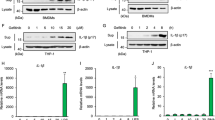
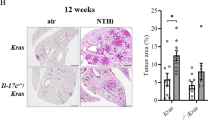
Abstract
The role of the AP-1 transcription factor Fra-1 (encoded by Fosl1) in inflammatory responses associated with lung disease is largely unknown. Here, we show that Fra-1 overexpression in mice reduced proinflammatory cytokine production in response to injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a Toll-like receptor (TLR)-ligand. Unexpectedly, Fra-1 transgenic mice died rapidly following LPS treatment, showing severe interstitial lung disease and displaying massive accumulation of macrophages and overproduction of several chemokines, including macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1, encoded by Ccl2). To assess the clinical relevance of Fra-1 in lung pathology, mice were treated with the anticancer drug gefitinib (Iressa), which can lead to interstitial lung disease in patients. Gefitinib-treated mice showed increased Fosl1 and Ccl2 expression and developed interstitial lung disease in response to LPS, endogenous TLR ligands and chemotherapy. Moreover, deletion of Fra-1 or blocking MCP-1 receptor signaling in mice attenuated gefitinib-enhanced lethality in response to LPS. Importantly, human alveolar macrophages showed enhanced LPS-induced FOSL1 and CCL2 expression after gefitinib treatment. These results indicate that Fra-1 is an important mediator of interstitial lung disease following gefitinib treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB . (2003). Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol 3: 745–756.
Bakiri L, Takada Y, Radolf M, Eferl R, Yaniv M, Wagner EF et al. (2007). Role of heterodimerization of c-Fos and Fra1 proteins in osteoclast differentiation. Bone 40: 867–875.
Bergers G, Graninger P, Braselmann S, Wrighton C, Busslinger M . (1995). Transcriptional activation of the fra-1 gene by AP-1 is mediated by regulatory sequences in the first intron. Mol Cell Biol 15: 3748–3758.
Bozec A, Bakiri L, Hoebertz A, Eferl R, Schilling AF, Komnenovic V et al. (2008). Osteoclast size is controlled by Fra-2 through LIF/LIF-receptor signalling and hypoxia. Nature 454: 221–225.
Bozec A, Bakiri L, Jimenez M, Schinke T, Amling M, Wagner EF . (2010). Fra-2/AP-1 controls bone formation by regulating osteoblast differentiation and collagen production. J Cell Biol 190: 1093–1106.
Brehmer D, Greff Z, Godl K, Blencke S, Kurtenbach A, Weber M et al. (2005). Cellular targets of gefitinib. Cancer Res 65: 379–382.
Cohen MH, Williams GA, Sridhara R, Chen G, Pazdur R . (2003). FDA drug approval summary: gefitinib (ZD1839) (Iressa) tablets. Oncologist 8: 303–306.
De Marzo AM, Platz EA, Sutcliffe S, Xu J, Gronberg H, Drake CG et al. (2007). Inflammation in prostate carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 7: 256–269.
Eferl R, Hasselblatt P, Rath M, Popper H, Zenz R, Komnenovic V et al. (2008). Development of pulmonary fibrosis through a pathway involving the transcription factor Fra-2/AP-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 10525–10530.
Eferl R, Hoebertz A, Schilling AF, Rath M, Karreth F, Kenner L et al. (2004). The Fos-related antigen Fra-1 is an activator of bone matrix formation. EMBO J 23: 2789–2799.
Eferl R, Wagner EF . (2003). AP-1: a double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 3: 859–868.
Finzer P, Soto U, Delius H, Patzelt A, Coy JF, Poustka A et al. (2000). Differential transcriptional regulation of the monocyte-chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) gene in tumorigenic and non-tumorigenic HPV 18 positive cells: the role of the chromatin structure and AP-1 composition. Oncogene 19: 3235–3244.
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, Tamura T, Nakagawa K, Douillard JY et al. (2003). Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial). J Clin Oncol 21: 2237–2246.
Giaccone G, Herbst RS, Manegold C, Scagliotti G, Rosell R, Miller V et al. (2004). Gefitinib in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial--INTACT 1. J Clin Oncol 22: 777–784.
