Abstract
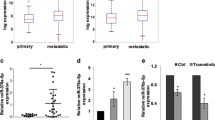
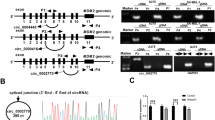
WEE1 kinase has been described as a major gate keeper at the G2 cell cycle checkpoint and to be involved in tumour progression in different malignant tumours. Here we analysed the expression levels of WEE1 in a series of melanoma patient samples and melanoma cell lines using immunoblotting, quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry. WEE1 expression was significantly downregulated in patient samples of metastatic origin as compared with primary melanomas and in melanoma cell lines of high aggressiveness as compared with cell lines of low aggressiveness. Moreover, there was an inverse correlation between the expression of WEE1 and WEE1-targeting microRNA miR-195. Further analyses showed that transfection of melanoma cell lines with miR-195 indeed reduced WEE1 mRNA and protein expression in these cells. Reporter gene analysis confirmed direct targeting of the WEE1 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) by miR-195. Overexpression of miR-195 in SK-Mel-28 melanoma cells was accompanied by WEE1 reduction and significantly reduced stress-induced G2-M cell cycle arrest, which could be restored by stable overexpression of WEE1. Moreover, miR-195 overexpression and WEE1 knockdown, respectively, increased melanoma cell proliferation. miR-195 overexpression also enhanced migration and invasiveness of melanoma cells. Taken together, the present study shows that WEE1 expression in malignant melanoma is directly regulated by miR-195. miR-195-mediated downregulation of WEE1 in metastatic lesions may help to overcome cell cycle arrest under stress conditions in the local tissue microenvironment to allow unrestricted growth of tumour cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGowan CH, Russell P . Human Wee1 kinase inhibits cell division by phosphorylating p34cdc2 exclusively on Tyr15. EMBO J 1993; 12: 75–85.
O'Connell MJ, Raleigh JM, Verkade HM, Nurse P . Chk1 is a wee1 kinase in the G2 DNA damage checkpoint inhibiting cdc2 by Y15 phosphorylation. EMBO J 1997; 16: 545–554.
Mir SE, De Witt Hamer PC, Krawczyk PM, Balaj L, Claes A, Niers JM et al. In silico analysis of kinase expression identifies WEE1 as a gatekeeper against mitotic catastrophe in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2010; 18: 244–257.
Talantov D, Mazumder A, Yu JX, Briggs T, Jiang Y, Backus J et al. Novel genes associated with malignant melanoma but not benign melanocytic lesions. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 7234–7242.
Hashimoto O, Ueno T, Kimura R, Ohtsubo M, Nakamura T, Koga H et al. Inhibition of proteasome-dependent degradation of Wee1 in G2-arrested Hep3B cells by TGF beta 1. Mol Carcinog 2003; 36: 171–182.
Wang Y, Li J, Booher RN, Kraker A, Lawrence T, Leopold WR et al. Radiosensitization of p53 mutant cells by PD0166285, a novel G(2) checkpoint abrogator. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 8211–8217.
Yoshida T, Tanaka S, Mogi A, Shitara Y, Kuwano H . The clinical significance of Cyclin B1 and Wee1 expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 2004; 15: 252–256.
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009; 136: 215–233.
Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ . Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 259–269.
Rai D, Kim SW, McKeller MR, Dahia PL, Aguiar RC . Targeting of SMAD5 links microRNA-155 to the TGF-beta pathway and lymphomagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 3111–3116.
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA . Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 2007; 449: 682–688.
Ma L, Reinhardt F, Pan E, Soutschek J, Bhat B, Marcusson EG et al. Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse mammary tumor model. Nat Biotechnol 2010; 28: 341–347.
Medina PP, Nolde M, Slack FJ . OncomiR addiction in an in vivo model of microRNA-21-induced pre-B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2010; 467: 86–90.
Swarbrick A, Woods SL, Shaw A, Balakrishnan A, Phua Y, Nguyen A et al. miR-380-5p represses p53 to control cellular survival and is associated with poor outcome in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. Nat Med 2010; 16: 1134–1140.
Miller AJ, Mihm MC . Melanoma. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 51–65.
Quintana E, Shackleton M, Sabel MS, Fullen DR, Johnson TM, Morrison SJ . Efficient tumour formation by single human melanoma cells. Nature 2008; 456: 593–598.
Felicetti F, Errico MC, Bottero L, Segnalini P, Stoppacciaro A, Biffoni M et al. The promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger-microRNA-221/-222 pathway controls melanoma progression through multiple oncogenic mechanisms. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 2745–2754.
Muller DW, Bosserhoff AK . Integrin beta 3 expression is regulated by let-7a miRNA in malignant melanoma. Oncogene 2008; 27: 6698–6706.
Philippidou D, Schmitt M, Moser D, Margue C, Nazarov PV, Muller A et al. Signatures of microRNAs and selected microRNA target genes in human melanoma. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 4163–4173.
