Abstract
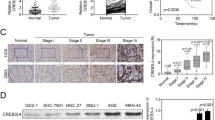
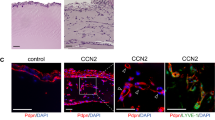
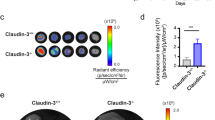
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-δ (C/EBP-δ), a transcription factor, is elevated in carcinoma compared with that in normal tissue. This study reports a novel function of C/EBP-δ in lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis. Genetic deletion of C/EBP-δ in mice resulted in a significant reduction of lymphangiogenesis and pulmonary metastases, with a dramatic reduction of vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) and its cognate receptor VEGF receptor-3 (VEGFR3) in lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs). By contrast, no difference of VEGF-C in tumor tissues and bone marrow was observed between null and wild-type mice. Consistently, forced expression of C/EBP-δ increased VEGF-C and VEGFR3 expression in cultured LECs. These findings suggest a specific and important role of C/EBP-δ in the regulation of VEGFR3 signaling in LECs. Furthermore, expression of C/EBP-δ in cultured LECs significantly increased cell motility, and knockdown of C/EBP-δ inhibited cell motility and lymphatic vascular network formation in vitro. Forced expression of VEGF-C, but not recombinant VEGF-C, rescued the knockdown of C/EBP-δ-induced cell apoptosis, indicative of autonomous VEGF-C autocrine signaling essential for LEC survival. Moreover, hypoxia induces C/EBP-δ expression and C/EBP-δ regulates HIF-1α expression. Blocking HIF-1α activity totally blocked CEBP-δ-induced VEGF-C and VEGFR3 expression in LECs. Together, these findings uncover a new function of CEBP-δ in lymphangiogenesis through regulation of VEGFR3 signaling in LECs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi K, Ikeda Y, Miyazaki M, Abe T, Kinoshita J, Maehara Y et al. (2000). Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) expression in human colorectal cancer tissues. Br J Cancer 83: 887–891.
Alitalo K, Carmeliet P . (2002). Molecular mechanisms of lymphangiogenesis in health and disease. Cancer Cell 1: 219–227.
Alitalo K, Tammela T, Petrova TV . (2005). Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature 438: 946–953.
Dumont DJ, Jussila L, Taipale J, Lymboussaki A, Mustonen T, Pajusola K et al. (1998). Cardiovascular failure in mouse embryos deficient in VEGF receptor-3. Science 282: 946–949.
He Y, Kozaki K, Karpanen T, Koshikawa K, Yla-Herttuala S, Takahashi T et al. (2002). Suppression of tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by blocking vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 signaling. J Natl Cancer Inst 94: 819–825.
Helotera H, Alitalo K . (2007). The VEGF family, the inside story. Cell 130: 591–592.
Irigoyen M, Anso E, Martinez E, Garayoa M, Martinez-Irujo JJ, Rouzaut A . (2007). Hypoxia alters the adhesive properties of lymphatic endothelial cells. A transcriptional and functional study. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773: 880–890.
Johnson PF . (2005). Molecular stop signs: regulation of cell-cycle arrest by C/EBP transcription factors. J Cell Sci 118: 2545–2555.
Kamiyama M, Pozzi A, Yang L, DeBusk LM, Breyer RM, Lin PC . (2006). EP2, a receptor for PGE2, regulates tumor angiogenesis through direct effects on endothelial cell motility and survival. Oncogene 25: 7019–7028.
Karkkainen MJ, Haiko P, Sainio K, Partanen J, Taipale J, Petrova TV et al. (2004). Vascular endothelial growth factor C is required for sprouting of the first lymphatic vessels from embryonic veins. Nat Immunol 5: 74–80.
Katsuta M, Miyashita M, Makino H, Nomura T, Shinji S, Yamashita K et al. (2005). Correlation of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha with lymphatic metastasis via vascular endothelial growth factor-C in human esophageal cancer. Exp Mol Pathol 78: 123–130.
Kim Y, Fischer SM . (1998). Transcriptional regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 in mouse skin carcinoma cells. Regulatory role of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins in the differential expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in normal and neoplastic tissues. J Biol Chem 273: 27686–27694.
Kitami Y, Fukuoka T, Hiwada K, Inagami T . (1999). A high level of CCAAT-enhancer binding protein-delta expression is a major determinant for markedly elevated differential gene expression of the platelet-derived growth factor-alpha receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells of genetically hypertensive rats. Circ Res 84: 64–73.
Kurokawa T, Miyamoto M, Kato K, Cho Y, Kawarada Y, Hida Y et al. (2003). Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible-factor 1alpha(HIF-1alpha) in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma correlates with lymph node metastasis and pathologic stage. Br J Cancer 89: 1042–1047.
Kuwai T, Kitadai Y, Tanaka S, Onogawa S, Matsutani N, Kaio E et al. (2003). Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is associated with tumor vascularization in human colorectal carcinoma. Int J Cancer 105: 176–181.
