Abstract
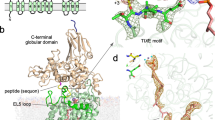
The crystal structure of E. coli maltodextrin phosphorylase co-crystallized with an oligosaccharide has been solved at 3.0 Å resolution, providing the first structure of an oligosaccharide bound at the catalytic site of an α-glucan phosphorylase. An induced fit mechanism brings together two domains across the catalytic site tunnel. A stacking interaction between the glucosyl residue and the aromatic group of a tyrosine residue at a sub-site remote (8 Å) from the catalytic site provides a key element in substrate recognition; mutation of this residue to Ala decreases the kcat/Km by 104. Extrapolation of the results to substrate binding across the site of attack by phosphorolysis indicates a likely alteration in the glycosidic torsion angles from their preferred values, an alteration that appears to be important for the catalytic mechanism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quiocho, F.A. Carbohydrate binding proteins: tertiary structures and protein sugar interactions. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 55, 287–315 (1986).
Johnson, L.N. et al. Protein-oligosaccharide interactions: lysozyme, phosphorylase, amylases. Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immunol. 139, 81–134 (1988).
Vyas, N.K. Atomic features of protein-carbohydrate interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1, 732–740 (1991).
Weiss, W.I. & Drickamer, K. Structural basis of lectin-carbohydrate recognition. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 65, 441–473 (1996).
Qian, M., Haser, R., Buisson, G., Duee, E. & Payan, F. The active centre of a mammalian α-amylase. Structure of the complex of a pancreatic α-amylase with a carbohydrate inhibitor refined to 2.2Å resolution. Biochemistry 33, 6284–6294 (1994).
Alzari, P.M., Souchon, H. & Dominguez, R. The crystal structure of endoglucanase CelA, a family 8 glycosl hydrolase from Clostridium thermocellum. Structure 4, 265–275 (1996).
Dutzler, R., Wang, Y.-F., Rizkallah, P.J., Rosenbusch, J.P. & Schirmer, T. Crystal structure of various maltooligosaccharides bound to maltoporin reveal a specific sugar translocation pathway. Structure 4, 127–134 (1996).
Nishio, M., Umezawa, Y., Hirota, M. & Takeuchi, Y., CH/π interaction significance in molecular recognition. Tetrahedron 51, 8665–8701 (1995).
Johnson, L.N., Acharya, K.R., Jordan, M.D. & McLaughlin, P.J. The refined crystal structure of the phosphorylase-heptulose 2-phosphate-oligosaccharide-AMP complex. J.Mol. Biol. 211, 645–661 (1990).
Martin, J.L., Withers, S.G. & Johnson, L.N. Comparison of the binding of glucose and glucose-1-phosphate derivatives to T state glycogen phosphorylase b. Biochemistry 29, 10745–10757 (1990).
Barford, D. & Johnson, L.N. The allosteric transition of glycogen phosphorylase. Nature 340, 609–614 (1989).
Barford, D., Hu, S.-H. & Johnson, L.N. The structural mechanism for glycogen phosphorylase control by phosphorylation and by AMP. J. Mol. Biol. 218, 233–260 (1991).
Sprang, S.R., Withers, S.G., Goldsmith, E.J., Fletterick, R.J. & Madsen, N.B. The structural basis for the association of phosphorylase b with AMP. Science 254, 1367–1371 (1991).
Kasvinsky, P., Madsen, N.B., Fletterick, R.J. & Sygusch, J. X-ray crystallographic and kinetic studies of oligosaccharide binding to phosphorylase. J. Biol. Chem. 253, 1290–1296 (1978).
Hu, H.-Y. & Gold, A.M. Kinetics of glycogen phosphorylase a with a series of semisynthetic, branched saccharides: a model for binding of polysaccharide substrates. Biochemistry 14, 2224–2230 (1975).
Hajdu, J. et al. Catalysis in the crystal: synchrotron radiation studies with glycogen phosphorylase b. EMBO J. 6, 539–546 (1987).
Raibaud, O. & Schwartz, M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Ann. Rev. Genet. 18, 207–231 (1984).
Schwartz, M. & Hofnung, M. La maltodextrine phosphorylase d'Escherichia coli. Eur. J. Biochem. 2, 132–145 (1967).
Palm, D., Goerl, R. & Burger, K.J. Evolution of catalytic and regulatory sites in phosphorylase. Nature 313, 500–502 (1985).
Becker, S., Schnackerz, K.D. & Schinzel, R. A study of binary complexes of Escherichia coli maltodextrin phosphorylase; α-D-glucose 1-methylenephosphonate as a probe of pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-substrate interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1243, 381–385 (1994).
Davies, G.D., Tolley, S.P., Henrissat, B., Hjort, C. & Schulein, M. Structures of oligosaccharide-bound forms of the endoglucanas V from Humicola insolens at 1. 9Å resolution. Biochemistry 34, 16210–16220 (1995).
