Abstract
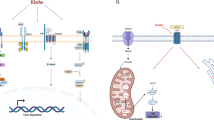
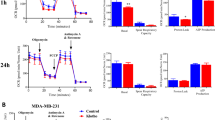
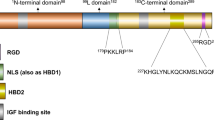
Klotho is an anti-aging gene, which has been shown to inhibit the insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) pathways in mice hepatocytes and myocytes. As IGF-1 and insulin regulate proliferation, survival and metastasis of breast cancer, we studied klotho expression and activities in human breast cancer. Immunohistochemistry analysis of klotho expression in breast tissue arrays revealed high klotho expression in normal breast samples, but very low expression in breast cancer. In cancer samples, high klotho expression was associated with smaller tumor size and reduced KI67 staining. Forced expression of klotho reduced proliferation of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells, whereas klotho silencing in MCF-7 cells, which normally express klotho, enhanced proliferation. Moreover, forced expression of klotho in these cells, or treatment with soluble klotho, inhibited the activation of IGF-1 and insulin pathways, and induced upregulation of the transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β, a breast cancer growth inhibitor that is negatively regulated by the IGF-1-AKT axis. Co-immunoprecipitation revealed an interaction between klotho and the IGF-1 receptor. Klotho is also a known modulator of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) pathway, a pathway that inhibits proliferation of breast cancer cells. Studies in breast cancer cells revealed increased activation of the FGF pathway by basic FGF following klotho overexpression. Klotho did not affect activation of the epidermal growth factor pathway in breast cancer cells. These data suggest klotho as a potential tumor suppressor and identify it as an inhibitor of the IGF-1 pathway and activator of the FGF pathway in human breast cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arking DE, Becker DM, Yanek LR, Fallin D, Judge DP, Moy TF et al. (2003). KLOTHO allele status and the risk of early-onset occult coronary artery disease. Am J Hum Genet 72: 1154–1161.
Arking DE, Krebsova A, Macek Sr M, Macek Jr M, Arking A, Mian IS et al. (2002). Association of human aging with a functional variant of klotho. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99: 856–861.
Bartucci M, Morelli C, Mauro L, Ando S, Surmacz E . (2001). Differential insulin-like growth factor I receptor signaling and function in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive MCF-7 and ER-negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 61: 6747–6754.
Cha S-K, Ortega B, Kurosu H, Rosenblatt KP, Kuro-o M, Huang C-L . (2008). Removal of sialic acid involving Klotho causes cell-surface retention of TRPV5 channel via binding to galectin-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105: 9805–9810.
Chang Q, Hoefs S, van der Kemp AW, Topala CN, Bindels RJ, Hoenderop JG . (2005). The {beta}-glucuronidase klotho hydrolyzes and activates the TRPV5 channel. Science 310: 490–493.
Chen C-D, Podvin S, Gillespie E, Leeman SE, Abraham CR . (2007). Insulin stimulates the cleavage and release of the extracellular domain of Klotho by ADAM10 and ADAM17. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104: 19796–19801.
Chihara Y, Rakugi H, Ishikawa K, Ikushima M, Maekawa Y, Ohta J et al. (2006). Klotho protein promotes adipocyte differentiation. Endocrinology 147: 3835–3842.
de Oliveira RM . (2006). Klotho RNAi induces premature senescence of human cells via a p53/p21 dependent pathway. FEBS Letters 580: 5753–5758.
den Dekker E, Hoenderop JGJ, Nilius B, Bindels RJM . (2003). The epithelial calcium channels, TRPV5 & TRPV6: from identification towards regulation. Cell Calcium 33: 497–507.
Fenig E, Szyper-Kravitz M, Yerushalmi R, Lahav M, Beery E, Wasserman L et al. (2002). Basic fibroblast growth factor mediated growth inhibition in breast cancer cells is independent of ras signaling pathway. Oncol Rep 9: 875–877.
Fenig E, Wieder R, Paglin S, Wang H, Persaud R, Haimovitz-Friedman A et al. (1997). Basic fibroblast growth factor confers growth inhibition and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in human breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 3: 135–142.
