Abstract
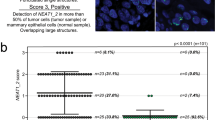
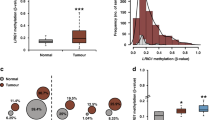
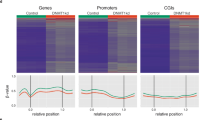
Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) is both a candidate oncogene and a candidate tumour suppressor gene. It not only encodes the heregulins and other mitogenic ligands for the ERBB family, but also causes apoptosis in NRG1-expressing cells. We found that most breast cancer cell lines had reduced or undetectable expression of NRG1. This included cell lines that had translocation breaks in the gene. Similarly, expression in cancers was generally comparable to or less than that in various normal breast samples. Many non-expressing cell lines had extensive methylation of the CpG island at the principal transcription start site at exon 2 of NRG1. Expression was reactivated by demethylation. Many tumours also showed methylation, whereas normal mammary epithelial fragments had none. Lower NRG1 expression correlated with higher methylation. Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated depletion of NRG1 increased net proliferation in a normal breast cell line and a breast cancer cell line that expressed NRG1. The short arm of chromosome 8 is frequently lost in epithelial cancers, and NRG1 is the most centromeric gene that is always affected. NRG1 may therefore be the major tumour suppressor gene postulated to be on 8p: it is in the correct location, is antiproliferative and is silenced in many breast cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adélaïde J, Huang HE, Murati A, Alsop AE, Orsetti B, Mozziconacci MJ et al. (2003). A recurrent chromosome translocation breakpoint in breast and pancreatic cancer cell lines targets the neuregulin/NRG1 gene. Gene Chromosome Canc 37: 333–345.
Agrelo R, Cheng WH, Setien F, Ropero S, Espada J, Fraga MF et al. (2006). Epigenetic inactivation of the premature aging Werner syndrome gene in human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 8822–8827.
Aguilar Z, Akita RW, Finn RS, Ramos BL, Pegram MD, Kabbinavar FF et al. (1999). Biologic effects of heregulin/neu differentiation factor on normal and malignant human breast and ovarian epithelial cells. Oncogene 18: 6050–6062.
Amin DN, Tuck D, Stern DF . (2005). Neuregulin-regulated gene expression in mammary carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res 309: 12–23.
Birnbaum D, Adélaïde J, Popovici C, Charafe-Jauffret E, Mozziconacci MJ, Chaffanet M . (2003). Chromosome arm 8p and cancer: a fragile hypothesis. Lancet Oncol 4: 639–642.
Bradbury JM, Arno J, Edwards PA . (1993). Induction of epithelial abnormalities that resemble human breast lesions by the expression of the neu/erbB-2 oncogene in reconstituted mouse mammary gland. Oncogene 8: 1551–1558.
Briand P, Petersen OW, Van Deurs B . (1987). A new diploid nontumorigenic human breast epithelial cell line isolated and propagated in chemically defined medium. In vitro Cell Dev Biol 23: 181–188.
Britsch S . (2007). The neuregulin-I/ErbB signaling system in development and disease. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 190: 1–65.
Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R . (2002). Stable suppression of tumorigenicity by virus-mediated RNA interference. Cancer Cell 2: 243–247.
Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C, Monville F, Finetti P, Adelaïde J, Cervera N et al. (2006). Gene expression profiling of breast cell lines identifies potential new basal markers. Oncogene 25: 2273–2284.
Chin SF, Teschendorff AE, Marioni JC, Wang Y, Barbosa-Morais NL, Thorne NP et al. (2007). High-resolution aCGH and expression profiling identifies a novel genomic subtype of ER negative breast cancer. Genome Biol 8: R215.
Ching TT, Maunakea AK, Jun P, Hong C, Zardo G, Pinkel D et al. (2005). Epigenome analyses using BAC microarrays identify evolutionary conservation of tissue-specific methylation of SHANK3. Nat Genet 37: 645–651.
Clarke C, Sandle J, Lakhani SR . (2005). Myoepithelial cells: pathology, cell separation and markers of myoepithelial differentiation. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 10: 273–280.
Cooke SL, Pole JCM, Chin S-F, Ellis IO, Caldas C, Edwards PAW . (2008). High-resolution array CGH clarifies events occurring on 8p in carcinogenesis. BMC Cancer 8: 288.
