Abstract
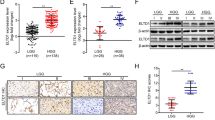
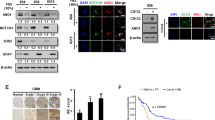
Eph receptors, the largest subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases, and their ephrin ligands play important roles in nervous system development. Recently, they have been implicated in tumorigenesis of different cancers. In this study, we showed that the expression of ephrinA5 was dramatically downregulated in primary gliomas compared with normal tissues. Forced expression of ephrinA5 reduced tumorigenicity of human glioma U373 cells. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which frequently acts as an oncoprotein in glioma, was greatly decreased in ephrinA5-transfected glioma cells, and the two molecules exhibited a mutually exclusive expression pattern in primary glioma samples. We found that ephrinA5 enhanced c-Cbl binding to EGFR, thus promoted ubiquitylation and degradation of the receptor. Either ephrinA5-Fc or EphA2-Fc treatment simulating bidirectional signaling of Eph/ephrin system resulted in EGFR decrease. This study discovered that ephrinA5 acted as a tumor suppressor in glioma, and its negative regulation of EGFR contributed to the suppressive effects. In addition to identifying a novel mechanism underlying tumor suppressor activity of ephrinA5, we also showed cross-talk between different receptor tyrosine kinase families in glioma. These findings may improve therapeutic strategies for glioma.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolz J, Uziel D, Muhlfriedel S, Gullmar A, Peuckert C, Zarbalis K et al. (2004). Multiple roles of ephrins during the formation of thalamocortical projections: maps and more. J Neurobiol 59: 82–94.
Bordier C . (1981). Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem 256: 1604–1607.
Brantley-Sieders DM, Fang WB, Hwang Y, Hicks D, Chen J . (2006). Ephrin-A1 facilitates mammary tumor metastasis through an angiogenesis-dependent mechanism mediated by EphA receptor and vascular endothelial growth factor in mice. Cancer Res 66: 10315–10324.
Davy A, Gale NW, Murray EW, Klinghoffer RA, Soriano P, Feuerstein C et al. (1999). Compartmentalized signaling by GPI-anchored ephrin-A5 requires the Fyn tyrosine kinase to regulate cellular adhesion. Genes Dev 13: 3125–3135.
Deng YZ, Chen PP, Wang Y, Yin D, Koeffler HP, Li B et al. (2007). Connective tissue growth factor is overexpressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and promotes tumorigenicity through beta-catenin-T-cell factor/Lef signaling. J Biol Chem 282: 36571–36581.
Finne EF, Munthe E, Aasheim HC . (2004). A new ephrin-A1 isoform (ephrin-A1b) with altered receptor binding properties abrogates the cleavage of ephrin-A1a. Biochem J 379: 39–46.
Gale NW, Holland SJ, Valenzuela DM, Flenniken A, Pan L, Ryan TE et al. (1996). Eph receptors and ligands comprise two major specificity subclasses and are reciprocally compartmentalized during embryogenesis. Neuron 17: 9–19.
Grossmann AH, Kolibaba KS, Willis SG, Corbin AS, Langdon WS, Deininger MW et al. (2004). Catalytic domains of tyrosine kinases determine the phosphorylation sites within c-Cbl. FEBS Lett 577: 555–562.
Hafner C, Schmitz G, Meyer S, Bataille F, Hau P, Langmann T et al. (2004). Differential gene expression of Eph receptors and ephrins in benign human tissues and cancers. Clin Chem 50: 490–499.
Halatsch ME, Schmidt U, Behnke-Mursch J, Unterberg A, Wirtz CR . (2006). Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition for the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme and other malignant brain tumours. Cancer Treat Rev 32: 74–89.
Herath NI, Spanevello MD, Sabesan S, Newton T, Cummings M, Duffy S et al. (2006). Over-expression of Eph and ephrin genes in advanced ovarian cancer: ephrin gene expression correlates with shortened survival. BMC Cancer 6: 144.
Huberman AD, Murray KD, Warland DK, Feldheim DA, Chapman B . (2005). Ephrin-As mediate targeting of eye-specific projections to the lateral geniculate nucleus. Nat Neurosci 8: 1013–1021.
Joazeiro CA, Wing SS, Huang H, Leverson JD, Hunter T, Liu YC . (1999). The tyrosine kinase negative regulator c-Cbl as a RING-type, E2-dependent ubiquitin-protein ligase. Science 286: 309–312.
Kuijper S, Turner CJ, Adams RH . (2007). Regulation of angiogenesis by Eph-ephrin interactions. Trends Cardiovasc Med 17: 145–151.
Larsen AB, Pedersen MW, Stockhausen MT, Grandal MV, van Deurs B, Poulsen HS . (2007). Activation of the EGFR gene target EphA2 inhibits epidermal growth factor-induced cancer cell motility. Mol Cancer Res 5: 283–293.
Levkowitz G, Waterman H, Ettenberg SA, Katz M, Tsygankov AY, Alroy I et al. (1999). Ubiquitin ligase activity and tyrosine phosphorylation underlie suppression of growth factor signaling by c-Cbl/Sli-1. Mol Cell 4: 1029–1040.
Li Z, Dong T, Proschel C, Noble M . (2007). Chemically diverse toxicants converge on Fyn and c-Cbl to disrupt precursor cell function. PLoS Biol 5: e35.
Liu DP, Wang Y, Koeffler HP, Xie D. . (2007). Ephrin-A1 is a negative regulator in glioma through down-regulation of EphA2 and FAK. Int J Oncol 30: 865–871.
