Abstract
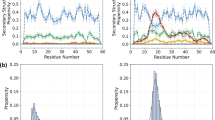
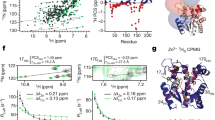
Non-native states of proteins populated at extremes of pH, or by mutation or truncation of the protein sequence, are thought to be equilibrium models for kinetic intermediates on the folding pathway. While the global physical properties of these molecules have been well characterized, analysis of their structure by NMR spectroscopy has proven difficult. Here we report the use of a new chemical cleavage technique, based on reactive oxygen species, to map the backbone fold of a truncated form of staphylococcal nuclease in a non-native state. The fragment adopts a native-like fold, however the technique also reveals regions of non-native structure.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, P.S. & Baldwin, R.L Intermediates in the folding reaction of small proteins. A. Rev. Biochem. 59, 631–660 (1990).
Matthews, C.R. Pathways of protein folding. A. Rev. Biochem. 62, 653–683 (1993).
Ptitsyn, O. in Protein Folding (ed. Creighton, T.E.) 243–300 (New York, W.H. Freeman and Company, 1992).
Buck, M., Radford, S.E. & Dobson, C.M. Amide hydrogen exchange in a highly denatured state. J. molec. Biol. 237, 247–254 (1994).
Baum, J., Dobson, C.M., Evans, P.A. & Hanley, C. Characterization of a partly folded protein by NMR methods: studies on the molten globule state of guinea pig a-lactalbumin. Biochemistry 28, 7–13 (1989).
Radford, S.E., Buck, M., Topping, K.D., Dobson, C.M. & Evans, P.A. Hydrogen exchange in native and denatured states of hen egg-white lysozyme. Proteins 14, 237–248 (1992).
Hughson, F.M., Wright, P.E. & Baldwin, R.L. Structural characterization of a partly folded apomyoglobin intermediate. Science 249, 1544–1548 (1990).
Chyan, C.L., Wormald, C., Dobson, C.M., Evans, P.A. & Baum, J. Structure and stability of a molten globule state of guinea pig a-lactalbumin: a hydrogen exchange study. Biochemistry 32, 5681–5691 (1993).
Koide, S., Dyson, H.J. & Wright, P.E. Characterization of a folding intermediate of apoplastocyanin trapped by proline isomerization. Biochemistry 32, 12299–12310 (1993).
Englander, S.W. & Mayne, L. Protein folding studied using hydrogen-exchange labeling and two-dimensional NMR. A Rev. biophys. biomol. Struct. 21, 243–265 (1992).
Baldwin, R.L. Pulsed H/D-exchange studies of folding intermediates. Curr. Opin. struct. Biol. 3, 84–91 (1993).
Jeng, M.F., Englander, S.W., Elove, G.A., Wand, A.J. & Roder, H. Structural description of acid denatured cytochrome c by hydrogen exchange and 2D NMR. Biochemistry 29, 10433–10437 (1990).
Alexandrescu, A.T., Evans, P.A., Pitkeathly, M., Baum, J. & Dobson, C.M. Structure and dynamic of the molten globule state of guinea pig a-lactalbumin: a two-dimensional NMR study. Biochemistry 32, 1707–1718 (1993).
Jennings, P.A. & Wright, P.E. Formation of a molten globule intermediate early in the kinetic folding pathway of apomyoglobin. Science 262, 892–896 (1993).
Ptitsyn, O.B. & Semisotnov, G.V. in Conformations and forces in protein folding (ed. Nail, B.T. & Dill, K.A.) 155–168 (American Association for the Advancement of Science, Washington, D. C. 1991).
Karplus, M. & Shakhnovich, E. in Protein Folding (ed. Creighton, T. E.) 127–195 (New York, W. H. Freeman and Company, 1992).
Peng, Z.Y & Kim, P.S. A protein dissection study of a molten globule. Biochemistry 33, 2136–2141 (1994).
Lattman, E.E., Fiebig, K.M. & Dill, K.A. Modeling compact denatured states of proteins. Biochemistry 33, 6158–6166 (1994)
Wagner, G., Hyberts, S.G. & Havel, T.F. NMR structure determination in solution: a critique and comparison with x-ray crystallography. A. Rev. biophys. biomolec. Struct 21, 167–198 (1992).
Dobson, CM., Hanley, C, Radford, S.E., Baum, J. & Evans, P.A. in Conformations and forces in protein folding (ed. Nall, B.T. & Dill, K.A.) 175–181 (American Association for the Advancement of Science, Washington, D.C, 1991).
Ermácora, M.R., Delfino, J.M., Cuenoud, B., Schepartz, A. & Fox, R.O. Conformation-dependent cleavage of staphylococcal nuclease with a disulfide-linked iron chelate. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 6383–6387 (1992).
Platis, I.E., Ermácora, M.R. & Fox, R.O. Oxidative polypeptide cleavage mediated by EDTA-Fe covalently linked to cysteine residues. Biochemistry 32, 12761–12767 (1993).