Crabbe L, Jauch A, Naeger CM, Holtgreve-Grez H, Karlseder J . (2007). Telomere dysfunction as a cause of genomic instability in Werner syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 2205–2210.
Deadwyler GD, Pouly S, Antel JP, Devries GH . (2000). Neuregulins and erbB receptor expression in adult human oligodendrocytes. Glia 32: 304–312.
Edwards PA, Brooks IM, Bunnage HJ, Foster AV, Ellison ML, O'Hare MJ . (1986). Clonal analysis of expression of epithelial antigens in cultures of normal human breast. J Cell Sci 80: 91–101.
Falls DL . (2003). Neuregulins: functions, forms, and signaling strategies. Exp Cell Res 284: 14–30.
Garcia MJ, Pole JC, Chin SF, Teschendorff A, Naderi A, Ozdag H et al. (2005). A 1 Mb minimal amplicon at 8p11–12 in breast cancer identifies new candidate oncogenes. Oncogene 24: 5235–5245.
Grigoriadis A, Mackay A, Reis-Filho JS, Steele D, Iseli C, Stevenson BJ et al. (2006). Establishment of the epithelial-specific transcriptome of normal and malignant human breast cells based on MPSS and array expression data. Breast Cancer Res 8: R56.
Grimm S, Leder P . (1997). An apoptosis-inducing isoform of neu differentiation factor (NDF) identified using a novel screen for dominant, apoptosis-inducing genes. J Exp Med 185: 1137–1142.
Grimm S, Weinstein EJ, Krane IM, Leder P . (1998). Neu differentiation factor (NDF), a dominant oncogene, causes apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med 188: 1535–1539.
Hayes NV, Gullick WJ . (2008). The neuregulin family of genes and their multiple splice variants in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 13: 205–214.
Huang HE, Chin SF, Ginestier C, Bardou VJ, Adélaïde J, Iyer NG et al. (2004). A recurrent chromosome breakpoint in breast cancer at the NRG1/neuregulin 1/heregulin gene. Cancer Res 64: 6840–6844.
Iyer NG, Chin SF, Ozdag H, Daigo Y, Hu DE, Cariati M . (2004). p300 regulates p53-dependent apoptosis after DNA damage in colorectal cancer cells by modulation of PUMA/p21 levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 7386–7391.
Jones FE, Jerry DJ, Guarino BC, Andrews GC, Stern DF . (1996). Heregulin induces in vivo proliferation and differentiation of mammary epithelium into secretory lobuloalveoli. Cell Growth Differ 7: 1031–1038.
Kalirai H, Clarke RB . (2006). Human breast epithelial stem cells and their regulation. J Pathol 208: 7–16.
Li L, Cleary S, Mandarano MA, Long W, Birchmeier C, Jones FE . (2002). The breast proto-oncogene, HRGalpha regulates epithelial proliferation and lobuloalveolar development in the mouse mammary gland. Oncogene 21: 4900–4907.
Liu X, Baker E, Eyre HJ, Sutherland GR, Zhou M . (1999). Gamma-heregulin: a fusion gene of DOC-4 and neuregulin-1 derived from a chromosome translocation. Oncogene 18: 7110–7114.
Muraoka-Cook RS, Caskey LS, Sandahl MA, Hunter DM, Husted C, Strunk KE et al. (2006). Heregulin-dependent delay in mitotic progression requires HER4 and BRCA1. Mol Cell Biol 26: 6412–6424.
Muraoka-Cook RS, Feng SM, Strunk KE, Earp HS . (2008). ErbB4/HER4: role in mammary gland development, differentiation and growth inhibition. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 13: 235–246.
Naderi A, Teschendorff AE, Beigel J, Cariati M, Ellis IO, Brenton JD et al. (2007). BEX2 is overexpressed in a subset of primary breast cancers and mediates nerve growth factor/nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition of apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 67: 6725–6736.
Neve RM, Chin K, Fridlyand J, Yeh J, Baehner FL, Fevr T et al. (2006). A collection of breast cancer cell lines for the study of functionally distinct cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 10: 515–527.
Pole JC, Courtay-Cahen C, Garcia MJ, Blood KA, Cooke SL, Alsop AE et al. (2006). High-resolution analysis of chromosome rearrangements on 8p in breast, colon and pancreatic cancer reveals a complex pattern of loss, gain and translocation. Oncogene 25: 5693–5706.
