Abstract
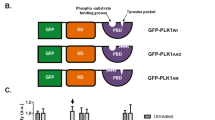
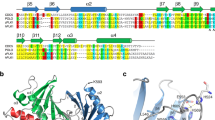
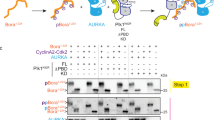
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is a master regulator of mitosis and is considered a potential drug target for cancer therapy. PLK1 is characterized by an N-terminal kinase domain (KD) and a C-terminal Polo-box domain (PBD). The KD and PBD are mutually inhibited, but the molecular mechanisms of the autoinhibition remain unclear. Here we report the 2.3-Å crystal structure of the complex of the Danio rerio KD and PBD together with a PBD-binding motif of Drosophila melanogaster microtubule-associated protein 205 (Map205PBM). The structure reveals that the PBD binds and rigidifies the hinge region of the KD in a distinct conformation from that of the phosphopeptide-bound PBD. This structure provides a framework for understanding the autoinhibitory mechanisms of PLK1 and also sheds light on the activation mechanisms of PLK1 by phosphorylation or phosphopeptide binding.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr, F.A., Sillje, H.H. & Nigg, E.A. Polo-like kinases and the orchestration of cell division. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 429–440 (2004).
Lowery, D.M., Lim, D. & Yaffe, M.B. Structure and function of Polo-like kinases. Oncogene 24, 248–259 (2005).
Archambault, V. & Glover, D.M. Polo-like kinases: conservation and divergence in their functions and regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 265–275 (2009).
van de Weerdt, B.C. & Medema, R.H. Polo-like kinases: a team in control of the division. Cell Cycle 5, 853–864 (2006).
Petronczki, M., Lenart, P. & Peters, J.M. Polo on the rise: from mitotic entry to cytokinesis with Plk1. Dev. Cell 14, 646–659 (2008).
Barr, F.A. & Gruneberg, U. Cytokinesis: placing and making the final cut. Cell 131, 847–860 (2007).
Eckerdt, F., Yuan, J. & Strebhardt, K. Polo-like kinases and oncogenesis. Oncogene 24, 267–276 (2005).
Strebhardt, K. & Ullrich, A. Targeting polo-like kinase 1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 321–330 (2006).
Schöffski, P. Polo-like kinase (PLK) inhibitors in preclinical and early clinical development in oncology. Oncologist 14, 559–570 (2009).
Strebhardt, K. Multifaceted polo-like kinases: drug targets and antitargets for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9, 643–660 (2010).
Lee, K.S., Grenfell, T.Z., Yarm, F.R. & Erikson, R.L. Mutation of the polo-box disrupts localization and mitotic functions of the mammalian polo kinase Plk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 9301–9306 (1998).
Jang, Y.J., Lin, C.Y., Ma, S. & Erikson, R.L. Functional studies on the role of the C-terminal domain of mammalian polo-like kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 1984–1989 (2002).
Seong, Y.S. et al. A spindle checkpoint arrest and a cytokinesis failure by the dominant-negative polo-box domain of Plk1 in U-2 OS cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 32282–32293 (2002).
Hanisch, A., Wehne, A., Nigg, E.A. & Sillje, H.H. Different Plk1 functions show distinct dependencies on polo-box domain-mediated targeting. Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 448–459 (2006).
Elia, A.E., Cantley, L.C. & Yaffe, M.B. Proteomic screen finds pSer/pThr-binding domain localizing Plk1 to mitotic substrates. Science 299, 1228–1231 (2003).
Mundt, K.E., Golsteyn, R.M., Lane, H.A. & Nigg, E.A. On the regulation and function of human polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1): effects of overexpression on cell cycle progression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 239, 377–385 (1997).
Elia, A.E. et al. The molecular basis for phosphodependent substrate targeting and regulation of Plks by the Polo-box domain. Cell 115, 83–95 (2003).
Qian, Y.W., Erikson, E. & Maller, J.L. Mitotic effects of a constitutively active mutant of the Xenopus polo-like kinase Plx1. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 8625–8632 (1999).
Jang, Y.J., Ma, S., Terada, Y. & Erikson, R.L. Phosphorylation of threonine 210 and the role of serine 137 in the regulation of mammalian polo-like kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 44115–44120 (2002).
Lindon, C. & Pines, J. Ordered proteolysis in anaphase inactivates Plk1 to contribute to proper mitotic exit in human cells. J. Cell Biol. 164, 233–241 (2004).
Macůrek, L. et al. Polo-like kinase-1 is activated by aurora A to promote checkpoint recovery. Nature 455, 119–123 (2008).
Seki, A., Coppinger, J.A., Jang, C.Y., Yates, J.R. & Fang, G. Bora and the kinase Aurora A cooperatively activate the kinase Plk1 and control mitotic entry. Science 320, 1655–1658 (2008).
van de Weerdt, B.C. et al. Uncoupling anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome activity from spindle assembly checkpoint control by deregulating polo-like kinase 1. Mol. Cell Biol. 25, 2031–2044 (2005).
Matsumoto, T. et al. Polo-like kinases mediate cell survival in mitochondrial dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 14542–14546 (2009).
Johnson, T.M., Antrobus, R. & Johnson, L.N. Plk1 activation by Ste20-like kinase (SLK) phosphorylation and polo-box phosphopeptide binding assayed with the substrate translationally controlled tumor protein (TCTP). Biochemistry 47, 3688–3696 (2008).
Goto, H. et al. Complex formation of Plk1 and INCENP required for metaphase–anaphase transition. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 180–187 (2006).
Kang, Y.H. et al. Self-regulated Plk1 recruitment to kinetochores by the Plk1–PBIP1 interaction is critical for proper chromosome segregation. Mol. Cell 24, 409–422 (2006).
