Abstract
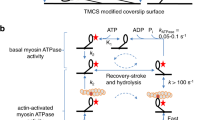
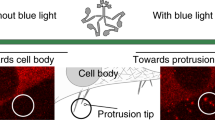
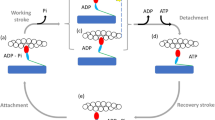
We combined protein engineering and single molecule measurements to directly record the step size of a series of myosin constructs with shortened and elongated artificial neck domains. Our results show that the step size has a clear linear dependence on the length of the neck domain and we also established that mechanical amplification in the myosin motor is based on a rotation of the neck domain relative to the actin-bound head. For all our constructs, including those with artificial necks, the magnitude of the neck rotation concurrent with the displacement step was ∼30°. The engineered change in the step size of myosin marks a significant advance in our ability to selectively modify the functional properties of molecular motors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rayment, I. et al. Science 261, 50–58 (1993).
Houdusse, A. & Cohen, C. Structure 4, 21–32 (1996).
Molloy, J.E., Burns, J.E., Kendrick-Jones, J., Tregear, R.T. & White, D.C.S. Nature 378, 209–212 (1995).
Finer, J.T., Simmons, R.M. & Spudich, J.A. Nature 368, 113–119 (1994).
Guilford, W.H. et al. Biophys. J. 72,1006–1021 (1997).
Kitamura, K., Tokunaga, M., Iwane, A.H. & Yanagida, T. Nature 397,129–134 (1999).
Anson, M., Geeves, M.A., Kurzawa, S.E. & Manstein, D.J. EMBO J. 15, 6069–6074 (1996).
Kurzawa, S.E., Manstein, D.J. & Geeves, M.A. Biochemistry 36, 317–323 (1997).
Ritchie, M.D., Geeves, M.A., Woodward, S.K.A. & Manstein, D.J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 8619–8623 (1993).
Veigel, C., Coluccio, L.M., Jontes, J.D., Sparrow, J.C., Milligan, R.A. & Molloy, J.E. Nature 398, 530–533 (1999).
Mehta, A.D., Finer, J.T. & Spudich, J.A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 7927–7931 (1997).
Tyska, M.J. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 4402–4407 (1999).
Uyeda, T.Q.P., Abramson, P.D. & Spudich, J.A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 4459–4464 (1996).
Kliche, W. et al. EMBO J. 20, 40–46 (2001).
Parry, D. A. D., Dixon, T.W. & Cohen, C. Biophys. J. 61, 858–867 (1992).
Flood, G. et al. J. Mol. Biol. 252, 227–234 (1995).
Djinovic-Caruga, K., Young, P., Gautel, M. & Saraste, M. Cell 98, 537–546 (1999).
Geeves, M.A. & Holmes, K.C. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 687–728 (1999).
Baker, J.E., Brust-Mascher, I., Ramachandran, S., LaConte, L.E.W. & Thomas, D.D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 2944–2949 (1998).
Corrie, J.E.T. et al. Nature 400, 425–430 (1999).
Hopkins, S.C., Sabido-David, C., Corrie, J.E.T., Irving, M. & Goldman, Y.E. Biophys. J. 74, 3093–3110 (1998).
Dominguez, R., Freyzon, Y., Trybus, K.M. & Cohen, C. Cell 94, 559–571 (1998).
Rayment, I. et al. Science 261, 58–65 (1993).
Manstein, D.J., Schuster, H.-P., Morandini, P. & Hunt, D.M. Gene 162, 129–134 (1995).
Furch, M., Geeves, M. A. & Manstein, D.J. Biochemistry 37, 6317–6326 (1998).
Manstein, D.J. & Hunt, D.M. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 16, 325–332 (1995).
Meyhöfer, E. & Howard, J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 574–578 (1995).
Ishijima, A. et al. Biophys. J. 70, 383–400 (1996).
Wells, A.L. et al. Nature 480, 505–508 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge technical assistance from D.M. Hunt, U. Rühl, P. Uta and S. Zimmermann and help of the Zentrale Forschungswerkstätten with the construction of equipment. We thank M.L.W. Knetsch, S. Fujita-Becker and G. Tsiavaliaris for generous help. T.Q.P. Uyeda, S. Adlerstein, B. Sodeik, J. Kull and E. Ungewickell critically reviewed different versions of the manuscript and made many helpful suggestions. This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (B.B., E.M.), Volkswagen-Stiftung (D.J.M., E.M.) and Max-Planck-Society (D.J.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruff, C., Furch, M., Brenner, B. et al. Single-molecule tracking of myosins with genetically engineered amplifier domains. Nat Struct Mol Biol 8, 226–229 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/84962
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/84962
This article is cited by
-
Synthetic biology approaches to dissecting linear motor protein function: towards the design and synthesis of artificial autonomous protein walkers
Biophysical Reviews (2020)
-
The role of mechanics in biological and bio-inspired systems
Nature Communications (2015)
-
Non-Processive Force Generation by Mammalian Axonemal Dynein In Situ on Doublet Microtubules
Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering (2013)
-
Stiffness, working stroke, and force of single-myosin molecules in skeletal muscle: elucidation of these mechanical properties via nonlinear elasticity evaluation
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2013)
-
Walking to work: roles for class V myosins as cargo transporters
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2012)