Abstract
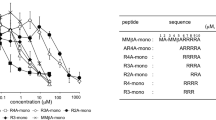
The three-dimensional structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin C2 has been determined at 2.7 Å resolution by X-ray diffraction, while the structures of enterotoxins A and E have been modelled based on their sequence homology to other staphylococcal enterotoxins. The T-cell receptor-binding sites of staphylococcal enterotoxin (SE) B and SEC2 are compared and the stereochemical interactions likely to be responsible for their differing Vβ specificities are identified. A similar comparison is made between SEA and SEE.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergdoll, M.S. Staphylococcal intoxications. In Food borne infections and intoxications.(Ed. Reimann, H. & Bryan, F.L.), 443–494 (Academic Press, New York; 1979).
Johnson, H.M., Russell, J.F. & Pontzer, C.H. Superantigens in human disease. Scientific American 92–101 (1992).
Kotzin, B.L., Leung, D.Y., Kappler, J. & Marrack, P. Superantigens and their potential role in human disease. Advances in Immunology 54, 99–166 (1993).
Kappler, J.W., Herman, A., Clements, J. & Marrack, P. Mutations defining functional regions of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J. exp. Med. 175, 387–396 (1992).
Mollick, J.A., McMasters, R.L., Grossman, D. & Rich, R.R. Localization of a site on bacterial superantigens that determine T cell receptor β-chain specificity. J. Exp. Med. 177, 283–293 (1993).
Irwin, M.J., Hudson, K.R., Fraser, J.D. & Gascoigne, N.R. Enterotoxin residues determining T-cell receptor Vβ binding specificity. Nature 359, 841–843 (1992).
Swaminathan, S., Furey, W., Pletcher, J. & Sax, M. Crystal structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin B, a superantigen. Nature 359, 801–806 (1992).
Murzin, A.G. OB (oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide binding)-fold: common structural and functional solution for non-homologous sequences. EMBO J. 12, 861–867 (1993).
Hoffmann, M. et al. Predictions of T-cell receptor and major histocompatibility complex binding sites on staphylococcal enterotoxin C1. Infection and Immunity 62, 3396–3407 (1994).
Acharya, K.R. et al. Structural basis of superantigen action inferred from crystal structure of toxic-shock syndrome toxin-1. Nature 367, 94–97 (1994).
Prasad, G.S., Earhart, C.A., Murray, D.L., Novick, R.R., Schlivert, P.M. & Ohlendorf, D.H. Structure of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. Biochemistry 32, 13761–13766 (1993).
Marrack, P. & Kappler, J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science 248, 705–711 (1990).
Jones, T.A. A graphics model building and refinement system for macromolecules. J. appl. Crystallogr. 11, 268–272 (1978).
Brünger, A.T., Kuriyan, J. & Karplus, M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science 235, 458–460 (1987).
Fraser, J.D., Urban, R.G., Strominger, J.L. & Robinson, H. Zinc regulates the function of two superantigens. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 5507–5511 (1992).
Fraser, J.D. Structural model of staphylococcal enterotoxin A interaction with MHC class II antigens. In Superantigens: A pathogen′s view of the immune system, 7. (Ed. Huber, B.T. & Palmer,E. ) 7–29 (Cold Spring Harbor Press; 1993).
Karp, D.R. & Long, E.O. Identification of HLA-DR1 b chain residues critical for binding staphylococcal enterotoxins A and E. J. exp. Med. 175, 415–424 (1992).
Jardetzky, T.S. et al. Three-dimensional structure of a human class II histocompatibilty molecule complexed with superantigen. Nature 368, 711–718 (1994).
Turner, T.N., Smith, C.L. & Bohach, G.A. Residues 20, 22 & 26 determine the subtype specificities of staphylococcal enterotoxin C1 & C2. Infection & Immunity 60, 694–697 (1992).
Swaminathan, S., Furey, W., Pletcher, J. & Sax, M., X-ray studies on two new crystal forms of staphylococcal enterotoxin C2. Acta. Crystallogr.D, in the press.
Weissman, L. in Computational Crystallography (ed. Sayre, D.) 56–63 (Clarendon Press, Oxford; 1982).
Fitzgerald, P.M.D. MERLOT: an integrated package of computer programs for the determination of crystal structures by molecular replacement. J. appl. Crystallogr. 21, 273–278 (1988).
Read, R.J., Fourier coefficients for maps using phases from partial structures with errors. Acta Crystallogr. A42, 140–149 (1986).
Wang, B.C. Resolution of phase ambiguity. Meths of Enzymol. 115, 90–106 (1985).
Furey, W. & Swaminathan, S. PHASES-95: A program package for the processing and analysis of diffraction data from macromolecules. in Macromolecular crystallography, Meths of Enzymol. (Eds Carter, C. & Sweet, B.) in the press (Academic Press, Orlando; 1995).
Engh, R.A. & Huber, R. Accurate bond and angle parameters for X-ray protein-structure refinement. Acta. Crystallogr. A47, 392–400 (1991).
Jones, C.L. & Khan, S.A. Nucleotide sequence of the enterotoxin B gene from staphylococcus aureus. J.Bacteriol. 166, 29–33 (1986).
Bohach, G.A. & Schlievert, P.M. Nucleotide sequence of the staphylococcal enterotoxin C1 gene and relatedness to other pyrogenic toxins. Mol.Gen. Genet. 209, 15–20 (1987)
Bohach, G.A. & Schlievert, P.M. Conservation of the biologically active portions of enterotoxins C1 and C2. Infection & Immunity 57, 2249–2252 (1989).
Hovde, C.J., Hackett, S.R. & Bohach, G.A. Nucleotide sequence of the staphylococcal enterotoxin C3 gene: Sequence comparison of all three type C staphylococcal enterotoxins. Mol. gen. Genet. 220, 329–333 (1990).
Carson, M. RIBBONS 2.0. J. appl Crystallogr. 24, 958–961 (1991).
Kraulis, P.J. MOLSCRIPT: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J.appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Ferrin, T.E. et al. THE MIDAS display system. J. molec. Graphics 6, 13–27 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swaminathan, S., Furey, W., Pletcher, J. et al. Residues defining Vβ specificity in staphylococcal enterotoxins. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2, 680–686 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0895-680
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0895-680
This article is cited by
-
Update on molecular diversity and multipathogenicity of staphylococcal superantigen toxins
Animal Diseases (2021)
-
Staphylococcus enterotoxin profile of China isolates and the superantigenicity of some novel enterotoxins
Archives of Microbiology (2017)
-
Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin C2 mutants: biological activity assay in vitro
Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology (2008)
-
Crystal structure of the streptococcal superantigen SPE-C: dimerization and zinc binding suggest a novel mode of interaction with MHC class II molecules
Nature Structural Biology (1997)