Abstract
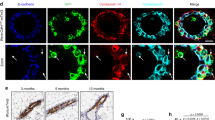
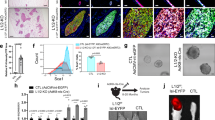
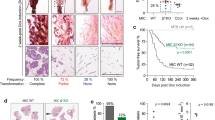
The constitutive activation of β-catenin signaling in the mammary basal epithelial cell layer in transgenic K5ΔNβcat mice leads to basal-type tumor development. Integrins of the β1 family and integrin-mediated signaling events have an important role in breast tumor growth and progression. We show here that the deletion of α3β1 integrin, a major laminin receptor, from the basal layer of the mammary epithelium of K5ΔNβcat mice completely prevented the tumorigenesis induced by β-catenin signaling. Moreover, the depletion of α3β1 integrin from a spontaneously transformed mouse mammary basal epithelial cell line (MEC) prevented the cells from forming colonies in soft agar and greatly reduced tumor development in orthotopic grafts. Inhibition of the integrin signaling intermediates Rac1 or PAK1 (P21-activated Kinase 1) in MEC affected tumor cell growth in soft agar, whereas the expression of activated forms of these effectors in α3-depleted cells rescued the capacity of these cells to grow in non-adherent conditions. Similarly, the tumorigenic potential of α3-depleted cells was restored by the expression of activated PAK1, as assessed by orthotopic transplantation assay. In three-dimensional Matrigel culture, MEC survival and proliferation were affected by the depletion of α3β1 integrin, which also significantly decreased the activation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK). Our data suggest that the activation of signaling cascades downstream from α3β1 and involving the Rac1/PAK1 pathway, MAPK and JNK, promotes prosurvival and proproliferative signals required for the malignant growth of basal mammary epithelial cells, providing further insight into the molecular mechanisms underlying breast cancer initiation and progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prat A, Ellis MJ, Perou CM . Practical implications of gene-expression-based assays for breast oncologists. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2011; 9: 48–57.
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 10869–10874.
Reis-Filho JS, Pusztai L . Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: classification, prognostication, and prediction. Lancet 2011; 378: 1812–1823.
Bertucci F, Finetti P, Birnbaum D . Basal breast cancer: a complex and deadly molecular subtype. Curr Mol Med 2012; 12: 96–110.
Koboldt DC, Fulton RS, McLellan MD, Schmidt H, Kalicki-Veizer J, McMichael JF et alCancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012; 490: 61–70.
DiMeo TA, Anderson K, Phadke P, Cheng F, Perou CM, Naber S et al. A novel lung metastasis signature links Wnt signaling with cancer cell self-renewal and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 5364–5373.
Khramtsov AI, Khramtsova GF, Tretiakova M, Huo D, Olopade OI, Goss KH . Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation is enriched in basal-like breast cancers and predicts poor outcome. Am J Pathol 2010; 76: 2911–2920.
Hynes RO . Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002; 110: 673–687.
Huveneers S, Danen EHJ . Adhesion signaling-crosstalk between integrins, Src and Rho. J Cell Sci 2009; 122: 1059–1069.
Raymond K, Faraldo MM, Deugnier MA, Glukhova MA . Integrins in mammary development. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2012; 23: 599–605.
Streuli CH, Akhtar N . Signal co-operation between integrins and other receptor systems. Biochem J 2009; 418: 491–506.
Cabodi S, del Pilar Camacho-Leal M, Di Stefano P, Defilippi P . Integrin signalling adaptors: not only figurants in the cancer story. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 858–870.
Rathinam R, Alahari SK . Important role of integrins in the cancer biology. Cancer Metast Rev 2010; 29: 223–237.
Lahlou H, Muller WJ . β1-Integrins, signaling and mammary tumor progression in transgenic mouse models: implications for human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 2011; 13: 229.
Jonjic N, Lucin K, Krstulja M, Iternicka Z, Mustac E . Expression of beta-1 integrins on tumor cells of invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract 1993; 189: 979–984.
Yao ES, Zhang H, Chen YY, Lee B, Chew K, Moore D et al. Increased β1 integrin is associated with decreased survival in invasive breast cancer. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 659–664.
Morini M, Mottolese M, Ferrari N, Ghiorzo F, Buglioni S, Mortarini R et al. The alpha 3 beta 1 integrin is associated with mammary carcinoma cell metastasis, invasion, and gelatinase B (MMP-9) activity. Int J Cancer 2000; 87: 336–342.
