Abstract
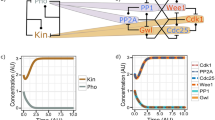
New data have recently established that protein phosphorylation during mitosis is the result of a controlled balance between kinase and phosphatase activities and that, as for mitotic kinases, phosphatases are also regulated during cell division. This regulation is at least in part induced by the activation of the Greatwall (Gwl) kinase at mitotic entry. Activated Gwl phosphorylates its substrates cAMP-regulated phospho protein 19 (Arpp19) and α-endosulfine (ENSA), promoting their binding to and the inhibition of PP2A. Interestingly, besides the role of the Gwl-Arpp19/ENSA in the control of mitotic division, new data in yeast support the involvement of this pathway in mRNA stabilization during G0 program initiation, although in this case the phosphatase PP2A appears not to be implicated. Finally, Gwl activity has been shown to be required for DNA checkpoint recovery. These new findings support the view that Gwl, Arpp19 and ENSA could function as the core of a new signalization pathway that, by targeting different final substrates, could participate in a variety of physiological functions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu J, Fleming SL, Williams B, Williams EV, Li Z, Somma P et al. Greatwall kinase: a nuclear protein required for proper chromosome condensation and mitotic progression in Drosophila. J Cell Biol 2004; 164: 487–492.
Bettencourt-Dias M, Giet R, Sinka R, Mazumdar A, Lock WG, Balloux F et al. Genome-wide survey of protein kinases required for cell cycle progression. Nature 2004; 432: 980–987.
Yu J, Zhao Y, Li Z, Galas S, Goldberg ML . Greatwall kinase participates in the Cdc2 autoregulatory loop in Xenopus egg extracts. Mol Cell 2006; 22: 83–91.
Vigneron S, Brioudes E, Burgess A, Labbe JC, Lorca T, Castro A . Greatwall maintains mitosis through regulation of PP2A. EMBO J 2009; 28: 2786–2793.
Gharbi-Ayachi A, Labbe JC, Burgess A, Vigneron S, Strub JM, Brioudes E et al. The substrate of Greatwall kinase, Arpp19, controls mitosis by inhibiting protein phosphatase 2A. Science 2010; 330: 1673–1677.
Mochida S, Maslen SL, Skehel M, Hunt T . Greatwall phosphorylates an inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A that is essential for mitosis. Science 2010; 330: 1670–1673.
Burgess A, Vigneron S, Brioudes E, Labbe JC, Lorca T, Castro A . Loss of human Greatwall results in G2 arrest and multiple mitotic defects due to deregulation of the cyclin B-Cdc2/PP2A balance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 12564–12569.
Manchado E, Guillamot M, de Carcer G, Eguren M, Trickey M, Garcia-Higuera I et al. Targeting mitotic exit leads to tumor regression in vivo: Modulation by Cdk1, Mastl, and the PP2A/B55alpha,delta phosphatase. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 641–654.
Voets E, Wolthuis RM . MASTL is the human orthologue of Greatwall kinase that facilitates mitotic entry, anaphase and cytokinesis. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 3591–3601.
Peng A, Wang L, Fisher LA . Greatwall and polo-like kinase 1 coordinate to promote checkpoint recovery. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 28996–29004.
Talarek N, Cameroni E, Jaquenoud M, Luo X, Bontron S, Lippman S et al. Initiation of the TORC1-regulated G0 program requires Igo1/2, which license specific mRNAs to evade degradation via the 5′-3′ mRNA decay pathway. Mol Cell 2010; 38: 345–355.
Zhao Y, Haccard O, Wang R, Yu J, Kuang J, Jessus C et al. Roles of Greatwall kinase in the regulation of cdc25 phosphatase. Mol Biol Cell 2008; 19: 1317–1327.
Lorca T, Bernis C, Vigneron S, Burgess A, Brioudes E, Labbe JC et al. Constant regulation of both the MPF amplification loop and the Greatwall-PP2A pathway is required for metaphase II arrest and correct entry into the first embryonic cell cycle. J Cell Sci 2010; 123: 2281–2291.
Janssens V, Goris J . Protein phosphatase 2A: a highly regulated family of serine/threonine phosphatases implicated in cell growth and signalling. Biochem J 2001; 353: 417–439.
Mochida S, Ikeo S, Gannon J, Hunt T . Regulated activity of PP2A-B55 delta is crucial for controlling entry into and exit from mitosis in Xenopus egg extracts. EMBO J 2009; 28: 2777–2785.