Guinea-Viniegra J, Zenz R, Scheuch H, Hnisz D, Holcmann M, Bakiri L et al. (2009). TNFα shedding and epidermal inflammation are controlled by Jun proteins. Genes Dev 23: 2663–2674.
Han J, Ulevitch RJ . (2005). Limiting inflammatory responses during activation of innate immunity. Nat Immunol 6: 1198–1205.
Inoue A, Saijo Y, Maemondo M, Gomi K, Tokue Y, Kimura Y et al. (2003). Severe acute interstitial pneumonia and gefitinib. Lancet 361: 137–139.
Ishii Y, Fujimoto S, Fukuda T . (2006). Gefitinib prevents bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174: 550–556.
Ishizaka A, Watanabe M, Yamashita T, Ogawa Y, Koh H, Hasegawa N et al. (2001). New bronchoscopic microsample probe to measure the biochemical constituents in epithelial lining fluid of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med 29: 896–898.
Jiang D, Liang J, Fan J, Yu S, Chen S, Luo Y et al. (2005). Regulation of lung injury and repair by Toll-like receptors and hyaluronan. Nat Med 11: 1173–1179.
Jochum W, David JP, Elliott C, Wutz A, Plenk Jr H, Matsuo K et al. (2000). Increased bone formation and osteosclerosis in mice overexpressing the transcription factor Fra-1. Nat Med 6: 980–984.
Johnson GB, Brunn GJ, Platt JL . (2004). Cutting edge: an endogenous pathway to systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)-like reactions through Toll-like receptor 4. J Immunol 172: 20–24.
Katzenstein AL, Myers JL . (1998). Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: clinical relevance of pathologic classification. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 157: 1301–1315.
Kawai T, Akira S . (2010). The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11: 373–384.
Kida H, Yoshida M, Hoshino S, Inoue K, Yano Y, Yanagita M et al. (2005). Protective effect of IL-6 on alveolar epithelial cell death induced by hydrogen peroxide. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288: L342–L349.
Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, Lynch Jr TJ, Prager D, Belani CP et al. (2003). Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA 290: 2149–2158.
Lee DH, Park K, Kim JH, Lee JS, Shin SW, Kang JH et al. (2010). Randomized phase III trial of gefitinib versus docetaxel in non-small cell lung cancer patients who have previously received platinum-based chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 16: 1307–1314.
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara S, Oizumi S, Isobe H et al. (2010). Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med 362: 2380–2388.
Matsuo K, Owens JM, Tonko M, Elliott C, Chambers TJ, Wagner EF . (2000). Fosl1 is a transcriptional target of c-Fos during osteoclast differentiation. Nat Genet 24: 184–187.
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N et al. (2009). Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361: 947–957.
Mollen KP, Anand RJ, Tsung A, Prince JM, Levy RM, Billiar TR . (2006). Emerging paradigm: toll-like receptor 4-sentinel for the detection of tissue damage. Shock 26: 430–437.
Morishita H, Saito F, Kayama H, Atarashi K, Kuwata H, Yamamoto M et al. (2009). Fra-1 negatively regulates lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammatory responses. Int Immunol 21: 457–465.
Paine III R, Rolfe MW, Standiford TJ, Burdick MD, Rollins BJ, Strieter RM . (1993). MCP-1 expression by rat type II alveolar epithelial cells in primary culture. J Immunol 150: 4561–4570.
Peters-Golden M, Thebert P . (1987). Inhibition by methylprednisolone of zymosan-induced leukotriene synthesis in alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis 135: 1020–1026.
Pircher A, Ploner F, Popper H, Hilbe W . (2010). Rationale of a relaunch of gefitinib in Caucasian non-small cell lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 69: 265–271.
Ray N, Kuwahara M, Takada Y, Maruyama K, Kawaguchi T, Tsubone H et al. (2006). c-Fos suppresses systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Int Immunol 18: 671–677.
Rollins BJ . (1997). Chemokines. Blood 90: 909–928.
Salojin KV, Owusu IB, Millerchip KA, Potter M, Platt KA, Oravecz T . (2006). Essential role of MAPK phosphatase-1 in the negative control of innate immune responses. J Immunol 176: 1899–1907.