Geier A, Beery R, Haimsohn M, Karasik A . (1995). Insulin-like growth factor-1 inhibits cell death induced by anticancer drugs in the MCF-7 cells: involvement of growth factors in drug resistance. Cancer Invest 13: 480–486.
Gery S, Tanosaki S, Bose S, Bose N, Vadgama J, Koeffler HP . (2005). Down-regulation and growth inhibitory role of C/EBP{alpha} in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11: 3184–3190.
Gomis RR, Alarcon C, Nadal C, Van Poznak C, Massague J . (2006). C/EBP[beta] at the core of the TGF[beta] cytostatic response and its evasion in metastatic breast cancer cells. Cancer Cell 10: 203–214.
Haimsohn M, Beery R, Karasik A, Kanety H, Geier A . (2002). Aurintricarboxylic acid induces a distinct activation of the IGF-I receptor signaling within MDA-231 cells. Endocrinology 143: 837–845.
Haluska P, Carboni JM, Loegering DA, Lee FY, Wittman M, Saulnier MG et al. (2006). In vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of the dual insulin-like growth factor-I/insulin receptor inhibitor, BMS-554417. Cancer Res 66: 362–371.
Hsiung R, Zhu W, Klein G, Qin W, Rosenberg A, Park P et al. (2002). High basic fibroblast growth factor levels in nipple aspirate fluid are correlated with breast cancer. Cancer J 8: 303–310.
Ikushima M, Rakugi H, Ishikawa K, Maekawa Y, Yamamoto K, Ohta J et al. (2006). Anti-apoptotic and anti-senescence effects of Klotho on vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 339: 827–832.
Imura A, Iwano A, Tohyama O, Tsuji Y, Nozaki K, Hashimoto N et al. (2004). Secreted Klotho protein in sera and CSF: implication for post-translational cleavage in release of Klotho protein from cell membrane. FEBS Lett 565: 143–147.
Imura A, Tsuji Y, Murata M, Maeda R, Kubota K, Iwano A et al. (2007). {alpha}-klotho as a regulator of calcium homeostasis. Science 316: 1615–1618.
Ito S, Kinoshita S, Shiraishi N, Nakagawa S, Sekine S, Fujimori T et al. (2000). Molecular cloning and expression analyses of mouse [beta]klotho, which encodes a novel Klotho family protein. Mech Dev 98: 115–119.
Kato Y, Arakawa E, Kinoshita S, Shirai A, Furuya A, Yamano K et al. (2000). Establishment of the anti-klotho monoclonal antibodies and detection of klotho protein in kidneys. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 267: 597–602.
Kim Y, Kim J-H, Nam YJ, Kong M, Kim YJ, Yu K-H et al. (2006). Klotho is a genetic risk factor for ischemic stroke caused by cardioembolism in Korean females. Neurosci Lett 407: 189–194.
Korah RM, Sysounthone V, Golowa Y, Wieder R . (2000). Basic fibroblast growth factor confers a less malignant phenotype in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 60: 733–740.
Kuro-o M, Matsumura Y, Aizawa H, Kawaguchi H, Suga T, Utsugi T et al. (1997). Mutation of the mouse klotho gene leads to a syndrome resembling ageing. Nature 390: 45–51.
Kurosu H, Ogawa Y, Miyoshi M, Yamamoto M, Nandi A, Rosenblatt KP et al. (2006). Regulation of fibroblast growth factor-23 signaling by Klotho. J Biol Chem 281: 6120–6123.
Kurosu H, Yamamoto M, Clark JD, Pastor JV, Nandi A, Gurnani P et al. (2005). Suppression of aging in mice by the hormone Klotho. Science 309: 1829–1833.
Lacroix M, Leclercq G . (2004). Relevance of breast cancer cell lines as models for breast tumours: an update. Breast Cancer Res Treatment 83: 249–289.
Li X, Kim JW, Gronborg M, Urlaub H, Lane MD, Tang Q-Q . (2007). Role of cdk2 in the sequential phosphorylation/activation of C/EBPbeta during adipocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104: 11597–11602.
