Abstract
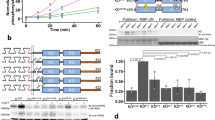
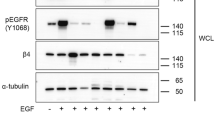
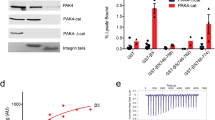
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) has a crucial role in integration of signals from integrins and growth factor receptors. In this study, we demonstrate that growth factor receptors including hepatocyte growth factor receptor Met, epidermal growth factor receptor, and platelet-derived growth factor receptor directly phosphorylate FAK on Tyr194 in the FERM domain (band 4.1 and ezrin/radixin/moesin homology domain). Upon binding to Met or phosphoinositides, FAK may undergo conformational changes, which renders Tyr194 accessible for phosphorylation. Substitution of Tyr194 with Phe significantly suppresses the activation of FAK by Met. In contrast, substitution of Tyr194 with Glu (Y194E substitution) leads to constitutive activation of FAK. The phosphorylation of FAK on Tyr194 may cause conformational changes in the FERM domain, which disrupts the intramolecular inhibitory interaction between the FERM and kinase domains of FAK. Moreover, substitution of the basic residues in the 216KAKTLRK222 patch in the FERM domain with Ala antagonizes the effect of the Y194E substitution on FAK activation, thus suggesting that the interactions between the phosphorylated Tyr194 and the basic resides in the 216KAKTLRK222 patch may allow FAK to be activated through relief of its autoinhibition. Collectively, this study provides the first example to explain how FAK is activated by receptor tyrosine kinases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai X, Lietha D, Ceccarelli DF, Karginov AV, Rajfur Z, Jacobson K et al. (2008). Spatial and temporal regulation of focal adhesion kinase activity in living cells. Mol Cell Biol 28: 201–214.
Calalb MB, Polte TR, Hanks SK . (1995). Tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase at sites in the catalytic domain regulates kinase activity: a role for Src family kinases. Mol Cell Biol 15: 954–963.
Chan PC, Liang CC, Yu KC, Chang MC, Ho WL, Chen BH et al. (2002). Synergistic effect of focal adhesion kinase overexpression and hepatocyte growth factor stimulation on cell transformation. J Biol Chem 277: 50373–50379.
Chen HC, Chan PC, Tang MJ, Cheng CH, Chang TJ . (1998). Tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase stimulated by hepatocyte growth factor leads to mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem 273: 25777–25782.
Chen LM, Bailey D, Fernandez-Valle C . (2000). Association of beta 1 integrin with focal adhesion kinase and paxillin in differentiating Schwann cells. J Neurosci 20: 3776–3784.
Chen R, Kim O, Li M, Xiong X, Guan JL, Kung HJ et al. (2001). Regulation of the PH-domain-containing tyrosine kinase Etk by focal adhesion kinase through the FERM domain. Nat Cell Biol 3: 439–444.
Chen SY, Chen HC . (2006). Direct interaction of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) with Met is required for FAK to promote hepatocyte growth factor-induced cell invasion. Mol Cell Biol 26: 5155–5167.
Cobb BS, Schaller MD, Leu TH, Parsons JT . (1994). Stable association of pp60src and pp59fyn with the focal adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase, pp125FAK. Mol Cell Biol 14: 147–155.
Cohen LA, Guan JL . (2005). Residues within the first subdomain of the FERM-like domain in focal adhesion kinase are important in its regulation. J Biol Chem 280: 8197–8207.
Cooper LA, Shen TL, Guan JL . (2003). Regulation of focal adhesion kinase by its amino-terminal domain through an autoinhibitory interaction. Mol Cell Biol 23: 8030–8041.
Dunty JM, Gabarra-Niecko V, King ML, Ceccarelli DF, Eck MJ, Schaller MD . (2004). FERM domain interaction promotes FAK signaling. Mol Cell Biol 24: 5353–5368.
Eide BL, Turck CW, Escobedo JA . (1995). Identification of Tyr-397 as the primary site of tyrosine phosphorylation and pp60src association in the focal adhesion kinase, pp125FAK. Mol Cell Biol 15: 2819–2827.
Guan JL, Shalloway D . (1992). Regulation of focal adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase by both cellular adhesion and oncogenic transformation. Nature 358: 690–692.
Hanks SK, Calalb MB, Harper MC, Patel SK . (1992). Focal adhesion protein-tyrosine kinase phosphorylated in response to cell attachment to fibronectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 8487–8489.