Prentice LM, Shadeo A, Lestou VS, Miller MA, deLeeuw RJ, Makretsov N et al. (2005). NRG1 gene rearrangements in clinical breast cancer: identification of an adjacent novel amplicon associated with poor prognosis. Oncogene 24: 7281–7289.
Rakyan VK, Down TA, Thorne NP, Flicek P, Kulesha E, Gräf S et al. (2008). An integrated resource for genome-wide identification and analysis of human tissue-specific differentially methylated regions (tDMRs). Genome Res 18: 1518–1529.
Schaefer G, Fitzpatrick VD, Sliwkowski MX . (1997). Gamma-heregulin: a novel heregulin isoform that is an autocrine growth factor for the human breast cancer cell line, MDA-MB-175. Oncogene 15: 1385–1394.
Stamps AC, Davies SC, Burman J, O'Hare MJ . (1994). Analysis of proviral integration in human mammary epithelial cell lines immortalized by retroviral infection with a temperature-sensitive SV40 T-antigen construct. Int J Cancer 57: 865–874.
Steinthorsdottir V, Stefansson H, Ghosh S, Birgisdottir B, Bjornsdottir S, Fasquel AC et al. (2004). Multiple novel transcription initiation sites for NRG1. Gene 342: 97–105.
Sundvall M, Iljin K, Kilpinen S, Sara H, Kallioniemi OP, Elenius K . (2008). Role of ErbB4 in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 13: 259–268.
Takizawa T, Nakashima K, Namihira M, Ochiai W, Uemura A, Yanagisawa M et al. (2001). DNA methylation is a critical cell-intrinsic determinant of astrocyte differentiation in the fetal brain. Dev Cell 1: 749–758.
Vermeer PD, Einwalter LA, Moninger TO, Rokhlina T, Kern JA, Zabner J et al. (2003). Segregation of receptor and ligand regulates activation of epithelial growth factor receptor. Nature 422: 322–326.
Wang XZ, Jolicoeur EM, Conte N, Chaffanet M, Zhang Y, Mozziconacci MJ et al. (1999). gamma-heregulin is the product of a chromosomal translocation fusing the DOC4 and HGL/NRG1 genes in the MDA-MB-175 breast cancer cell line. Oncogene 18: 5718–5721.
Weinstein EJ, Grimm S, Leder P . (1998). The oncogene heregulin induces apoptosis in breast epithelial cells and tumors. Oncogene 17: 2107–2113.
Weinstein EJ, Leder P . (2000). The extracellular region of heregulin is sufficient to promote mammary gland proliferation and tumorigenesis but not apoptosis. Cancer Res 60: 3856–3861.
Yang AS, Estécio MR, Doshi K, Kondo Y, Tajara EH, Issa JP . (2004). A simple method for estimating global DNA methylation using bisulfite PCR of repetitive DNA elements. Nucleic Acids Res 32: e38.
Yang Y, Spitzer E, Meyer D, Sachs M, Niemann C, Hartmann G et al. (1995). Sequential requirement of hepatocyte growth factor and neuregulin in the morphogenesis and differentiation of the mammary gland. J Cell Biol 131: 215–226.
Acknowledgements
We thank Huai-En Huang for some exploratory expression analysis. This study was funded principally by the Breast Cancer Campaign and also by Cancer Research UK, Hutchison-Whampoa Ltd. (who endowed the buildings in which the work was done) and the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chua, Y., Ito, Y., Pole, J. et al. The NRG1 gene is frequently silenced by methylation in breast cancers and is a strong candidate for the 8p tumour suppressor gene. Oncogene 28, 4041–4052 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.259
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.259
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Epigenetic regulation of Neuregulin 1 promotes breast cancer progression associated to hyperglycemia
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Exploring the Binding Mechanism of NRG1–ERBB3 Complex and Discovery of Potent Natural Products to Reduce Diabetes-Assisted Breast Cancer Progression
Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational Life Sciences (2023)
-
The impact of NRG1 expressions and methylation on multifactorial Hirschsprung disease
BMC Pediatrics (2022)
-
Genetic alteration of Chinese patients with rectal mucosal melanoma
BMC Cancer (2021)
-
NRG1 fusions in breast cancer
Breast Cancer Research (2021)