Castilho PV, Williams BC, Mochida S, Zhao Y, Goldberg ML . The M phase kinase Greatwall (Gwl) promotes inactivation of PP2A/B55delta, a phosphatase directed against CDK phosphosites. Mol Biol Cell 2009; 20: 4777–4789.
Schmitz MH, Held M, Janssens V, Hutchins JR, Hudecz O, Ivanova E et al. Live-cell imaging RNAi screen identifies PP2A-B55alpha and importin-beta1 as key mitotic exit regulators in human cells. Nat Cell Biol 2010; 12: 886–893.
Wang P, Pinson X, Archambault V . PP2A-twins is antagonized by greatwall and collaborates with polo for cell cycle progression and centrosome attachment to nuclei in drosophila embryos. PLoS Genet 2011; 7: e1002227.
Yamamoto TM, Blake-Hodek K, Williams BC, Lewellyn AL, Goldberg ML, Maller JL . Regulation of Greatwall kinase during Xenopus oocyte maturation. Mol Biol Cell 2011; 22: 2157–2164.
Von Stetina JR, Tranguch S, Dey SK, Lee LA, Cha B, Drummond-Barbosa D . alpha-Endosulfine is a conserved protein required for oocyte meiotic maturation in Drosophila. Development 2008; 135: 3697–3706.
Rangone H, Wegel E, Gatt MK, Yeung E, Flowers A, Debski J et al. Suppression of scant identifies Endos as a substrate of greatwall kinase and a negative regulator of protein phosphatase 2A in mitosis. PLoS Genet 2011; 7: e1002225.
Vigneron S, Gharbi-Ayachi A, Raymond AA, Burgess A, Labbe JC, Labesse G et al. Characterization of the mechanisms controlling Greatwall activity. Mol Cell Biol 2011; 31: 2262–2275.
Pearce LR, Komander D, Alessi DR . The nuts and bolts of AGC protein kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2010; 11: 9–22.
Steegmaier M, Hoffmann M, Baum A, Lenart P, Petronczki M, Krssak M et al. BI 2536, a potent and selective inhibitor of polo-like kinase 1, inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Curr Biol 2007; 17: 316–322.
Sumara I, Gimenez-Abian JF, Gerlich D, Hirota T, Kraft C, de la Torre C et al. Roles of polo-like kinase 1 in the assembly of functional mitotic spindles. Curr Biol 2004; 14: 1712–1722.
Peng A, Yamamoto TM, Goldberg ML, Maller JL . A novel role for greatwall kinase in recovery from DNA damage. Cell Cycle 2011; 9: 4364–4369.
Archambault V, Zhao X, White-Cooper H, Carpenter AT, Glover DM . Mutations in Drosophila Greatwall/Scant reveal its roles in mitosis and meiosis and interdependence with Polo kinase. PLoS Genet 2007; 3: e200.
White-Cooper H, Carmena M, Gonzalez C, Glover DM . Mutations in new cell cycle genes that fail to complement a multiply mutant third chromosome of Drosophila. Genetics 1996; 144: 1097–1111.
Gandhi MJ, Cummings CL, Drachman JG . FLJ14813 missense mutation: a candidate for autosomal dominant thrombocytopenia on human chromosome 10. Hum Hered 2003; 55: 66–70.
Johnson HJ, Gandhi MJ, Shafizadeh E, Langer NB, Pierce EL, Paw BH et al. In vivo inactivation of MASTL kinase results in thrombocytopenia. Exp Hematol 2009; 37: 901–908.
Eichhorn PJ, Creyghton MP, Bernards R . Protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunits and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1795: 1–15.
Galvin JE, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ . Synucleinopathies: clinical and pathological implications. Arch Neurol 2001; 58: 186–190.
Woods WS, Boettcher JM, Zhou DH, Kloepper KD, Hartman KL, Ladror DT et al. Conformation-specific binding of alpha-synuclein to novel protein partners detected by phage display and NMR spectroscopy. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 34555–34567.
Acknowledgements
We thank A Burgess and K Hached for comments and suggestions on the manuscript. Research in the laboratory of TL and AC has received funding from the ‘Agence Nationale de la Recherche’ (Programme Blanc) and from ‘The Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer’ (Equipe Labelissée).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lorca, T., Castro, A. The Greatwall kinase: a new pathway in the control of the cell cycle. Oncogene 32, 537–543 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.79
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.79
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MASTL induces Colon Cancer progression and Chemoresistance by promoting Wnt/β-catenin signaling
Molecular Cancer (2018)
-
Identification of new inhibitors against human Great wall kinase using in silico approaches
Scientific Reports (2018)