Hildebrand JD, Schaller MD, Parsons JT . (1993). Identification of sequences required for the efficient localization of the focal adhesion kinase, pp125FAK, to cellular focal adhesions. J Cell Biol 123: 993–1005.
Jácamo RO, Rozengurt E . (2005). A truncated FAK lacking the FERM domain displays high catalytic activity but retains responsiveness to adhesion-mediated signals. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334: 1299–1304.
Lai JF, Kao SC, Jiang ST, Tang MJ, Chan PC, Chen HC . (2000). Involvement of focal adhesion kinase in hepatocyte growth factor-induced scatter of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Biol Chem 275: 7474–7480.
Lehr S, Kotzka J, Herkner A, Klein E, Siethoff C, Knebel B et al. (1999). Identification of tyrosine phosphorylation sites in human Gab-1 protein by EGF receptor kinase in vitro. Biochemistry 38: 151–159.
Lehr S, Kotzka J, Herkner A, Sikmann A, Meyer HE, Krone W et al. (2000). Identification of major tyrosine phosphorylation sites in the human insulin receptor substrate Gab-1 by insulin receptor kinase in vitro. Biochemistry 39: 10898–10907.
Lietha D, Cai X, Ceccarelli DF, Li Y, Schaller MD, Eck MJ . (2007). Structural basis for the autoinhibition of focal adhesion kinase. Cell 129: 1177–1187.
Matsumoto K, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Kramer RH . (1994). Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor induces tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK) and promotes migration and invasion by oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 269: 31807–31813.
McLean GW, Carragher NO, Avizienyte E, Evans J, Brunton VG, Frame MC . (2005). The Role of focal adhesion kinase in cancer—a new therapeutic opportunity. Nat Rev Cancer 5: 505–515.
Mitra SK, Hanson DA, Schlaepfer DD . (2005). Focal adhesion kinase: in command and control of cell motility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6: 56–68.
Poullet P, Gautreau A, Kadare G, Girault JA, Louvard D, Arpin M . (2001). Ezrin interacts with focal adhesion kinase and induces its activation independently of cell-matrix adhesion. J Biol Chem 276: 37686–37691.
Rankin S, Rozengurt E . (1994). Platelet-derived growth factor modulation of focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK) and paxillin tyrosine phosphorylation in Swiss 3T3 cells. Bell-shaped dose response and cross-talk with bombesin. J Biol Chem 269: 704–710.
Schaller MD, Borgman CA, Cobb BS, Vines RR, Reynold AB, Parsons JT . (1992). pp125FAK a structurally distinctive protein-tyrosine kinase associated with focal adhesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 5192–5196.
Schaller MD, Hindebrand JD, Shannon JD, Fox JX, Vines RR, Parsons JT . (1994). Autophosphorylation of the focal adhesion kinase, pp125FAK, directs SH2-dependent binding of pp60src. Mol Cell Biol 14: 1680–1688.
Schaller MD, Otey CA, Hildebrand JD, Parsons JT . (1995). Focal adhesion kinase and paxillin bind to peptides mimicking beta integrin cytoplasmic domains. J Cell Biol 130: 1181–1187.
Serrels B, Serrels A, Brunton VG, Holt M, McLean GW, Gray CH et al. (2007). Focal adhesion kinase controls actin assembly via a FERM-mediated interaction with the Arp2/3 complex. Nat Cell Biol 9: 1046–1056.
Sieg DJ, Hauck CR, Ilic D, Klingbeil CK, Schaefer E, Damsky CH et al. (2000). FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration. Nat Cell Biol 2: 249–256.
Xing Z, Chen HC, Nowlen JK, Taylor SJ, Shalloway D, Guan JL . (1994). Direct interaction of v-Src with the focal adhesion kinase mediated by the Src SH2 domain. Mol Biol Cell 5: 413–421.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Grants NSC97-3112-B-005-001 and NSC97-2628-B-005-001-MY3 from the National Science Council, Taiwan and NHRI-EX97-9730BI from the National Health Research Institutes, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, TH., Chan, PC., Chen, CL. et al. Phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase on tyrosine 194 by Met leads to its activation through relief of autoinhibition. Oncogene 30, 153–166 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.398
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.398
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Focal adhesion kinase: from biological functions to therapeutic strategies
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2023)
-
EGFRvIII-mediated transactivation of receptor tyrosine kinases in glioma: mechanism and therapeutic implications
Oncogene (2015)