Lee S, Chen TT, Barber CL, Jordan MC, Murdock J, Desai S et al. (2007). Autocrine VEGF signaling is required for vascular homeostasis. Cell 130: 691–703.
Makinen T, Veikkola T, Mustjoki S, Karpanen T, Catimel B, Nice EC et al. (2001). Isolated lymphatic endothelial cells transduce growth, survival and migratory signals via the VEGF-C/D receptor VEGFR-3. EMBO J 20: 4762–4773.
Milde-Langosch K, Loning T, Bamberger AM . (2003). Expression of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins C/EBPalpha, C/EBPbeta and C/EBPdelta in breast cancer: correlations with clinicopathologic parameters and cell-cycle regulatory proteins. Breast Cancer Res Treat 79: 175–185.
Ota H, Katsube K, Ogawa J, Yanagishita M . (2007). Hypoxia/Notch signaling in primary culture of rat lymphatic endothelial cells. FEBS Lett 581: 5220–5226.
Poli V . (1998). The role of C/EBP isoforms in the control of inflammatory and native immunity functions. J Biol Chem 273: 29279–29282.
Rabek JP, Scott S, Hsieh CC, Reisner PD, Papaconstantinou J . (1998). Regulation of LPS-mediated induction of C/EBP delta gene expression in livers of young and aged mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1398: 137–147.
Ramji DP, Foka P . (2002). CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: structure, function and regulation. Biochem J 365: 561–575.
Schoppmann SF, Fenzl A, Schindl M, Bachleitner-Hofmann T, Nagy K, Gnant M et al. (2006). Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha correlates with VEGF-C expression and lymphangiogenesis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 99: 135–141.
Semenza GL . (1998). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: master regulator of O2 homeostasis. Curr Opin Genet Dev 8: 588–594.
Simiantonaki N, Jayasinghe C, Michel-Schmidt R, Peters K, Hermanns MI, Kirkpatrick CJ . (2008). Hypoxia-induced epithelial VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 upregulation in carcinoma cell lines. Int J Oncol 32: 585–592.
Skobe M, Hawighorst T, Jackson DG, Prevo R, Janes L, Velasco P et al. (2001). Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nat Med 7: 192–198.
Stacker SA, Achen MG, Jussila L, Baldwin ME, Alitalo K . (2002). Lymphangiogenesis and cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 573–583.
Sterneck E, Paylor R, Jackson-Lewis V, Libbey M, Przedborski S, Tessarollo L et al. (1998). Selectively enhanced contextual fear conditioning in mice lacking the transcriptional regulator CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 10908–10913.
Takata Y, Kitami Y, Yang ZH, Nakamura M, Okura T, Hiwada K . (2002). Vascular inflammation is negatively autoregulated by interaction between CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-delta and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Circ Res 91: 427–433.
Tanaka T, Yoshida N, Kishimoto T, Akira S . (1997). Defective adipocyte differentiation in mice lacking the C/EBPbeta and/or C/EBPdelta gene. EMBO J 16: 7432–7443.
Tang N, Wang L, Esko J, Giordano FJ, Huang Y, Gerber HP et al. (2004). Loss of HIF-1alpha in endothelial cells disrupts a hypoxia-driven VEGF autocrine loop necessary for tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 6: 485–495.
Tang Y, Pacary E, Freret T, Divoux D, Petit E, Schumann-Bard P et al. (2006). Effect of hypoxic preconditioning on brain genomic response before and following ischemia in the adult mouse: identification of potential neuroprotective candidates for stroke. Neurobiol Dis 21: 18–28.
Thangaraju M, Rudelius M, Bierie B, Raffeld M, Sharan S, Hennighausen L et al. (2005). C/EBPdelta is a crucial regulator of proapoptotic gene expression during mammary gland involution. Development 132: 4675–4685.
Yang ZH, Kitami Y, Takata Y, Okura T, Hiwada K . (2001). Targeted overexpression of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-delta evokes enhanced gene transcription of platelet-derived growth factor alpha-receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 89: 503–508.
Yonemura Y, Endo Y, Fujita H, Fushida S, Ninomiya I, Bandou E et al. (1999). Role of vascular endothelial growth factor C expression in the development of lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 5: 1823–1829.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from NIH (CA108856, NS45888 and AR053718).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Min, Y., Ghose, S., Boelte, K. et al. C/EBP-δ regulates VEGF-C autocrine signaling in lymphangiogenesis and metastasis of lung cancer through HIF-1α. Oncogene 30, 4901–4909 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.187
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.187
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
CEBPD is a master transcriptional factor for hypoxia regulated proteins in glioblastoma and augments hypoxia induced invasion through extracellular matrix-integrin mediated EGFR/PI3K pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
p97/VCP is highly expressed in the stem-like cells of breast cancer and controls cancer stemness partly through the unfolded protein response
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
CD146, from a melanoma cell adhesion molecule to a signaling receptor
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2020)
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta regulates the stemness of glioma stem-like cells through activating PDGFA expression upon inflammatory stimulation
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2019)
-
C/EBPδ links IL-6 and HIF-1 signaling to promote breast cancer stem cell-associated phenotypes
Oncogene (2019)