Watson, K.A., Schinzel, R., Palm, D. & Johnson, L.N. The crystal structure of E. coli maltodextrin phosphorylase provides an explanation for the activity without control in this basic archetype of a phosphorylase. EMBOJ. 16, 1–14 (1997).
Takusagawa, F. & Jacobson, R.A. The crystal structure of maltose. Acta Crystallogr. D34, 213 (1978).
Drueckes, P., Boeck, B., Palm, D. & Schinzel, R. Mutational analysis of the oligosaccharide recognition site at the active site of Escherichia coli maltodextrin phosphorylase. Biochemistry 35, 6727–6734 (1996).
Barford, D. & Johnson, L.N. The molecular mechanism for the tetrameric association of glycogen phosphorylase promoted by protein phosphorylation. Protein Sci. 1, 472–493 (1992).
Meyer, F., Heilmeyer, L.M.G., Hashke, R.H. & Fischer, E.H. Control of phosphorylase in the glycogen particle. I. Isolation and characterisation of the protein glycogen complex. J.Biol. Chem. 245, 6642–6648 (1970).
Johnson, L.N. et al. Glycogen phosphorylase b. in Allosteric Enzymes (ed. Herve, G.) 81–127 (CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 1989).
Mitchell, E.P. et al. Ternary complex crystal structures of glycogen phosphorylase with a transition state analogue nojirimycin tetrazole and phosphate in the T and R states. Biochemistry 35, 7341–7355 (1996).
Rees, D.A. & Smith, P.J.C. Polysaccharide conformation. Part IX. Monte Carlo calculation of conformational energies for disaccharides and comparison with experiment. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin II, 836–840 (1975).
Mikami, B., Degano, M., Hehre, E.J. & Sacchettinin, J.C. Crystal structures of Soybean β-amylase reacted with β-maltose and maltal: active site components and their apparent roles in catalysis. Biochemistry 33, 7779–7787 (1994).
Machius, M., Vertesy, L., Huber, R. & Wiegland, G. Carbohydrate and protein-based inhibitors of porcine pancreatic α-amylase: structure analysis and comparison of their binding characteristics. J. Mol. Biol. 260, 409–421 (1996).
Barford, D. et al. Channels at the catalytic site of glycogen phosphorylase b: binding and kinetic studies with the β-glycosidase inhibitor D-gluconohydroximo-1,5-lactone N-phenylurethane. Biochemistry 27, 6733–6741 (1988).
Johnson, L.N., Hu, S.-H. & Barford, D. Catalytic mechanism of glycogen phosphorylase. Faraday Disc. 93, 131–142 (1992).
Palm, D., Klein, H.W., Schinzel, R., Buehner, M. & Helmreich, E.J.M. The role of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate in glycogen phosphorylase catalysis. Biochemistry 29, 1099–1107 (1990).
Otwinowski, Z.DENZO. in Data Collection and Processing. (eds Sawyer, L., Isaacs, N. & Bailey, S.) 56–62, SERC Laboratory, Daresbury, Warrington, UK. DL/SC1/R34, 1993).
The CCP4 (Collaborative Computational Project Number 4) suite: programmes for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D50, 760–763 (1994).
Navaza, J. AMoRe: an automated package for molecular replacement. Acta Crystallogr. A50, 157–163 (1990).
Brunger, A.T. X-PLOR: Version 3.1; a system for protein crystallography and NMR., (Yale University Press, New Haven, 1992).
Engh, R.A. & Huber, R. Accurate bond length and angle parameters for X-ray protein structure refinement. Acta Crystallogr. A47, 392–400 (1991).
Cowtan, K. DM: an automated procedure for phase improvement by density modification. Joint CCP4 and ESF-EACBM Newsletter on Protein Crystallography 31, 34–38 (1994).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.-Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A47, 110–119 (1991).
Ho, S.N., Hunt, H.D., Horton, R.M., Pullen, J.K. & Pease, L. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 77, 51–59 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Reilly, M., Watson, K., Schinzel, R. et al. Oligosaccharide substrate binding in Escherichia coli maltodextrin phosphorylase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 4, 405–412 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0597-405
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0597-405
This article is cited by
-
Thermostable alpha-glucan phosphorylases: characteristics and industrial applications
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2018)
-
A compact review on the comparison of conventional and non-conventional interactions on the structural stability of therapeutic proteins
Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational Life Sciences (2011)
-
Cloning, characterisation and comparative analysis of a starch synthase IV gene in wheat: functional and evolutionary implications
BMC Plant Biology (2008)
-
Structure of the sucrose-specific porin ScrY from Salmonella typhimurium and its complex with sucrose
Nature Structural Biology (1998)