Suzuki H, Aoshiba K, Yokohori N, Nagai A . (2003). Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition augments a murine model of pulmonary fibrosis. Cancer Res 63: 5054–5059.
Takada Y, Fang X, Jamaluddin MS, Boyd DD, Aggarwal BB . (2004). Genetic deletion of glycogen synthase kinase-3β abrogates activation of IκBα kinase, JNK, Akt, and p44/p42 MAPK but potentiates apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem 279: 39541–39554.
Takada Y, Ray N, Ikeda E, Kawaguchi T, Kuwahara M, Wagner EF et al. (2010). Fos proteins suppress dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis through inhibition of NF-κB. J Immunol 184: 1014–1021.
Tallquist MD, Soriano P . (2000). Epiblast-restricted Cre expression in MORE mice: a tool to distinguish embryonic vs. extra-embryonic gene function. Genesis 26: 113–115.
Toney LM, Cattoretti G, Graf JA, Merghoub T, Pandolfi PP, Dalla-Favera R et al. (2000). BCL-6 regulates chemokine gene transcription in macrophages. Nat Immunol 1: 214–220.
Ulich TR, Watson LR, Yin SM, Guo KZ, Wang P, Thang H et al. (1991). The intratracheal administration of endotoxin and cytokines. I. Characterization of LPS-induced IL-1 and TNF mRNA expression and the LPS-, IL-1-, and TNF-induced inflammatory infiltrate. Am J Pathol 138: 1485–1496.
Vogl T, Tenbrock K, Ludwig S, Leukert N, Ehrhardt C, van Zoelen MA et al. (2007). Mrp8 and Mrp14 are endogenous activators of Toll-like receptor 4, promoting lethal, endotoxin-induced shock. Nat Med 13: 1042–1049.
Watanabe M, Ishizaka A, Ikeda E, Ohashi A, Kobayashi K . (2003). Contributions of bronchoscopic microsampling in the supplemental diagnosis of small peripheral lung carcinoma. Ann Thorac Surg 76: 1668–1673.
Wolter S, Doerrie A, Weber A, Schneider H, Hoffmann E, von der Ohe J et al. (2008). c-Jun controls histone modifications, NF-κB recruitment and RNA polymerase II function to activate the ccl2 gene. Mol Cell Biol 28: 4407–4423.
Yamaguchi T, Takada Y, Maruyama K, Shimoda K, Arai Y, Nango N et al. (2009). Fra-1/AP-1 impairs inflammatory responses and chondrogenesis in fracture healing. J Bone Miner Res 24: 2056–2065.
Zenz R, Eferl R, Kenner L, Florin L, Hummerich L, Mehic D et al. (2005). Psoriasis-like skin disease and arthritis caused by inducible epidermal deletion of Jun proteins. Nature 437: 369–375.
Zhang Q, Adiseshaiah P, Kalvakolanu DV, Reddy SP . (2006). A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-regulated Akt-independent signaling promotes cigarette smoke-induced FRA-1 expression. J Biol Chem 281: 10174–10181.
Zhao C, Irie N, Takada Y, Shimoda K, Miyamoto T, Nishiwaki T et al. (2006). Bidirectional ephrinB2-EphB4 signaling controls bone homeostasis. Cell Metab 4: 111–121.
Acknowledgements
We thank A Oide, M Asakawa and S Fukuse for technical support; T Yamaguchi for Fra-1 mouse maintenance; A Dent, A Ueda and M Busslinger for plasmids; H Daub for AX14596; and H Handa, S Sakamoto, K Maruyama, T Mitsudomi and L Bakiri for helpful input. We thank the Core Instrumentation Facility, Keio University School of Medicine, for technical assistance. This work was funded by a grant-in-aid from the global COE program, a grant-in-aid for Scientific Research (B) from MEXT of Japan (21390425), and a grant-in-aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas and the Naito Foundation (YT). LG was funded by an EMBO Long-Term Fellowship. IMP is funded by Boehringer Ingelheim.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takada, Y., Gresh, L., Bozec, A. et al. Interstitial lung disease induced by gefitinib and Toll-like receptor ligands is mediated by Fra-1. Oncogene 30, 3821–3832 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.101
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.101