Abstract
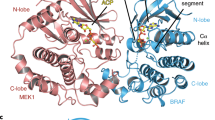
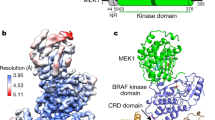
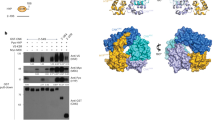
The RAF proteins are cytosolic protein kinases that regulate cell responses to extracellular signals. There are three RAF proteins in cells, ARAF, BRAF and CRAF, and recent studies have shown that the formation of complexes by these different isoforms has an important role in their activation, particularly in response to RAF inhibitors. Here, we investigated the role of ARAF in cancer cell signaling and examined the role of ARAF in mediating paradoxical activation of the MAPK pathway in cells treated with RAF inhibitors. We show that two mutations that occur in ARAF in cancer inactivate the kinase. We also show that ARAF is not functionally redundant with CRAF and cannot substitute for CRAF downstream of RAS. We further show that ARAF binds to and is activated by BRAF and that ARAF also forms complexes with CRAF. Critically, ARAF seems to stabilize BRAF:CRAF complexes in cells treated with RAF inhibitors and thereby regulate cell signaling in a subtle manner to ensure signaling efficiency.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mercer KE, Pritchard CA . Raf proteins and cancer: B-Raf is identified as a mutational target. Biochim Biophys Acta 2003; 1653: 25–40.
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 2002; 417: 949–954.
Emuss V, Garnett M, Mason C, Marais R. . Mutations of C-RAF are rare in human cancer because C-RAF has a low basal kinase activity compared with B-RAF. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 9719–9726.
Wellbrock C, Karasarides M, Marais R . The RAF proteins take centre stage. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004; 5: 875–885.
Flaherty KT, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A, McArthur GA, Sosman JA et al. Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: 809–819.
Bollag G, Hirth P, Tsai J, Zhang J, Ibrahim PN, Cho H et al. Clinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor needs broad target blockade in BRAF-mutant melanoma. Nature 2010; 467: 596–599.
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: 2507–2516.
Dhomen N, Marais R . New insight into BRAF mutations in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2007; 17: 31–39.
Wan PT, Garnett MJ, Roe SM, Lee S, Niculescu-Duvaz D, Good VM et al. Mechanism of activation of the RAF-ERK signaling pathway by oncogenic mutations of B-RAF. Cell 2004; 116: 855–867.
Garnett MJ, Rana S, Paterson H, Barford D, Marais R . Wild-type and mutant B-RAF activate C-RAF through distinct mechanisms involving heterodimerization. Mol Cell 2005; 20: 963–969.
Dumaz N, Hayward R, Martin J, Ogilvie L, Hedley D, Curtin JA et al. In melanoma, RAS mutations are accompanied by switching signaling from BRAF to CRAF and disrupted cyclic AMP signaling. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 9483–9491.
Blasco RB, Francoz S, Santamaria D, Canamero M, Dubus P, Charron J et al. c-Raf, but not B-Raf, is essential for development of K-Ras oncogene-driven non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2011; 19: 652–663.
Karreth FA, Frese KK, DeNicola GM, Baccarini M, Tuveson DA . C-Raf Is Required for the Initiation of Lung Cancer by K-RasG12D. Cancer Discovery 2011; 1: 128–136.
Heidorn SJ, Milagre C, Whittaker S, Nourry A, Niculescu-Duvas I, Dhomen N et al. Kinase-dead BRAF and oncogenic RAS cooperate to drive tumor progression through CRAF. Cell 2010; 140: 209–221.
Hatzivassiliou G, Song K, Yen I, Brandhuber BJ, Anderson DJ, Alvarado R et al. RAF inhibitors prime wild-type RAF to activate the MAPK pathway and enhance growth. Nature 2010; 464: 431–435.
Poulikakos PI, Zhang C, Bollag G, Shokat KM, Rosen N . RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signalling in cells with wild-type BRAF. Nature 2010; 464: 427–430.
Lee JW, Soung YH, Kim SY, Park WS, Nam SW, Min WS et al. Mutational analysis of the ARAF gene in human cancers. Apmis 2005; 113: 54–57.
Greenman C, Stephens P, Smith R, Dalgliesh GL, Hunter C, Bignell G et al. Patterns of somatic mutation in human cancer genomes. Nature 2007; 446: 153–158.
Marais R, Light Y, Paterson HF, Mason CS, Marshall CJ . Differential regulation of Raf–1, A-Raf, and B-Raf by oncogenic ras and tyrosine kinases. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 4378–4383.
Zhang BH, Guan KL . Activation of B-Raf kinase requires phosphorylation of the conserved residues Thr598 and Ser601. EMBO J 2000; 19: 5429–5439.
Chong H, Lee J, Guan KL . Positive and negative regulation of Raf kinase activity and function by phosphorylation. Embo J 2001; 20: 3716–3727.
Garnett MJ, Marais R . Guilty as charged: B-RAF is a human oncogene. Cancer Cell 2004; 6: 313–319.
Moretti S, De Falco V, Tamburrino A, Barbi F, Tavano M, Avenia N et al. Insights into the molecular function of the inactivating mutations of B-Raf involving the DFG motif. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009; 1793: 1634–1645.
Ritt DA, Monson DM, Specht SI, Morrison DK . Impact of feedback phosphorylation and Raf heterodimerization on normal and mutant B-Raf signaling. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30: 806–819.
Villanueva J, Vultur A, Lee JT, Somasundaram R, Fukunaga-Kalabis M, Cipolla AK et al. Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors mediated by a RAF kinase switch in melanoma can be overcome by cotargeting MEK and IGF-1R/PI3K. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 683–695.
Hu J, Yu H, Kornev AP, Zhao J, Filbert EL, Taylor SS et al. Mutation that blocks ATP binding creates a pseudokinase stabilizing the scaffolding function of kinase suppressor of Ras, CRAF and BRAF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 6067–6072.
McKay MM, Ritt DA, Morrison DK . RAF inhibitor-induced KSR1/B-RAF binding and its effects on ERK cascade signaling. Curr Biol 2011; 21: 563–568.
Packer LM, Rana S, Hayward R, O'Hare T, Eide CA, Rebocho A et al. Nilotinib and MEK Inhibitors Induce Synthetic Lethality through Paradoxical Activation of RAF in Drug-Resistant Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2011; 20: 715–727.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (SFRH/BD/15904/2005), the Institute of Cancer Research and Cancer Research UK (Ref: C107/A10433). We thank Professor Caroline Springer for providing sorafenib and PD184352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rebocho, A., Marais, R. ARAF acts as a scaffold to stabilize BRAF:CRAF heterodimers. Oncogene 32, 3207–3212 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.330
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.330
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Somatic ARAF mutations in pediatric Langerhans cell histiocytosis: clinicopathologic, genetic and functional profiling
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2023)
-
ARAF mutations confer resistance to the RAF inhibitor belvarafenib in melanoma
Nature (2021)
-
The ubiquitin system: orchestrating cellular signals in non-small-cell lung cancer
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2020)
-
Molecular Profiling of Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (2020)
-
EIF5A1 promotes trophoblast migration and invasion via ARAF-mediated activation of the integrin/ERK signaling pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2018)