Matsumura Y, Aizawa H, Shiraki-Iida T, Nagai R, Kuro-o M, Nabeshima Y . (1998). Identification of the human Klotho gene and its two transcripts encoding membrane and secreted Klotho protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 242: 626–630.
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades NS, McMullan CJ, Poulaki V, Shringarpure R, Akiyama M et al. (2004). Inhibition of the insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 tyrosine kinase activity as a therapeutic strategy for multiple myeloma, other hematologic malignancies, and solid tumors. Cancer Cell 5: 221–230.
Ohyama Y, Kurabayashi M, Masuda H, Nakamura T, Aihara Y, Kaname T et al. (1998). Molecular cloning of rat klotho cDNA: markedly decreased expression of klotho by acute inflammatory stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 251: 920–925.
Shiraki-Iida T, Aizawa H, Matsumura Y, Sekine S, Iida A, Anazawa H et al. (1998). Structure of the mouse klotho gene and its two transcripts encoding membrane and secreted protein. FEBS Lett 424: 6–10.
Urakawa I, Yamazaki Y, Shimada T, Iijima K, Hasegawa H, Okawa K et al. (2006). Klotho converts canonical FGF receptor into a specific receptor for FGF23. Science 444: 770–774.
Utsugi T, Ohno T, Ohyama Y, Uchiyama T, Saito Y, Matsumura Y et al. (2000). Decreased insulin production and increased insulin sensitivity in the klotho mutant mouse, a novel animal model for human aging. Metabolism 49: 1118–1123.
Vandermoere F, El Yazidi-Belkoura I, Adriaenssens E, Lemoine J, Hondermarck H . (2005). The antiapoptotic effect of fibroblast growth factor-2 is mediated through nuclear factor-[kappa]B activation induced via interaction between Akt and I[kappa]B kinase-[beta] in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 24: 5482–5491.
Wolf I, Bose S, Williamson EA, Miller CW, Karlan BY, Koeffler HP . (2007). FOXA1: Growth inhibitor and a favorable prognostic factor in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer 120: 1013–1022.
Wolf I, O'Kelly J, Rubinek T, Tong M, Nguyen A, Lin BT et al. (2006a). 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase is a tumor suppressor of human breast cancer. Cancer Res 66: 7818–7823.
Wolf I, Sadetzki S, Gluck I, Oberman B, Ben-David M, Papa MZ et al. (2006b). Association between diabetes mellitus and adverse characteristics of breast cancer at presentation. Eur J Cancer 42: 1077–1082.
Yee D . (2006). Targeting insulin-like growth factor pathways. Br J Cancer 94: 465–468.
Zarrabeitia M, Hernández JL, Valero C, Zarrabeitia A, Ortiz F, Gonzalez-Macias J et al. (2007). Klotho gene polymorphism and male bone mass. Calcif Tissue Int 80: 10–14.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by grants from the United States–Israel Binational Science Foundation (BSF), Jerusalem, Israel; Koschitzky Family Foundation; the Israel Cancer Association; the Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv Israel; The Talpiot Medical Leadership Program, Sheba Medical Center; the Inger Fund, Rountree Trust and the Mary Barry Foundation and by grants from the Women's Cancer Research Institute, Samuel Oschin Comprehensive Cancer Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center. HPK is a member of the Molecular Biology Institute and Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center at UCLA and holds the endowed Mark Goodson Chair of Oncology Research at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center/UCLA School of Medicine. IW is the Mary Barry Medical Bridges Foundation Fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolf, I., Levanon-Cohen, S., Bose, S. et al. Klotho: a tumor suppressor and a modulator of the IGF-1 and FGF pathways in human breast cancer. Oncogene 27, 7094–7105 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.292
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.292
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
PKC regulates αKlotho gene expression in MDCK and NRK-52E cells
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2024)
-
Klotho increases antioxidant defenses in astrocytes and ubiquitin–proteasome activity in neurons
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Klotho inhibits IGF1R/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway and protects the heart from oxidative stress during ischemia/reperfusion injury
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Platelet factors are induced by longevity factor klotho and enhance cognition in young and aging mice
Nature Aging (2023)
-
Longevity factor klotho enhances cognition in aged nonhuman primates
Nature Aging (2023)