 311–318.
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2012; 2: 401–404.
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal 2013; 6 pl1.
Madden SF, Clarke C, Gaule P, Aherne ST, O'Donovan N, Clynes M et al. BreastMark: an integrated approach to mining publicly available transcriptomic datasets relating to breast cancer outcome. Breast Cancer Res 2013; 15: R52.
Osborne CK, Schiff R . Mechanisms of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Annu Rev Med 2011; 62: 233–247.
Jung YS, Qian Y, Chen X . Examination of the expanding pathways for the regulation of p21 expression and activity. Cell Signal 2010; 22: 1003–1012.
Niculescu AB III, Chen X, Smeets M, Hengst L, Prives C, Reed SI . Effects of p21(Cip1/Waf1) at both the G1/S and the G2/M cell cycle transitions: pRb is a critical determinant in blocking DNA replication and in preventing endoreduplication. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 629–643.
Hlobilkova A, Knillova J, Svachova M, Skypalova P, Krystof V, Kolar Z . Tumour suppressor PTEN regulates cell cycle and protein kinase B/Akt pathway in breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res 2006; 26: 1015–1022.
Muller PA, Vousden KH . P53 mutations in cancer. Nat Cell Biol 2013; 15: 2–8.
Han S, Sidell N, Fisher PB, Roman J . Up-regulation of p21 gene expression by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in human lung carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 1911–1919.
Lu S, Jenster G, Epner DE . Androgen induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 gene: role of androgen receptor and transcription factor Sp1 complex. Mol Endocrinol 2000; 14: 753–760.
Mandal S, Davie JR . Estrogen regulated expression of the p21 Waf1/Cip1 gene in estrogen receptor positive human breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol 2010; 224: 28–32.
Kawai H, Li H, Avraham S, Jiang S, Avraham HK . Overexpression of histone deacetylase HDAC1 modulates breast cancer progression by negative regulation of estrogen receptor alpha. Int J Cancer 2003; 107: 353–358.
Yamaguchi T, Cubizolles F, Zhang Y, Reichert N, Kohler H, Seiser C et al. Histone deacetylases 1 and 2 act in concert to promote the G1-to-S progression. Genes Dev 2010; 24: 455–469.
Zupkovitz G, Grausenburger R, Brunmeir R, Senese S, Tischler J, Jurkin J et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 is a crucial target for histone deacetylase 1 as a regulator of cellular proliferation. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30: 1171–1181.
Ai N, Hu X, Ding F, Yu B, Wang H, Lu X et al. Signal-induced Brd4 release from chromatin is essential for its role transition from chromatin targeting to transcriptional regulation. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 39: 9592–9604.
Sanders DA, Ross-Innes CS, Beraldi D, Carroll JS, Balasubramanian S . Genome-wide mapping of FOXM1 binding reveals co-binding with estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer cells. Genome Biol 2013; 14: R6.
Jangal M, Couture JP, Bianco S, Magnani L, Mohammed H, Gevry N . The transcriptional co-repressor TLE3 suppresses basal signaling on a subset of estrogen receptor alpha target genes. Nucleic Acids Res 2014; 42: 11339–11348.
Svotelis A, Bianco S, Madore J, Huppe G, Nordell-Markovits A, Mes-Masson AM et al. H3K27 demethylation by JMJD3 at a poised enhancer of anti-apoptotic gene BCL2 determines ERalpha ligand dependency. EMBO J 2011; 30: 3947–3961.
Boyle AP, Guinney J, Crawford GE, Furey TS . F-Seq: a feature density estimator for high-throughput sequence tags. Bioinformatics 2008; 24: 2537–2538.
Thorvaldsdottir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP . Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform 2013; 14: 178–192.
Heinz S, Benner C, Spann N, Bertolino E, Lin YC, Laslo P et al. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol Cell 2010; 38: 576–589.
Acknowledgements
We thank Alain Lavigueur and Bruce Murphy for critical comments on the manuscript. We are also grateful to Robert Clark for providing the MCF7/LCC2 and MCF7/LCC9 cell lines and Mien-Chie Hung for the MCF7/HER2-18 cell line. This work was supported with fund from the Canadian Institute of Health Research (CIHR) to NG. SB was the recipient of a postdoctoral fellowship from the Réseau Québécois en Reproduction (RQR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bianco, S., Jangal, M., Garneau, D. et al. LRH-1 controls proliferation in breast tumor cells by regulating CDKN1A gene expression. Oncogene 34, 4509–4518 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.382
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.382
This article is cited by
-
Liver receptor homolog-1: structures, related diseases, and drug discovery
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2024)
-
Inhibiting NR5A2 targets stemness in pancreatic cancer by disrupting SOX2/MYC signaling and restoring chemosensitivity
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2023)
-
FOXA1 of regulatory variant associated with risk of breast cancer through allele-specific enhancer in the Chinese population
Breast Cancer (2022)
-
NR5A2 transcriptional activation by BRD4 promotes pancreatic cancer progression by upregulating GDF15
Cell Death Discovery (2021)
-
Prediction of blood-based biomarkers and subsequent design of bisulfite PCR-LDR-qPCR assay for breast cancer detection
BMC Cancer (2020)