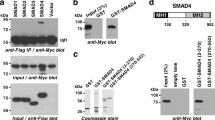
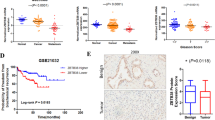
Abstract
The forced overexpression of c-Myc in mouse prostate and in normal human prostate epithelial cells results in tumor transformation with an invasive phenotype. How c-Myc regulates cell invasion is poorly understood. In this study, we have investigated the interplay of c-Myc and androgens in the regulation of prostate cancer cell invasion. We found that c-Myc induces cell invasion and anchorage-independent growth by regulating ezrin protein expression in the presence of androgens. The activity of the ezrin promoter is controlled by androgens through c-Myc, which binds to a phylogenetically conserved E-Box located in the proximal promoter region. Besides, we also show that ezrin is an important regulator of c-Myc protein levels. These effects are achieved through androgen-induced changes in ezrin phosphorylation, which results in the regulation of downstream signals. These downstream signals involve the modulation of Akt and GSK-3β activity resulting in increased c-Myc protein synthesis and inhibition of its degradation. In summary, we have shown a key role for ezrin as a mediator of c-Myc-induced tumorigenesis in prostate cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amir AL, Barua M, McKnight NC, Cheng S, Yuan X, Balk SP . (2003). A direct beta-catenin-independent interaction between androgen receptor and T cell factor 4. J Biol Chem 278: 30828–30834.
Asano T, Yao Y, Zhu J, Li D, Abbruzzese JL, Reddy SA . (2004). The PI 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway is activated due to aberrant Pten expression and targets transcription factors NF-kappaB and c-Myc in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 23: 8571–8580.
Bernard D, Pourtier-Manzanedo A, Gil J, Beach DH . (2003). Myc confers androgen-independent prostate cancer cell growth. J Clin Invest 112: 1724–1731.
Bonaccorsi L, Carloni V, Muratori M, Salvadori A, Giannini A, Carini M et al. (2000). Androgen receptor expression in prostate carcinoma cells suppresses alpha6beta4 integrin-mediated invasive phenotype. Endocrinology 141: 3172–3182.
Bouchard C, Staller P, Eilers M . (1998). Control of cell proliferation by Myc. Trends Cell Biol 8: 202–206.
Chuan YC, Pang ST, Cedazo-Minguez A, Norstedt G, Pousette A, Flores-Morales A . (2006). Androgen induction of prostate cancer cell invasion is mediated by ezrin. J Biol Chem 281: 29938–29948.
D'Angelo R, Aresta S, Blangy A, Del Maestro L, Louvard D, Arpin M . (2007). Interaction of ezrin with the novel guanine nucleotide exchange factor PLEKHG6 promotes RhoG-dependent apical cytoskeleton rearrangements in epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell 18: 4780–4793.
Feldman BJ, Feldman D . (2001). The development of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 1: 34–45.
Fievet BT, Gautreau A, Roy C, Del Maestro L, Mangeat P, Louvard D et al. (2004). Phosphoinositide binding and phosphorylation act sequentially in the activation mechanism of ezrin. J Cell Biol 164: 653–659.
Gautreau A, Louvard D, Arpin M . (2000). Morphogenic effects of ezrin require a phosphorylation-induced transition from oligomers to monomers at the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol 150: 193–203.
Gautreau A, Poullet P, Louvard D, Arpin M . (1999). Ezrin, a plasma membrane-microfilament linker, signals cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 7300–7305.
Gil J, Kerai P, Lleonart M, Bernard D, Cigudosa JC, Peters G et al. (2005). Immortalization of primary human prostate epithelial cells by c-Myc. Cancer Res 65: 2179–2185.
Graff JR, Konicek BW, McNulty AM, Wang Z, Houck K, Allen S et al. (2000). Increased AKT activity contributes to prostate cancer progression by dramatically accelerating prostate tumor growth and diminishing p27Kip1 expression. J Biol Chem 275: 24500–24505.
Greenhalgh CJ, Metcalf D, Thaus AL, Corbin JE, Uren R, Morgan PO et al. (2002). Biological evidence that SOCS-2 can act either as an enhancer or suppressor of growth hormone signaling. J Biol Chem 277: 40181–40184.
Hellerstedt BA, Pienta KJ . (2003). The truth is out there: an overall perspective on androgen deprivation. Urol Oncol 21: 272–281.
Jenkins RB, Qian J, Lieber MM, Bostwick DG . (1997). Detection of c-myc oncogene amplification and chromosomal anomalies in metastatic prostatic carcinoma by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cancer Res 57: 524–531.
Joshua AM, Evans A, Van der Kwast T, Zielenska M, Meeker AK, Chinnaiyan A et al. (2007). Prostatic preneoplasia and beyond. Biochim Biophys Acta.
Lapointe J, Li C, Giacomini CP, Salari K, Huang S, Wang P et al. (2007). Genomic profiling reveals alternative genetic pathways of prostate tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 67: 8504–8510.
Liao X, Thrasher JB, Holzbeierlein J, Stanley S, Li B . (2004). Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta activity is required for androgen-stimulated gene expression in prostate cancer. Endocrinology 145: 2941–2949.
Liu J, Levens D . (2006). Making myc. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 302: 1–32.
Murillo H, Huang H, Schmidt LJ, Smith DI, Tindall DJ . (2001). Role of PI3K signaling in survival and progression of LNCaP prostate cancer cells to the androgen refractory state. Endocrinology 142: 4795–4805.
