Abstract
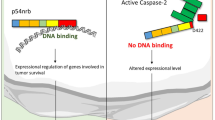
Far upstream element-binding protein-1 (FBP-1) binds to an upstream element of the c-myc promoter and regulates the c-myc mRNA level. Earlier, FBP-1 was identified as a candidate substrate of caspase-7. Here, we report that FBP-1 is cleaved by executor caspases, both in vitro and during apoptosis. Cleavage occurs at the caspase consensus site (DQPD74) located within the classical bipartite nuclear localization signal sequence. In cells subjected to apoptotic stimuli, the caspase-mediated cleavage of FBP-1 leads to its decreased presence in the nucleus, concomitant with the marked downregulation of c-Myc and its various target proteins. By contrast, cells transfected with a non-cleavable mutant of FBP-1 (D74A) maintain higher levels of c-Myc and are protected from apoptosis. On the basis of these results, we suggest that the oncogenic potential of c-Myc is ‘switched off’ after apoptosis induction as a consequence of the caspase-mediated cleavage of FBP-1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blackwood EM, Eisenman RN . (1991). Max: a helix–loop–helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science 251: 1211–1217.
Cao X, Bennett RL, May WS . (2008). c-Myc and caspase-2 are involved in activating Bax during cytotoxic drug-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 283: 14490–14496.
Chung H-J, Levens D . (2005). c-Myc expression: keep the noise down!. Mol Cells 20: 157–166.
Chung H-J, Liu J, Dundr M, Nie Z, Sanford S, Levens D . (2006). FBPs are calibrated molecular tools to adjust gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 26: 6584–6597.
Denault JB, Salvesen GS . (2002). Caspases: keys in the ignition of cell death. Chem Rev 102: 4489–4500.
Fischer U, Jänicke RU, Schulze-Osthoff K . (2003). Many cuts to ruin: a comprehensive update of caspase substrates. Cell Death Differ 10: 76–100.
He L, Liu J, Collins I, Sanford S, O’Connell B, Benham CJ et al. (2000a). Loss of FBP1 function arrests cellular proliferation and extinguishes c-Myc expression. EMBO J 19: 1034–1044.
He L, Weber A, Levens D . (2000b). Nuclear targeting determinants of the far upstream element binding protein, a c-myc transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res 28: 4558–4565.
Jang M, Park BC, Lee AY, Na KS, Kang S, Bae K-H et al. (2007). Caspase-7 mediated cleavage of proteasome subunits during apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363: 388–394.
Krysko DV, Denecker G, Festjens N, Gabriels S, Parthoens E, D’Herde K et al. (2006). Macrophages use different internalization mechanisms to clear apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cell Death Differ 13: 2011–2022.
Lalier L, Cartron P-F, Juin P, Nedelkina S, Manon S, Bechinger B et al. (2007). Bax activation and mitochondrial insertion during apoptosis. Apoptosis 12: 887–896.
Lee AY, Park BC, Jang M, Cho S, Lee DH, Lee SC et al. (2004). Identification of caspase-3 degradome by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight analysis. Proteomics 4: 3429–3436.
Lee MW, Hirai I, Wang HG . (2003). Caspase-3-mediated cleavage of Rad9 during apoptosis. Oncogene 22: 6340–6346.
Liu J, Li J, Sidell N . (2007). Modulation by phenylacetate of early estrogen-mediated events in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 59: 217–225.
Nicholson DW . (1999). Caspase structure, proteolytic substrates, and function during apoptotic cell death. Cell Death Differ 6: 1028–1042.
Nieminen AI, Partanen JI, Klefstrom J . (2007). c-Myc blazing a trail of death: coupling of the mitochondrial and death receptor apoptosis pathways by c-Myc. Cell Cycle 6: 2464–2472.
Pelengaris S, Khan M, Evan G . (2002). c-MYC: more than just a matter of life and death. Nat Rev Cancer 10: 764–776.
Raff M . (1998). Cell suicide for beginners. Nature 396: 119–122.
Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS . (1999). Caspases: preparation and characterization. Methods 17: 313–319.
Thiede B, Dimmler C, Siejak F, Rudel T . (2001). Predominant identification of RNA-binding proteins in Fas-induced apoptosis by proteome analysis. J Biol Chem 276: 26044–26050.
Timmer JC, Salvesen GS . (2007). Caspase substrates. Cell Death Differ 14: 66–72.
Vindigni A, Ochem A, Triolo G, Falaschi A . (2001). Identification of human DNA helicase V with the far upstream element-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res 29: 1061–1067.
Wierstra I, Alves J . (2008). The c-myc promoter: still MysterY and challenge. Adv Cancer Res 99: 113–333.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Young Il Yeom, Seung Jun Kim and Do Hee Lee for their helpful advices. This study was supported by a grant sponsored by KRIBB (to K-H Bae) and Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (Basic Research Program no. 2008-01050) (to SG Park).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, M., Park, B., Kang, S. et al. Far upstream element-binding protein-1, a novel caspase substrate, acts as a cross-talker between apoptosis and the c-myc oncogene. Oncogene 28, 1529–1536 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.11
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.11
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Circulating autoantibodies to alpha-enolase (ENO1) and far upstream element-binding protein 1 (FUBP1) are negative prognostic factors for pancreatic cancer patient survival
Clinical and Experimental Medicine (2023)
-
NORAD orchestrates endometrial cancer progression by sequestering FUBP1 nuclear localization to promote cell apoptosis
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
The master regulator FUBP1: its emerging role in normal cell function and malignant development
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2019)
-
FOXC1-induced non-canonical WNT5A-MMP7 signaling regulates invasiveness in triple-negative breast cancer
Oncogene (2018)
-
MiR-16 mediates trastuzumab and lapatinib response in ErbB-2-positive breast and gastric cancer via its novel targets CCNJ and FUBP1
Oncogene (2016)