Liu XW, Katagiri Y, Jiang H, Gong LJ, Guo LY, Shibutani M et al. (2000). Cloning and characterization of the promoter region of the rat epidermal growth factor receptor gene and its transcriptional regulation by nerve growth factor in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 275: 7280–7288.
Munthe E, Rian E, Holien T, Rasmussen A, Levy FO, Aasheim H . (2000). Ephrin-B2 is a candidate ligand for the Eph receptor, EphB6. FEBS Lett 466: 169–174.
Nicholas MK, Lukas RV, Jafri NF, Faoro L, Salgia R . (2006). Epidermal growth factor receptor - mediated signal transduction in the development and therapy of gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 12: 7261–7270.
Oksvold MP, Thien CB, Widerberg J, Chantry A, Huitfeldt HS, Langdon WY . (2003). Serine mutations that abrogate ligand-induced ubiquitination and internalization of the EGF receptor do not affect c-Cbl association with the receptor. Oncogene 22: 8509–8518.
Otal R, Burgaya F, Frisen J, Soriano E, Martinez A . (2006). Ephrin-A5 modulates the topographic mapping and connectivity of commissural axons in murine hippocampus. Neuroscience 141: 109–121.
Poliakov A, Cotrina M, Wilkinson DG . (2004). Diverse roles of eph receptors and ephrins in the regulation of cell migration and tissue assembly. Dev Cell 7: 465–480.
Qin XF, An DS, Chen IS, Baltimore D . (2003). Inhibiting HIV-1 infection in human T cells by lentiviral-mediated delivery of small interfering RNA against CCR5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 183–188.
Ravid T, Heidinger JM, Gee P, Khan EM, Goldkorn T . (2004). c-Cbl-mediated ubiquitinylation is required for epidermal growth factor receptor exit from the early endosomes. J Biol Chem 279: 37153–37162.
Sharfe N, Freywald A, Toro A, Roifman CM . (2003). Ephrin-A1 induces c-Cbl phosphorylation and EphA receptor down-regulation in T cells. J Immunol 170: 6024–6032.
Sun ZJ, Wang Y, Cai Z, Chen PP, Tong XJ, Xie D . (2008). Involvement of Cyr61 in growth, migration, and metastasis of prostate cancer cells. Br J Cancer 99: 1656–1667.
Surawska H, Ma PC, Salgia R . (2004). The role of ephrins and Eph receptors in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15: 419–433.
Varelias A, Koblar SA, Cowled PA, Carter CD, Clayer M . (2002). Human osteosarcoma expresses specific ephrin profiles: implications for tumorigenicity and prognosis. Cancer 95: 862–869.
Walker-Daniels J, Riese II DJ, Kinch MS . (2002). c-Cbl-dependent EphA2 protein degradation is induced by ligand binding. Mol Cancer Res 1: 79–87.
Wang Y, Ota S, Kataoka H, Kanamori M, Li Z, Band H et al. (2002). Negative regulation of EphA2 receptor by Cbl. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 296: 214–220.
Waterman H, Yarden Y . (2001). Molecular mechanisms underlying endocytosis and sorting of ErbB receptor tyrosine kinases. FEBS Lett 490: 142–152.
Xie D, Yin D, Tong X, O’Kelly J, Mori A, Miller C et al. (2004). Cyr61 is overexpressed in gliomas and involved in integrin-linked kinase-mediated Akt and beta-catenin-TCF/Lef signaling pathways. Cancer Res 64: 1987–1996.
Xu J, Thompson KL, Shephard LB, Hudson LG, Gill GN . (1993). T3 receptor suppression of Sp1-dependent transcription from the epidermal growth factor receptor promoter via overlapping DNA-binding sites. J Biol Chem 268: 16065–16073.
Yarden RI, Wilson MA, Chrysogelos SA . (2001). Estrogen suppression of EGFR expression in breast cancer cells: a possible mechanism to modulate growth. J Cell Biochem Suppl 36: 232–246.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Alfred C Johnson for the EGFR promoter reporter plasmid, Dr Yosef Yarden for the hEGFR and hEGFR (Y1045F) plasmids, Dr De Camilli P for pcDNA3.1-HA-Ubiquitin plasmid and Dr Hans-Christian Aasheim for CD19-Fc and EphA2-Fc constructs.
We also would like to thank Dr H Phillip Koeffler (Cedars-Sinai Medical Center) for helpful discussions, suggestions and critical reading of this paper.
This work was supported by Ministry of Science and Technology 863 Program 2007AA02Z474, 973 Program 2007CB914704, and 2008ZX10207, National Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar 30725010, National Natural Science Foundation of China 90813023 and 30528003. Chinese Academy of Sciences Grant KSCX2-YW-R-152 and KSCX-YW-R-73, and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality 08140902300 to D Xie.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, JJ., Liu, DP., Liu, GT. et al. EphrinA5 acts as a tumor suppressor in glioma by negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor. Oncogene 28, 1759–1768 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.15
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.15
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Expression characteristic, immune signature, and prognosis value of EFNA family identified by multi-omics integrative analysis in pan-cancer
BMC Cancer (2022)
-
Polycomb-mediated repression of EphrinA5 promotes growth and invasion of glioblastoma
Oncogene (2020)
-
PRMT1 promotes pancreatic cancer growth and predicts poor prognosis
Cellular Oncology (2020)
-
BMP10 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PTPRS–STAT3 axis
Oncogene (2019)
-
EPH receptor A2 governs a feedback loop that activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in gastric cancer
Cell Death & Disease (2018)