Qi, W., Tang, Z. & Yu, H. Phosphorylation- and polo-box-dependent binding of Plk1 to Bub1 is required for the kinetochore localization of Plk1. Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 3705–3716 (2006).
Wong, O.K. & Fang, G. Cdk1 phosphorylation of BubR1 controls spindle checkpoint arrest and Plk1-mediated formation of the 3F3/2 epitope. J. Cell Biol. 179, 611–617 (2007).
Archambault, V., D'Avino, P.P., Deery, M.J., Lilley, K.S. & Glover, D.M. Sequestration of Polo kinase to microtubules by phosphopriming-independent binding to Map205 is relieved by phosphorylation at a CDK site in mitosis. Genes Dev. 22, 2707–2720 (2008).
Park, J.E. et al. Polo-box domain: a versatile mediator of polo-like kinase function. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 67, 1957–1970 (2010).
Kothe, M. et al. Structure of the catalytic domain of human polo-like kinase 1. Biochemistry 46, 5960–5971 (2007).
Cheng, K.Y., Lowe, E.D., Sinclair, J., Nigg, E.A. & Johnson, L.N. The crystal structure of the human polo-like kinase-1 polo box domain and its phospho-peptide complex. EMBO J. 22, 5757–5768 (2003).
Yun, S.M. et al. Structural and functional analyses of minimal phosphopeptides targeting the polo-box domain of polo-like kinase 1. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 16, 876–882 (2009).
Elling, R.A., Fucini, R.V. & Romanowski, M.J. Structures of the wild-type and activated catalytic domains of Brachydanio rerio Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1): changes in the active-site conformation and interactions with ligands. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 64, 909–918 (2008).
Liu, F. et al. Serendipitous alkylation of a Plk1 ligand uncovers a new binding channel. Nat. Chem. Biol. 7, 595–601 (2011).
Śledź, P. et al. From crystal packing to molecular recognition: prediction and discovery of a binding site on the surface of polo-like kinase 1. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn Engl. 50, 4003–4006 (2011).
Parthasarathy, S. & Murthy, M.R.N. Analysis of temperature factor distribution in high-resolution protein structures. Protein Sci. 6, 2561–2567 (1997).
Huse, M. & Kuriyan, J. The conformational plasticity of protein kinases. Cell 109, 275–282 (2002).
Deindl, S. et al. Structural basis for the inhibition of tyrosine kinase activity of ZAP-70. Cell 129, 735–746 (2007).
Masterson, L.R. et al. Dynamics connect substrate recognition to catalysis in protein kinase A. Nat. Chem. Biol. 6, 821–828 (2010).
Sicheri, F., Moarefi, I. & Kuriyan, J. Crystal structure of the Src family tyrosine kinase Hck. Nature 385, 602–609 (1997).
Xu, W., Harrison, S.C. & Eck, M.J. Three-dimensional structure of the tyrosine kinase c-Src. Nature 385, 595–602 (1997).
Nagar, B. et al. Structural basis for the autoinhibition of c-Abl tyrosine kinase. Cell 112, 859–871 (2003).
Lietha, D. et al. Structural basis for the autoinhibition of focal adhesion kinase. Cell 129, 1177–1187 (2007).
Chao, L.H. et al. A mechanism for tunable autoinhibition in the structure of a human Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II holoenzyme. Cell 146, 732–745 (2011).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
McCoy, A.J. et al. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 40, 658–674 (2007).
Adams, P.D. et al. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 213–221 (2010).
Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2126–2132 (2004).
Murshudov, G.N., Vagin, A.A. & Dodson, E.J. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 53, 240–255 (1997).
Winn, M.D. et al. Overview of the CCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 67, 235–242 (2011).
Roskoski, R. Jr. Assays of protein kinase. Methods Enzymol. 99, 3–6 (1983).
Barker, S.C. et al. Characterization of pp60c-src tyrosine kinase activities using a continuous assay: autoactivation of the enzyme is an intermolecular autophosphorylation process. Biochemistry 34, 14843–14851 (1995).
Reindl, W., Strebhardt, K. & Berg, T. A high-throughput assay based on fluorescence polarization for inhibitors of the polo-box domain of polo-like kinase 1. Anal. Biochem. 383, 205–209 (2008).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by funds from the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology 2012CB722602 (to J.Q.), 2013CB911501 (to T.W.) and NSFC21290180 (to J.Q.), and the Shenzhen municipal Shuang Bai Project and Science and Technology innovation program CXB201005260059A (to J.Q.), ZDSY20120614144410389 and JCYJ20120614150904060 (to T.W.). We thank the staff of beamline BL17U at Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility for the technical assistance during data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.X. and J.Q. designed all experiments. J.X. and C.S. performed the experiments. T.W. contributed to crystallization, X-ray diffraction data collection and structural determination. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript. J.Q. supervised all aspects of the project and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–6 and Supplementary Table 1 (PDF 4088 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Shen, C., Wang, T. et al. Structural basis for the inhibition of Polo-like kinase 1. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20, 1047–1053 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2623
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2623
This article is cited by
-
Hornerin mediates phosphorylation of the polo-box domain in Plk1 by Chk1 to induce death in mitosis
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
The phosphorylation and dephosphorylation switch of VCP/p97 regulates the architecture of centrosome and spindle
Cell Death & Differentiation (2022)
-
A dimerization-dependent mechanism regulates enzymatic activation and nuclear entry of PLK1
Oncogene (2022)
-
Bora phosphorylation substitutes in trans for T-loop phosphorylation in Aurora A to promote mitotic entry
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Distinct surfaces on Cdc5/PLK Polo-box domain orchestrate combinatorial substrate recognition during cell division
Scientific Reports (2020)