Abstract
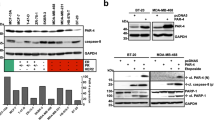
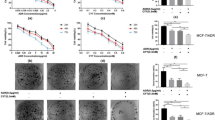
Protein kinase Cɛ (PKCɛ) acts as an antiapoptotic protein and inhibits tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Members of the TNF receptor superfamily trigger apoptosis independent of the tumor suppressor protein p53, which primarily affects DNA damage-induced apoptosis. We have previously shown that PKCɛ acts upstream of Akt to inhibit receptor-initiated cell death. Since Akt can regulate p53, we have examined the involvement of p53 in PKCɛ-mediated TRAIL resistance. Overexpression of PKCɛ in MCF-7 cells (MCF-7/PKCɛ) caused a decrease in p53 and an increase in human homolog of murine double minute 2 (Hdm2) and phospho-Hdm2. Depletion of p53 by siRNA attenuated, whereas depletion of Hdm2 enhanced TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Knockdown of Akt decreased Hdm2 phosphorylation, increased p53 level and potentiated TRAIL-induced cell death. Depletion of PKCɛ from MCF-7 cells caused an increase in p53, whereas knockdown of p53 caused a decrease in Bid mRNA. Depletion of Akt from MCF-7/PKCɛ cells resulted in an increase in p53 and Bid. These results suggest that PKCɛ mediates TRAIL resistance by Akt-mediated phosphorylation of Hdm2 resulting in suppression of p53 expression and downregulation of Bid in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Hdm2:
-
human homolog of Mdm2
- Mdm2:
-
murine double minute 2
- PARP:
-
poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PKB:
-
protein kinase B
- PKC:
-
protein kinase C
- SDS–PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor-α
- TRAIL:
-
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
References
Basu A, Akkaraju GR . (1999). Regulation of caspase activation and cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)-induced cell death by protein kinase C. Biochemistry 38: 4245–4251.
Basu A, Lu D, Sun B, Moor AN, Akkaraju GR, Huang J . (2002). Proteolytic activation of protein kinase C-epsilon by caspase-mediated processing and transduction of antiapoptotic signals. J Biol Chem 277: 41850–41856.
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS et al. (1999). Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96: 857–868.
Chen J, Marechal V, Levine AJ . (1993). Mapping of the p53 and mdm-2 interaction domains. Mol Cell Biol 13: 4107–4114.
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA . (1995). Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378: 785–789.
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y et al. (1997). Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91: 231–241.
Ehrhardt H, Hacker S, Wittmann S, Maurer M, Borkhardt A, Toloczko A et al. (2008). Cytotoxic drug-induced, p53-mediated upregulation of caspase-8 in tumor cells. Oncogene 27: 783–793.
Eskes R, Desagher S, Antonsson B, Martinou JC . (2000). Bid induces the oligomerization and insertion of Bax into the outer mitochondrial membrane. Mol Cell Biol 20: 929–935.
Feng J, Tamaskovic R, Yang Z, Brazil DP, Merlo A, Hess D et al. (2004). Stabilization of Mdm2 via decreased ubiquitination is mediated by protein kinase B/Akt-dependent phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 279: 35510–35517.
Gross A, Yin XM, Wang K, Wei MC, Jockel J, Milliman C et al. (1999). Caspase cleaved BID targets mitochondria and is required for cytochrome c release, while BCL-XL prevents this release but not tumor necrosis factor-R1/Fas death. J Biol Chem 274: 1156–1163.
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A, Oren M . (1997). Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature 387: 296–299.
Kelley SK, Ashkenazi A . (2004). Targeting death receptors in cancer with Apo2L/TRAIL. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4: 333–339.
Kubbutat MH, Jones SN, Vousden KH . (1997). Regulation of p53 stability by Mdm2. Nature 387: 299–303.
Li S, Zhou Y, Wang R, Zhang H, Dong Y, Ip C . (2007). Selenium sensitizes MCF-7 breast cancer cells to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis through modulation of phospho-Akt and its downstream substrates. Mol Cancer Ther 6: 1031–1038.
Liu X, Yue P, Khuri FR, Sun SY . (2004). p53 upregulates death receptor 4 expression through an intronic p53 binding site. Cancer Res 64: 5078–5083.
Lu D, Huang J, Basu A . (2004). Deregulation of PKB influences antiapoptotic signaling by PKC in breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol 25: 671–676.
Lu D, Huang J, Basu A . (2006). Protein kinase Cepsilon activates protein kinase B/Akt via DNA-PK to protect against tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 281: 22799–22807.
Mayo LD, Donner DB . (2001). A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway promotes translocation of Mdm2 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 11598–11603.
Miyashita T, Reed JC . (1995). Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell 80: 293–299.