Cance WG, Harris JE, Iacocca MV, Roche E, Yang X, Chang J et al. Immunohistochemical analyses of focal adhesion kinase expression in benign and malignant human breast and colon tissues: correlation with preinvasive and invasive phenotypes. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6: 2417–2423.
Luo M, Guan JL . Focal adhesion kinase: a prominent determinant in breast cancer initiation, progression and metastasis. Cancer Lett 2010; 289: 127–139.
Lambert AW, Ozturk S, Thiagalingam S . Integrin signaling in mammary epithelial cells and breast cancer. ISRN Oncol 2012; 2012: 493283.
Pylayeva Y, Gillen KM, Gerald W, Beggs HE, Reichardt LF, Giancotti FG . Ras- and PI3K-dependent breast tumorigenesis in mice and humans requires focal adhesion kinase signaling. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 252–266.
Bianchi-Smiraglia A, Paesante S, Bakin AV . Integrin β5 contributes to the tumorigenic potential of breast cancer cells through the Src-FAK and MEK-ERK signaling pathways. Oncogene 2013; 32: 3049–3058.
Taddei I, Faraldo MM, Teulière J, Deugnier MA, Thiery JP, Glukhova MA . Integrins in mammary gland development and differentiation of mammary epithelium. J Mam Gland Biol Neopl 2003; 8: 383–394.
Raymond K, Cagnet S, Kreft M, Janssen H, Sonnneberg A, Glukhova MA . Control of mammary myoepithelial cell contractile function by α3β1 integrin signalling. EMBO J 2011; 30: 1896–1906.
Mitchell K, Svenson KB, Longmate WM, Gkirtzimanaki K, Sadej R, Wang X et al. Suppression of integrin alpha3beta1 in breast cancer cells reduces cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression and inhibits tumorigenesis, invasion, and cross-talk to endothelial cells. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 6359–6367.
Novitskaya V, Romanska H, Dawoud M, Jones JL, Berditchevski F . Tetraspanin CD151 regulates growth of mammary epithelial cells in three-dimensional extracellular matrix: implication for mammary ductal carcinoma in situ. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 4698–4708.
Subbaram S, Dipersio CM . Integrin α3β1 as a breast cancer target. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2011; 15: 1197–1210.
Teulière J, Faraldo MM, Deugnier MA, Shtutman M, Ben-Ze'ev A, Thiery JP et al. Targeted activation of beta-catenin signaling in basal mammary epithelial cells affects mammary development and leads to hyperplasia. Development 2005; 132: 267–277.
Moumen M, Chiche A, Decraene C, Petit V, Gandarillas A, Deugnier MA et al. Myc is required for beta-catenin-mediated mammary stem cell amplification and tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer (in revision).
Peltonen J, Larjava H, Jaakkola S, Gralnick H, Akiyama SK, Yamada SS et al. Localization of integrin receptors for fibronectin, collagen, and laminin in human skin. Variable expression in basal and squamous cell carcinomas. J Clin Invest 1989; 84: 1916–1923.
Elben ST, Slack JK, Weber MJ, Calting AD . Rac-PAK signaling stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation by regulating formation of MEK1–ERK complexes. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 6023–6033.
Oktay M, Wary KK, Dans M, Birge RB, Giancotti FG . Integrin-mediated activation of focal adhesion is required for signaling to Jun NH2-terminal kinase and progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. J Cell Biol 1999; 145: 1461–1469.
Roskoski R Jr . ERK1/2 MAP kinases: structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol Res 2012; 66: 105–143.
Choma DP, Pumiglia K, DiPersio CM . Integrin a3b1 directs the stabilization of a polarized lamellipodium in epithelial cells through activation of Rac1. J Cell Sci 2004; 117: 3947–3959.
Choma DP, Vincenzo M, Pumiglia KM, DiPersio CM . Integrin a3b1-dependent activation of FAK/Src regulates Rac1-mediated keratinocyte polarization on laminin-5. J Inv Dermatol 2007; 127: 31–40.
Manohar A, Shome SG, Lamar J, Stirling L, Iyer V, Pumiglia K et al. Alpha 3 beta 1 integrin promotes keratinocyte cell survival through activation of a MEK/ERK signaling pathway. J Cell Sci 2004; 117: 4043–4054.
Bafico A, Liu G, Goldin L, Harris V, Aaronson SA . An autocrine mechanism for constitutive Wnt pathway activation in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2004; 6: 497–506.