Qi J, Yu JY, Shcherbata HR, Mathieu J, Wang AJ, Seal S et al. microRNAs regulate human embryonic stem cell division. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 3729–3741.
Liu L, Chen L, Xu Y, Li R, Du X . microRNA-195 promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity of human colorectal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010; 400: 236–240.
Ujifuku K, Mitsutake N, Takakura S, Matsuse M, Saenko V, Suzuki K et al. miR-195, miR-455-3p and miR-10a(*) are implicated in acquired temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Cancer Lett 2010; 296: 241–248.
Levati L, Alvino E, Pagani E, Arcelli D, Caporaso P, Bondanza S et al. Altered expression of selected microRNAs in melanoma: antiproliferative and proapoptotic activity of miRNA-155. Int J Oncol 2009; 35: 393–400.
Jewell R, Conway C, Mitra A, Randerson-Moor J, Lobo S, Nsengimana J et al. Patterns of expression of DNA repair genes and relapse from melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 5211–5221.
Bueno MJ, Malumbres M . MicroRNAs and the cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011; 1812: 592–601.
Li D, Zhao Y, Liu C, Chen X, Qi Y, Jiang Y et al. Analysis of MiR-195 and MiR-497 expression, regulation and role in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 1722–1730.
Xu T, Zhu Y, Xiong Y, Ge YY, Yun JP, Zhuang SM . MicroRNA-195 suppresses tumorigenicity and regulates G1/S transition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 2009; 50: 113–121.
Meltzer PS . Cancer genomics: small RNAs with big impacts. Nature 2005; 435: 745–746.
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 2005; 435: 828–833.
O'Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT . c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 2005; 435: 839–843.
Zhang L, Huang J, Yang N, Greshock J, Megraw MS, Giannakakis A et al. microRNAs exhibit high frequency genomic alterations in human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 9136–9141.
Yu Z, Wang C, Wang M, Li Z, Casimiro MC, Liu M et al. A cyclin D1/microRNA 17/20 regulatory feedback loop in control of breast cancer cell proliferation. J Cell Biol 2008; 182: 509–517.
Lee J, Kumagai A, Dunphy WG . Positive regulation of Wee1 by Chk1 and 14-3-3 proteins. Mol Biol Cell 2001; 12: 551–563.
van Vugt MA, Bras A, Medema RH . Polo-like kinase-1 controls recovery from a G2 DNA damage-induced arrest in mammalian cells. Mol Cell 2004; 15: 799–811.
Wang F, Zhu Y, Huang Y, McAvoy S, Johnson WB, Cheung TH et al. Transcriptional repression of WEE1 by Kruppel-like factor 2 is involved in DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2005; 24: 3875–3885.
Hirai H, Iwasawa Y, Okada M, Arai T, Nishibata T, Kobayashi M et al. Small-molecule inhibition of Wee1 kinase by MK-1775 selectively sensitizes p53-deficient tumor cells to DNA-damaging agents. Mol Cancer Ther 2009; 8: 2992–3000.
Hirai H, Arai T, Okada M, Nishibata T, Kobayashi M, Sakai N et al. MK-1775, a small molecule Wee1 inhibitor, enhances anti-tumor efficacy of various DNA-damaging agents, including 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Biol Ther 2010; 9: 514–522.
Beck H, Nahse V, Larsen MS, Groth P, Clancy T, Lees M et al. Regulators of cyclin-dependent kinases are crucial for maintaining genome integrity in S phase. J Cell Biol 2010; 188: 629–638.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011; 144: 646–674.
Schultz J, Lorenz P, Gross G, Ibrahim S, Kunz M . MicroRNA let-7b targets important cell cycle molecules in malignant melanoma cells and interferes with anchorage-independent growth. Cell Res 2008; 18: 549–557.
Acknowledgements
We thank T Magin, Translational Centre for Regenerative Medicine (TRM), Division of Cell and Developmental Biology, University of Leipzig, for helpful advice and discussion. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, grant number KU 1320/5-1 to MK and grant number WO 991/4-1 to WO.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharya, A., Schmitz, U., Wolkenhauer, O. et al. Regulation of cell cycle checkpoint kinase WEE1 by miR-195 in malignant melanoma. Oncogene 32, 3175–3183 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.324
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.324
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Panels of circulating microRNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2022)
-
Circulating microRNAs miR-331 and miR-195 differentiate local luminal a from metastatic breast cancer
BMC Cancer (2019)
-
miR-195 targets cyclin D3 and survivin to modulate the tumorigenesis of non-small cell lung cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
Cell Cycle Regulation of Stem Cells by MicroRNAs
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2018)
-
MicroRNA-195 inhibits proliferation, invasion and metastasis in breast cancer cells by targeting FASN, HMGCR, ACACA and CYP27B1
Scientific Reports (2015)