Nakano K, Vousden KH . (2001). PUMA, a novel proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell 7: 683–694.
O'toole A, Moule SK, Lockyer PJ, Halestrap AP . (2001). Tumour necrosis factor-α activation of protein kinase B in WEHI-164 cells is accompanied by increased phosphorylation of Ser473, but not Thr308. Biochem J 359: 119–127.
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, Nemoto J, Shibue T, Yamashita T et al. (2000). Noxa, a BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family and candidate mediator of p53-induced apoptosis. Science 288: 1053–1058.
Ogawara Y, Kishishita S, Obata T, Isazawa Y, Suzuki T, Tanaka K et al. (2002). Akt enhances Mdm2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p53. J Biol Chem 277: 21843–21850.
Oren M . (1999). Regulation of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. J Biol Chem 274: 36031–36034.
Owen-Schaub LB, Zhang W, Cusack JC, Angelo LS, Santee SM, Fujiwara T et al. (1995). Wild-type human p53 and a temperature-sensitive mutant induce Fas/APO-1 expression. Mol Cell Biol 15: 3032–3040.
Rozan LM, El-Deiry WS . (2007). p53 downstream target genes and tumor suppression: a classical view in evolution. Cell Death Differ 14: 3–9.
Rudner J, Jendrossek V, Lauber K, Daniel PT, Wesselborg S, Belka C . (2005). Type I and type II reactions in TRAIL-induced apoptosis—results from dose-response studies. Oncogene 24: 130–140.
Sax JK, Fei P, Murphy ME, Bernhard E, Korsmeyer SJ, El-Deiry WS . (2002). BID regulation by p53 contributes to chemosensitivity. Nat Cell Biol 4: 842–849.
Schuler M, Bossy-Wetzel E, Goldstein JC, Fitzgerald P, Green DR . (2000). p53 induces apoptosis by caspase activation through mitochondrial cytochrome c release. J Biol Chem 275: 7337–7342.
Sivaprasad U, Shankar E, Basu A . (2007). Downregulation of Bid is associated with PKCepsilon-mediated TRAIL resistance. Cell Death Differ 14: 851–860.
Toledo F, Wahl GM . (2006). Regulating the p53 pathway: in vitro hypotheses, in vivo veritas. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 909–923.
Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ . (2000). Surfing the p53 network. Nature 408: 307–310.
Vousden KH . (2006). Outcomes of p53 activation—spoilt for choice. J Cell Sci 119: 5015–5020.
Vousden KH, Lu X . (2002). Live or let die: the cell's response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 594–604.
Wang S, El-Deiry WS . (2003). TRAIL and apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene 22: 8628–8633.
Weber HO, Ludwig RL, Morrison D, Kotlyarov A, Gaestel M, Vousden KH . (2005). HDM2 phosphorylation by MAPKAP kinase 2. Oncogene 24: 1965–1972.
Wu GS, Burns TF, McDonald III ER, Jiang W, Meng R, Krantz ID et al. (1997). KILLER/DR5 is a DNA damage-inducible p53-regulated death receptor gene. Nat Genet 17: 141–143.
Yu J, Zhang L, Hwang PM, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . (2001). PUMA induces the rapid apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cell 7: 673–682.
Zauberman A, Barak Y, Ragimov N, Levy N, Oren M . (1993). Sequence-specific DNA binding by p53: identification of target sites and lack of binding to p53—MDM2 complexes. EMBO J 12: 2799–2808.
Zhou BP, Liao Y, Xia W, Zou Y, Spohn B, Hung MC . (2001). HER-2/neu induces p53 ubiquitination via Akt-mediated MDM2 phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol 3: 973–982.
Acknowledgements
We thank Chandreyi Basu for technical assistance and Dr Arvind Virmani and Dr Adi Gazdar for providing us HCC1806 cells. This work is supported by the grant CA71727 from the NCI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shankar, E., Sivaprasad, U. & Basu, A. Protein kinase Cɛ confers resistance of MCF-7 cells to TRAIL by Akt-dependent activation of Hdm2 and downregulation of p53. Oncogene 27, 3957–3966 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.39
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.39
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A bismuth diethyldithiocarbamate compound induced apoptosis via mitochondria-dependent pathway and suppressed invasion in MCF-7 breast cancer cells
BioMetals (2021)
-
Design, Expression, Purification and Characterization of the Recombinant Immunotoxin 4D5 scFv-TRAIL
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2020)
-
Distinctive requirement of PKCε in the control of Rho GTPases in epithelial and mesenchymally transformed lung cancer cells
Oncogene (2019)
-
Non-canonical kinase signaling by the death ligand TRAIL in cancer cells: discord in the death receptor family
Cell Death & Differentiation (2013)
-
Curcumin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis of breast cancer cells by regulating apoptosis-related proteins
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2013)