Abstract
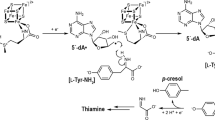
The most divergent of two tryptophanyl tRNA synthetases (TrpRS II) found in Deinococcus radiodurans interacts with a nitric oxide synthase protein that produces 4-nitro-tryptophan (4-NRP). TrpRS II efficiently charges transfer RNATrp with 4-NRP and 5-hydroxy-tryptophan (5-HRP). The crystal structures of TrpRS II bound to tryptophan and 5-HRP reveal residue substitutions that accommodate modified indoles. A class of auxiliary bacterial TrpRSs conserve this capacity to charge tRNA with nonstandard amino acids.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ibba, M. & Soll, D. Genes Dev. 18, 731–738 (2004).
Blight, S.K. et al. Nature 431, 333–335 (2004).
Lovato, M.A., Chihade, J.W. & Schimmel, P. EMBO J. 20, 4846–4853 (2001).
Buddha, M.R., Keery, K.M. & Crane, B.R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 15881–15886 (2004).
Buddha, M.R., Tao, T. Parry, R.J. & Crane, B.R. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 49567–49570 (2004).
Kers, J.A. et al. Nature 429, 79–82 (2004).
Retailleau, P. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 325, 39–63 (2003).
Yadong, Y. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 8378–8388 (2004).
Yang, X.L. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 15376–15380 (2003).
Praetorius-Ibba, M. et al. Biochemistry 39, 13136–13143 (2000).
Zhang, Z. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 8882–8887 (2004).
Senear, D.F. et al. Anal. Biochem. 300, 77–86 (2002).
Nomanbhoy, T.K., Hendrickson, T.L. & Schimmel, P. Mol. Cell 4, 519–528 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank R.J. Parry and T. Tao for providing synthetic 4-NRP, A.M. Bilwes for help with refinement, and Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source and the National Synchrotron Light Source for access to data collection facilities. Support from the US National Science Foundation and the US National Institutes of Health is gratefully achnowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Characterization of 4-NRP incorporation into tRNA by TrpRS II. (PDF 197 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Multisequence alignment of TrpRS Is and TrpRS IIs. (PDF 162 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Diffraction data collection and refinement statistics. (PDF 81 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buddha, M., Crane, B. Structure and activity of an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase that charges tRNA with nitro-tryptophan. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12, 274–275 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb907
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb907
This article is cited by
-
Stationary‐phase expression and aminoacylation of a transfer‐RNA‐like small RNA
EMBO reports (2005)