O'Sullivan AC, Sullivan GJ, McStay B . (2002). UBF binding in vivo is not restricted to regulatory sequences within the vertebrate ribosomal DNA repeat. Mol Cell Biol 22: 657–668.
Pang ST, Dillner K, Wu X, Pousette A, Norstedt G, Flores-Morales A . (2002). Gene expression profiling of androgen deficiency predicts a pathway of prostate apoptosis that involves genes related to oxidative stress. Endocrinology 143: 4897–4906.
Pang ST, Fang X, Valdman A, Norstedt G, Pousette A, Egevad L et al. (2004a). Expression of ezrin in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Urology 63: 609–612.
Pang ST, Flores-Morales A, Skoog L, Chuan YC, Nordstedt G, Pousette A . (2004b). Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 13 expression by androgen in prostate cancer. Oncol Rep 11: 1187–1192.
Prag S, Parsons M, Keppler MD, Ameer-Beg SM, Barber P, Hunt J et al. (2007). Activated ezrin promotes cell migration through recruitment of the GEF Dbl to lipid rafts and preferential downstream activation of Cdc42. Mol Biol Cell 18: 2935–2948.
Sadi MV, Barrack ER . (1991). Determination of growth fraction in advanced prostate cancer by Ki-67 immunostaining and its relationship to the time to tumor progression after hormonal therapy. Cancer 67: 3065–3071.
Sawyer TK . (2004). Cancer metastasis therapeutic targets and drug discovery: emerging small-molecule protein kinase inhibitors. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 13: 1–19.
Sears R, Nuckolls F, Haura E, Taya Y, Tamai K, Nevins JR . (2000). Multiple Ras-dependent phosphorylation pathways regulate Myc protein stability. Genes Dev 14: 2501–2514.
Shi Y, Sharma A, Wu H, Lichtenstein A, Gera J . (2005). Cyclin D1 and c-myc internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-dependent translation is regulated by AKT activity and enhanced by rapamycin through a p38 MAPK- and ERK-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 280: 10964–10973.
Sun J, Liu W, Adams TS, Sun J, Li X, Turner AR et al. (2007). DNA copy number alterations in prostate cancers: a combined analysis of published CGH studies. Prostate 67: 692–700.
Sun M, Yang L, Feldman RI, Sun XM, Bhalla KN, Jove R et al. (2003). Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway by androgen through interaction of p85alpha, androgen receptor, and Src. J Biol Chem 278: 42992–43000.
Taichman RS, Loberg RD, Mehra R, Pienta KJ . (2007). The evolving biology and treatment of prostate cancer. J Clin Invest 117: 2351–2361.
Valdman A, Fang X, Pang ST, Nilsson B, Ekman P, Egevad L . (2005). Ezrin expression in prostate cancer and benign prostatic tissue. Eur Urol 48: 852–857.
Vidal OM, Merino R, Rico-Bautista E, Fernandez-Perez L, Chia DJ, Woelfle J et al. (2007). In vivo transcript profiling and phylogenetic analysis identifies suppressor of cytokine signaling 2 as a direct signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b target in liver. Mol Endocrinol 21: 293–311.
Vlietstra RJ, van Alewijk DC, Hermans KG, van Steenbrugge GJ, Trapman J . (1998). Frequent inactivation of PTEN in prostate cancer cell lines and xenografts. Cancer Res 58: 2720–2723.
Wan X, Mendoza A, Khanna C, Helman LJ . (2005). Rapamycin inhibits ezrin-mediated metastatic behavior in a murine model of osteosarcoma. Cancer Res 65: 2406–2411.
Wang S, Gao J, Lei Q, Rozengurt N, Pritchard C, Jiao J et al. (2003). Prostate-specific deletion of the murine Pten tumor suppressor gene leads to metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 4: 209–221.
Williams K, Fernandez S, Stien X, Ishii K, Love HD, Lau YF et al. (2005). Unopposed c-MYC expression in benign prostatic epithelium causes a cancer phenotype. Prostate 63: 369–384.
Wu YM, Robinson DR, Kung HJ . (2004). Signal pathways in up-regulation of chemokines by tyrosine kinase MER/NYK in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 64: 7311–7320.
Acknowledgements
We thank Maria Henriksson for providing the c-Myc expression plasmid. The work carried out in this study was in part supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Protein Research, Karolinska Institutet, Cancerfonden (45576-B01-01XAB), Swedish Research Council (VR- 529-2002-6766) and the Robert Lundberg Memorial Foundation (2007Lund0045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chuan, YC., Iglesias-Gato, D., Fernandez-Perez, L. et al. Ezrin mediates c-Myc actions in prostate cancer cell invasion. Oncogene 29, 1531–1542 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.442
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.442
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Dissecting transcription of the 8q24-MYC locus in prostate cancer recognizes the equilibration between androgen receptor direct and indirect dual-functions
Journal of Translational Medicine (2023)
-
Nuclear factor IX promotes glioblastoma development through transcriptional activation of Ezrin
Oncogenesis (2020)
-
microRNA-211 regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration/invasion in human osteosarcoma via targeting EZRIN
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019)
-
Ezrin promotes breast cancer progression by modulating AKT signals
British Journal of Cancer (2019)
-
A glimpse of the ERM proteins
Journal of Biomedical Science (2016)