Ermácora, M.R., Ledman, D.W., Hellinga, H.W., Hsu, G.W. & Fox, R.O. Mapping staphylococcal nuclease conformation using an EDTA-Fe derivative attached to genetically engineered cysteine residues. Biochemistry 33, 13625–13641 (1994).
Shortle, D. & Meeker, A.K. Mutant forms of staphylococcal nuclease with altered patterns of guanidine hydrochloride and urea denaturation. Proteins 1, 81–89 (1986).
Carra, J.H. & Privalov, P.L Energetics of denaturation and m values of staphylococcal nuclease mutants. Biochemistry 34, 2034–2041 (1995).
Wynn, R., Anderson, C.L., Richards, F.M. & Fox, R.O. Interactions in nonnative and truncated forms of staphylococcal nuclease as indicated by mutational free energy changes. Protein Sci. 4, 1815–1823 (1995).
Shortle, D. & Meeker, A.K. Residual structure in large fragments of staphylococcal nuclease: effects of amino acid substitutions. Biochemistry 28, 936–944 (1989).
Flanagan, J.M., Kataoka, M., Shortle, D. & Engelman, D.M. Truncated staphylococcal nuclease is compact but disordered. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 748–752 (1992).
Griko, Y.V., Gittis, A., Lattman, E.E. & Privalov, P.L. Residual structure in a staphylococcal nuclease fragment. Is it a molten globule and is its unfolding a first-order phase transition? J. molec. Biol. 243, 93–99 (1994).
Flanagan, J.M., Kataoka, M., Fujisawa, T. & Engelman, D.M. Mutations can cause large changes in the conformation of a denatured protein Biochemistry 32, 10359–10370 (1993).
Nakano, T., Antonino, LC, Fox, R.O. & Fink, A.L Effect of proline mutation on the stability and kinetics of folding of staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry 32, 2534–2541 (1993).
Chen, H.M., Markin, V.S. & Tsong, T.Y. pH induced folding/unfolding of staphylococcal nuclease: determination of kinetic parameters by the sequential-jump method. Biochemistry 31, 1483–1491 (1992).
Evans, P.A., Kautz, R.A., Fox, R.O. & Dobson, CM. A magnetic transfer resonance study of the folding of staphylococcal nuclease. Biochemistry 28, 362–370 (1989).
Alexandrescu, A.T., Ulrich, E.L & Markley, J.L Hydrogen-1 NMR evidence for three interconverting forms of staphylococcal nuclease: effects of mutations and solution conditions on their distribution. Biochemistry 28, 204–211 (1989).
Hodel, A., Kautz, R.A., Jacobs, M.D. & Fox, R.O. Stress and strain in staphylococcal nuclease. Prot Sci. 2, 838–850 (1993).
Shortle, D. & Abeygunawardana, C. NMR analysis of the residual structure in the denatured state of an unusual mutant of staphylococcal nuclease. Structure 1, 121–134 (1993).
Alexandrescu, A.T., Gittis, A.G., Abeygunawardana, C. & Shortle, D. NMR structure of a stable OB fold sub-domain isolated from staphylococcal nuclease. J. molec. Biol. 250, 134–143 (1995).
Alexandrescu, A.T., Abeygunawardana, C. & Shortle, D. Structure and dynamic of a denatured 131 residue fragment of staphylococcal nuclease: a heteronuclear study. Biochemistry 33, 1063–1072 (1994).
Hynes, T.R., Kautz, R.A., Goodman, M.A., Gill, J.F. & Fox, R.O. Transfer of a β-turn structure to a new protein context. Nature 339, 73–76 (1989).
Penefsky, H.S. A centrifuged-column procedure for the measurement of ligand binding by beef heart F1. Meths. Enzymol. 56, 527–530 (1979).
Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 82, 70–77 (1959).
Kratzin, H.D., Wiltfang, J., Karas, M., Neuhoff, V. & Hilschmann, N. Gas-phase sequencing after electroblotting on polyvinylidene difluoride membranes assigns correct molecular weights to myoglobin molecular weight markers. Analyt. Biochem. 183, 18 (1989).
Matsudaira, P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J. biol. Chem. 262, 10035–10038 (1987).
Uversky, V.N. Use of fast protein size-exclusion liquid chromatography to study the unfolding of proteins which denature through the molten globule. Biochemistry 32, 13288–13298 (1993).
Miller, W.G. & Goebel, C.V. Dimensions of protein random coils. Biochemistry 7, 3925–3935 (1968).
Hynes, T.R. & Fox, R.O. The crystal structure of staphylococcal nuclease refined at 1.7Å resolution. Proteins 10, 92–105 (1991).
Brünger, A.T. A system for X-ray crystallography and NMR (Yale Univ. Press, New Haven, CT, 1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ermácora, M., Ledman, D. & Fox, R. Mapping the structure of a non-native state of staphylococcal nuclease. Nat Struct Mol Biol 3, 59–66 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0196-59
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0196-59