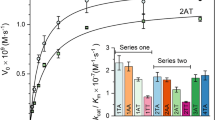
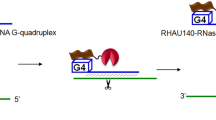
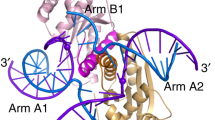
Abstract
The crystal structure of the HincII restriction endonuclease–DNA complex shows that degenerate specificity for blunt-ended cleavage at GTPyPuAC sequences arises from indirect readout of conformational preferences at the center pyrimidine-purine step. Protein-induced distortion of the DNA is accomplished by intercalation of glutamine side chains into the major groove on either side of the recognition site, generating bending by either tilt or roll at three distinct loci. The intercalated side chains propagate a concerted shift of all six target-site base pairs toward the minor groove, producing an unusual cross-strand purine stacking at the center pyrimidine–purine step. Comparison of the HincII and EcoRV cocrystal structures suggests that sequence-dependent differences in base–stacking free energies are a crucial underlying factor mediating protein recognition by indirect readout.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Rhodes, D., Schwabe, J.W.R., Chapman, L. & Fairall, L. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 351, 501–509 (1996).
Luscombe, N.M., Austin, S.E., Berman, H.M. & Thornton, J.M. Genome Biol. 1, REVIEWS001.1–REVIEWS001.37 (2000).
Schumacher, M.A., Hurlburt, B.K. & Brennan, R.G. Nature 409, 215–219 (2001).
Bareket-Samish, A., Cohen, I. & Haran, T.E. J. Mol. Biol. 299, 965–977 (2000).
Bareket-Samish, A., Cohen, I. & Haran, T.E. J. Mol. Biol. 277, 1071–1080 (1998).
Kovall, R.A. & Matthews, B.W. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 3, 578–583 (1999).
Kostrewa, D. & Winkler, F.K. Biochemistry 34, 683–696 (1995).
Martin, A.M., Sam, M.D., Reich, N.O. & Perona, J.J. Nature Struct. Biol. 6, 269–277 (1999).
Olson, W.K., Gorin, A.A., Lu, X.J., Hock, L.M. & Zhurkin, V.B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 11163–11168 (1998).
Crothers, D.M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 15163–15165 (1998).
El Hassan, M.A. & Calladine, C.R. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 355, 43–100 (1997).
Packer, M.J., Dauncey, M.P. & Hunter, C.A. J. Mol. Biol. 295, 71–83 (2000).
Dickerson, R.E. Nucleic Acids Res. 26, 1906–1926 (1998).
Kelly, T.J. Jr. & Smith, H.O. J. Mol. Biol. 51, 393–409 (1970).
Winkler, F.K. et al. EMBO J. 12, 1781–1795 (1993).
Athanasiadis, A. et al. Nature Struct. Biol. 1, 469–475 (1994).
Huai, Q. et al. EMBO J. 19, 3110–3118 (2000).
Liepinsh, E., Andersson, M., Ruysschaert, J. M. & Otting, G. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 793–795 (1997).
Ravishanker, G., Swaminathan, S., Beveridge, D.L., Lavery, R. & Sklenar, H. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 6, 669–699 (1989).
Werner, M.H., Gronenborn, A.M. & Clore, G.M. Science 271, 778–784 (1996).
Lewis, M. et al. Science 271, 1247–1254 (1996).
Tsutakawa, S.E., Jingami, H. & Morikawa, K. Cell 99, 615–623 (1999).
Ban, C. & Yang, W. EMBO J. 17, 1526–1534 (1998).
Lavery, R., Zakrzewska, K. & Sklenar, H. Comp. Phys. Com. 91, 135–158 (1995).
Calladine, C.R. J. Mol. Biol. 161, 343–352 (1982).
Dickerson, R.E. J. Mol. Biol. 166, 419–441 (1983).
Hobza, P. & Sponer, J. Chem. Rev. 99, 3247–3276 (1999).
Horton, N.C. & Perona, J.J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 5729–5734 (2000).
Horton, N.C., Dorner, L.F., Schildkraut, I. & Perona, J.J. Acta Crystallogr. D 55, 1943–1945 (1999).
Leslie, A.G. Acta Crystallogr. D 55, 1696–1702 (1999).
Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4. (SERC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington, UK; 1979).
Terwilliger, T.C. & Berendzen, J. Acta Crystallogr. D 55, 849–861 (1999).
de la Fortelle, E. & Bricogne, G. Methods Enzymol. 276, 472–494 (1999).
Cowtan, K. Joint CCP4 and ESF-EACBM Newsletter on Protein Crystallography 31, 34–38 (1994).
Sack, J.S. J. Mol. Graph. 6, 224–225 (1988).
Finzel, B.C. Acta Crystallogr. D 51, 450–457 (1995).
Brünger, A.T., Kuriyan, J. & Karplus, M. Science 235, 458–460 (1987).
Read, R. Acta Crystallogr. A 42, 140–149 (1986).
Brünger, A.T. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998).
Esnouf, R.M. Acta Crystallogr. D 55, 938–940 (1999).
Kraulis, P.J. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Merritt, E.A. & Murphy, M.E.P. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 869–873 (1994).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the NIH (to J.J.P.), and by an American Cancer Society Postdoctoral Fellowship and a NSF-POWRE award (to N.C.H.). Portions of this research were carried out at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, a national user facility operated by Stanford University on behalf of the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences. The SSRL Structural Molecular Biology Program is supported by the Department of Energy, Office of Biological and Environmental Research, and by the National Institutes of Health, National Center for Research Resouces, Biomedical Technology Program, and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horton, N., Dorner, L. & Perona, J. Sequence selectivity and degeneracy of a restriction endonuclease mediated by DNA intercalation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 9, 42–47 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb741
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb741
This article is cited by
-
A structure-based method for identifying DNA-binding proteins and their sites of DNA-interaction
Journal of Structural and Functional Genomics (2005)
-
A structure-based method for identifying DNA-binding proteins and their sites of DNA-interaction
Journal of Structural and Functional Genomics (2004)