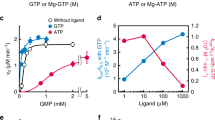
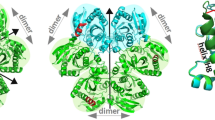
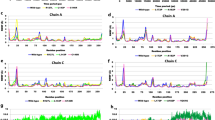
Abstract
The bifunctional enzyme dihydrofolate reductase–thymidylate synthase catalyses both the reductive methylation of 2′–deoxyuridylate and the subsequent reduction of dihydrofolate to yield 2′–deoxythymidylate and tetrahydrofolate at two spacially discrete sites situated on different protein domains. The X–ray structure of dihydrofolate reductase–thymidylate synthase from Leishmania major indicates that transfer of dihydrofolate between these sites does not occur by transient binding at both sites but rather by movement of dihydrofolate across the surface of the protein. The enzyme has an unusual surface charge distribution that could account for this channelling of dihydrofolate between active sites.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferone, R. & Roland, S. Dihydrofolate reductase:thymidylate synthase, a bifunctional polypeptide from Crithidia fasciculata. Proc. natn Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 5802–5806 (1980).
Ivanetich, K.M. & Santi, D.V. Bifunctional thymidylate synthase-dihydrofolate reductase in protozoa FASEB J. 4, 1591–1597 (1990).
Cella, R., Carbonera, D., Orsi, R., Ferri, G. & ladarola, P. Proteolytic and partial sequencing studies of the bifunctional dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase from Daucus carota Plant molec. Biol. 16, 975–982 (1991).
Lazar, G., Zhang, H. & Goodman, H.M. The origin of the bifunctional dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase isogenes of Arabidopsis thaliana Plant J. 3, 657–668 (1993).
Meek, T.D., Garvey, E.P. & Santi, D.V. Purification and characterization of the bifunctional thymidylate synthase-dihydrofolate reductase from methotrexate-resistantle Leishmania tropica Biochemistry 24, 678–686 (1985).
Kraut, J. & Matthews, D.A. in Biological Macromolecules and Assemblies, Vol. 3: Active Sites of Enzymes (eds Jurnak, F.A. & McPherson, A.) 1–71 (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1987).
Bolin, J.T., Filman, D.J., Matthews, D.A., Hamlin, R.C. & Kraut, J. Crystal structures of Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus casei dihydrofolate reductase refined at 1.7 Å resolution: II General features and binding of methotrexate J. biol. Chem. 257, 13650–13662 (1982).
Filman, D.J., Bolin, J.T., Matthews, D.A. & Kraut, J. Crystal structures of Escherichia coli and Lactobacillus casei dihydrofolate reductase refined at 1.7 Å resolution: II. Environment of bound NADPH and implications for catalysis J. biol. Chem. 257, 13663–13672 (1982).
Davies, J.F., II et al. Crystal structures of recombinant human dihydrofolate reductase complexed with folate and 5-deazafolate Biochemistry 29, 9467–9479 (1990).
Perry, K.M. et al. Plastic adaptation toward mutations in proteins: structural comparison of thymidylate synthases Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 8, 315–333 (1990).
Hardy, L.W. et al. Atomic structure of thymidylate synthase: target for rational drug design Science 235, 448–455 (1987).
Finer-Moore, J. et al. Refined structures of substrate-bound and phosphate-bound thymidylate synthase from Lactobacillus casei J. molec. Biol. 232, 1101–1116 (1993).
Matthews, D.A., Appelt, K., Oatley, S.J. & Xuong, N.H. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli thymidylate synthase containing bound 5-fluoro-2′-deoxyuridylateand 10-propargyl-5,8-dideazafolate J. molec. Biol. 214, 923–936 (1990).
Matthews, D.A. et al. Stereochemical mechanism of action for thymidylate synthase based on the X-ray structure of the covalent inhibitory ternary complex with 5-fluoro-2′-deoxyuridylate and 5, 10-methylenetetrahydrofolate J. molec. Biol. 214, 937–948 (1990).
Montfort, W.R. et al. Structure, multiple site binding, and segmental accommodation in thymidylate synthase on binding dUMP and an anti-folate Biochemistry 29, 6964–6977 (1990).
Perry, K.M., Carreras, C.W., Chang, L.C., Santi, D.V. & Stroud, R.M. Structures of thymidylate synthase with a C-terminal deletion: role of the C-terminus in alignment of 2′-deoxyuridine 5′-monophosphateand 5, 10-methylenetetrahydrofolate Biochemistry 32, 7116–7125 (1993).
Ovadi, J. Physiological significance of metabolic channeling. J. theor. Biol. 152, 1–22 (1991).
Anderson, K.S., Miles, E.W. & Johnson, K.A. Serine modulates substrate channeling in tryptophan synthase: a novel intersubunit triggering mechanism J. biol. Chem. 266, 8020–3033 (1991).
Hyde, C.C., Ahmed, S.A., Padlan, E.A., Miles, E.W. & Davies, D.R. Three-dimensional structure of the tryptophan synthase α2β2 multienzyme complex from Salmonella typhimurium J. biol. Chem. 263, 17857–17871 (1988).