Sachs N, Secades P, van Hulst L, Kreft M, Song JY, Sonnenberg A . Loss of integrin α3 prevents skin tumor formation by promoting epidermal turnover and depletion of slow-cycling cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 21468–21473.
Zeng YA, Nusse R . Wnt proteins are self-renewal factors for mammary stem cells and promote their long-term expansion in culture. Cell Stem Cell 2011; 6: 568–577.
Korkaya H, Paulson A, Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C, Brown M, Dutcher J et al. Regulation of mammary stem/progenitor cells by PTEN/Akt/ β-catenin signaling. PLoS Biol 2009; 7: e1000121.
Taddei I, Deugnier MA, Faraldo MM, Petit V, Bouvard D, Medina D et al. Beta1 integrin deletion from the basal compartment of the mammary epithelium affects stem cells. Nat Cell Biol 2008; 10: 716–722.
Lim E, Vaillant F, Wu D, Forrest NC, Pal B, Hart AH et al. Aberrant luminal progenitors as the candidate target population for basal tumor development in BRCA1 mutation carriers. Nat Med 2009; 15: 907–913.
Molyneux G, Geyer FC, Magnay FA, McCarthy A, Kendrick H, Natrajan R et al. BRCA1 basal-like breast cancers originate from luminal epithelial progenitors and not from basal stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2010; 7: 403–417.
Ramirez A, Page A, Gandarillas A, Zanet J, Pibre S, Vidal M et al. A keratin K5Cre transgenic line appropriate for tissue- specific or generalized Cre-mediated recombination. Genesis 2004; 39: 52–57.
Margadant C, Raymond K, Kreft M, Sachs N, Janssen H, Sonnenberg A . Integrin α3β1 inhibits directional migration and wound re-epithelialization in the skin. J Cell Sci 2009; 122: 278–288.
Raymond K, Kreft M, Janssen H, Calafat J, Sonnenberg A . Keratinocytes display normal proliferation, survival and differentiation in conditional beta4-integrin knockout mice. J Cell Sci 2005; 118: 1045–1060.
Sachs N, Kreft M, van den Bergh Weerman MA, Beynon AJ, Peters TA, Weening JJ et al. Kidney failure in mice lacking the tetraspanin CD151. J Cell Biol 2006; 175: 33–39.
Moumen M, Chiche A, Deugnier MA, Petit V, Gandarillas A, Glukhova MA et al. The proto-oncogene Myc is essential for mammary stem cell function. Stem cells 2012; 30: 1246–1254.
Korinek V, Barker N, Morin PJ, van Wichen D, de Weger R, Kinzler KW et al. Constitutive transcriptional activation by a beta-catenin–Tcf complex in APC−/− colon carcinoma. Science 1997; 275: 1784–1787.
Salomon D, Sacco PA, Roy SG, Simcha I, Johnson KR, Wheelock MJ et al. Regulation of beta-catenin levels and localization by overexpression of plakoglobin and inhibition of the ubiquitin proteasome system. J Cell Biol 1997; 139: 1325–1335.
Acknowledgements
We are particularly grateful to Dr JL Jorcano for providing K5Cre transgenic mice. We thank Dr I Grandjean and S Jannet for excellent assistance with animal care, Z Maciorowski, A Viguier and S Grondin for excellent assistance with FACS analyses and M Denoyelle and A Di Cicco for technical help. We also thank the Nikon Imaging Centre at Institut Curie-CNRS for providing confocal microscopy facilities. This work was supported by La Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (Equipe Labélisée 2009, 2013) and a grant from the Agence Nationale de la Recherche ANR-08-BLAN-0078-01 to MAG. SC received funding from Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer; MAG is Directeur de Recherche and MMF and KR are Chargé de Recherche at the Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cagnet, S., Faraldo, M., Kreft, M. et al. Signaling events mediated by α3β1 integrin are essential for mammary tumorigenesis. Oncogene 33, 4286–4295 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.391
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.391
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ADAMTS18 deficiency associates extracellular matrix dysfunction with a higher risk of HER2-positive mammary tumorigenesis and metastasis
Breast Cancer Research (2024)
-
Membrane to cortex attachment determines different mechanical phenotypes in LGR5+ and LGR5- colorectal cancer cells
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Control cell migration by engineering integrin ligand assembly
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Integrins regulate stemness in solid tumor: an emerging therapeutic target
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2021)
-
Absence of integrin α3β1 promotes the progression of HER2-driven breast cancer in vivo
Breast Cancer Research (2019)