Westerhoff, H.V. & Welch, G.R. Enzyme organization and the direction of metabolic flow: physicochemical considerations Curr. Topics cell. Reg. 33, 361–390 (1992).
Koppenol, W.H. & Margoliash, E. The asymmetric distribution of charges on the surface of horse cytochrome c: functional implications J. biol. Chem. 257, 4426–4437 (1982).
Ripoll, D.R., Faerman, C.H., Axelsen, P.H., Silman, I. & Sussman, J.L. An electrostatic mechanism for substrate guidance down the aromatic gorge of acetylcholinesterase Proc. natn Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 5128–5132 (1993).
Tan, R.C., Truong, T.N., McCammon, J.A. & Sussman, J.L. Acetylcholinesterase: electrostatic steering increases the rate of ligand binding Biochemistry 32, 401–403 (1993).
Getzoff, E.D. et al. Electrostatic recognition between superoxide and copper, zinc superoxide dismutase Nature 306, 287–290 (1983).
Getzoff, E.D. et al. Faster superoxide dismutase mutants designed by enhancing electrostatic guidance Nature 358, 347–351 (1992).
McGuire, J.J. & Coward, J.K. in Folates and Pterins (eds Blakley, R.L. & Benkovic, S.J.) 135–190 (Wiley Interscience, New York, 1984).
Kisliuk, R.L. & Gaumont, Y. Polyglutamyl derivatives of folate as substrates and inhibitors of thymidylate synthetase J. biol. Chem. 249, 4100–4103 (1974).
Kisliuk, R.L., Gaumont, Y., Baugh, C.M., Galivan, J.H., Maley, G.F., & Maley, F. in Chemistry and Biology of Pteridines (eds Kisliuk, R.L. & Brown, G.M.) 431–435 (Elsevier North Holland, New York, 1979).
Maley, G.F., Maley, F. & Baugh, C.M. Studies on identifying the folylpolyglutamate binding sites of Lactobacillus casei thymidylate synthetase Archs. Biochem. Biophys. 216, 551–558 (1982).
Kamb, A., Finer-Moore, J., Calvert, A.H. & Stroud, R. Structural basis for recognition of polyglutamyl folates by thymidylate synthase Biochemistry 41, 9883–9890 (1993).
Roos, D.S. Primary structure of the dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene from Toxoplasma gondii J. biol. Chem. 268, 6269–6280 (1993).
Beverley, S.M., Ellenberg, T.E., Cordingley, J.S. Primary structure of the gene encoding the bifunctional dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase of Leishmania major Proc. natn. Acad. Sci U.S.A. 83, 2584–2588 (1986).
Kunkel, T.A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 488–492 (1985).
Ghrayeb, J. et al. Secretion cloning vectors in Escherichia coli EMBO J. 3, 2437–2442 (1984).
Brunger, A.T., Kuriyan, J. & Karplus, M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics Science 235, 458–460 (1987).
Read, R. Improved Fourier coefficients for maps using phases from partial structures with errors Acta crystallogr. A42, 140–149 (1986).
Bernstein, F.C. et al. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures J. molec. Biol. 112, 535–542 (1977).
Tronrud, D.E. Conjugate-direction minimization—an improved method for the refinement of macromolecules Acta crystallogr. A48, 912–916 (1992).
Tronrud, D.E., Ten Eyck, L.F. & Matthews, B.W. An efficient general-purpose least-squares refinement program for macromolecular structures Acta crystallogr. A43, 489–501 (1987).
Jones, T.A. A graphics model building and refinement system for macromolecules J. appl. Crystallogr. 11, 268–272 (1978).
Weiner, S.J. et al. A new force field for molecular mechanical simulation of nucleic acids and proteins J. Am. chem. Soc. 106, 765–784 (1984).
Gilson, M.K., Sharp, K.A. & Honig, B.H. Calculating the electrostatic potential of molecules in solution: method and error assessment J. comput. Chem. 9, 327–335 (1987).
Jayaram, B., Sharp, K. & Honig, B. The electrostatic potential of B-DNA Biopolymers 28, 975–993 (1989).
Kraulis, P.J. MOLSCRIPT: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures J. appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knighton, D., Kan, CC., Howland, E. et al. Structure of and kinetic channelling in bifunctional dihydrofolate reductase–thymidylate synthase. Nat Struct Mol Biol 1, 186–194 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0394-186
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0394-186
This article is cited by
-
Homology modelling, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulations reveal the inhibition of Leishmania donovani dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase enzyme by Withaferin-A
BMC Research Notes (2018)
-
An artificial transport metabolon facilitates improved substrate utilization in yeast
Nature Chemical Biology (2017)
-
Substrate channelling as an approach to cascade reactions
Nature Chemistry (2016)
-
Structural basis of the substrate preference towards CMP for a thymidylate synthase MilA involved in mildiomycin biosynthesis
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Insights into the role of the junctional region of Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase
Malaria Journal (2013)