Key Points
-
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic disease that can affect almost every organ system, including the kidney
-
Diagnosis of IgG4-RD is based on characteristic pathology: a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate enriched with IgG4+ plasma cells, and storiform fibrosis
-
Serum IgG4 levels are elevated in most patients with IgG4-RD, but are neither sufficiently sensitive nor sufficiently specific to enable diagnosis of the disease
-
IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis is the most common form of IgG4-related kidney disease; the condition is characterized by unique findings on contrast-enhanced CT and the hallmark pathology of IgG4-RD
-
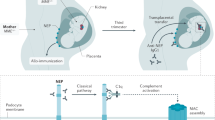
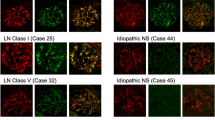
Membranous glomerulonephropathy secondary to IgG4-RD is a rare manifestation of IgG4-RD that is not associated with antibodies against the secretory phospholipase A2 receptor
-
Glucocorticoids are the standard therapy for IgG4-RD, but frequent relapses and adverse effects limit their use; B-cell depletion is an alternative approach
Abstract
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic fibroinflammatory condition that involves almost every organ system. In this Review, we summarize current knowledge of IgG4-RD and its most frequent manifestations in the kidney—IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) and membranous glomerulonephropathy (MGN). Diagnosis of IgG4-RD relies on histopathology: the typical features are a dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate and storiform fibrosis. A high percentage of plasma cells observed within lesions stain positively for IgG4. IgG4-related TIN bears the hallmark pathological findings of IgG4-RD; distinctive radiographic characteristics are also frequently observed with use of contrast-enhanced CT. MGN secondary to IgG4-RD seems to be distinct from idiopathic MGN. Humoral and cell-mediated immunity seem to have roles in the pathophysiology of IgG4-RD, but the details of these roles remain unclear. The IgG4 molecule itself is unlikely to be the primary driver of inflammation; rather, it probably downregulates the immune response. Fibrosis might be caused by activation of innate immune cells by polarized CD4+ T cells. Glucocorticoids are the standard initial treatment for IgG4-RD, but their long-term adverse effects and the high frequency of relapse and renal damage associated with use of this treatment has prompted a search for more effective options. B-cell depletion and the targeting of plasmablasts are both promising approaches.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stone, J. H., Zen, Y. & Deshpande, V. IgG4-related disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 366, 539–551 (2012).
Hamano, H. et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 344, 732–738 (2001).
Deshpande, V. et al. Subclassification of autoimmune pancreatitis: a histologic classification with clinical significance. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 35, 26–35 (2011).
Kamisawa, T. et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J. Gastroenterol. 38, 982–984 (2003).
Saeki, T. et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 78, 1016–1023 (2010).
Zen, Y. & Nakanuma, Y. IgG4-related disease: a cross-sectional study of 114 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 34, 1812–1819 (2010).
Cheuk, W. & Chan, J. K. IgG4-related sclerosing disease: a critical appraisal of an evolving clinicopathologic entity. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 17, 303–332 (2010).
Deshpande, V. et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod. Pathol. 25, 1181–1192 (2012).
Raissian, Y. et al. Diagnosis of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 22, 1343–1352 (2011).
Khosroshahi, A. et al. Brief report: spuriously low serum IgG4 concentrations caused by the prozone phenomenon in patients with IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66, 213–217 (2014).
Ryu, J. H., Horie, R., Sekiguchi, H., Peikert, T. & Yi, E. S. Spectrum of disorders associated with elevated serum IgG4 levels encountered in clinical practice. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 232960 (2012).
Carruthers, M. N., Khosroshahi, A., Augustin, T., Deshpande, V. & Stone, J. H. The diagnostic utility of serum IgG4 concentrations in IgG4-related disease. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 74, 14–18 (2015).
Wallace, Z. et al. IgG4-related disease: baseline clinical and laboratory features in 125 patients with biopsy-proven disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/art.39205
Kamisawa, T. et al. Standard steroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 58, 1504–1507 (2009).
Sah, R. P. & Chari, S. T. Serologic issues in IgG4-related systemic disease and autoimmune pancreatitis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 23, 108–113 (2011).
Nirula, A., Glaser, S. M., Kalled, S. L. & Taylor, F. R. What is IgG4? A review of the biology of a unique immunoglobulin subtype. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 23, 119–124 (2011).
Aalberse, R. C., Stapel, S. O., Schuurman, J. & Rispens, T. Immunoglobulin G4: an odd antibody. Clin. Exp. Allergy 39, 469–477 (2009).
Mattoo, H. et al. De novo oligoclonal expansions of circulating plasmablasts in active and relapsing IgG4-related disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 134, 679–687 (2014).
Zen, Y. et al. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions are increased in immunoglobin G4-related sclerosing pancreatitis and cholangitis. Hepatology 45, 1538–1546 (2007).
Okazaki, K. et al. Autoimmune-related pancreatitis is associated with autoantibodies and a Th1/Th2-type cellular immune response. Gastroenterology 118, 573–581 (2000).
Zen, Y. & Nakanuma, Y. Pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 23, 114–118 (2011).
Khosroshahi, A., Bloch, D. B., Deshpande, V. & Stone, J. H. Rituximab therapy leads to rapid decline of serum IgG4 levels and prompt clinical improvement in IgG4-related systemic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 62, 1755–1762 (2010).
Khosroshahi, A. et al. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related disease: lessons from 10 consecutive patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 91, 57–66 (2012).
Vaseemuddin, M., Schwartz, M. M., Dunea, G. & Kraus, M. A. Idiopathic hypocomplementemic immune-complex-mediated tubulointerstitial nephritis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 3, 50–58 (2007).
Baker, R. J. & Pusey, C. D. The changing profile of acute tubulointerstitial nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 19, 8–11 (2004).
Takahashi, N., Kawashima, A., Fletcher, J. G. & Chari, S. T. Renal involvement in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis: CT and MR imaging findings. Radiology 242, 791–801 (2007).
Cornell, L. D. et al. Pseudotumors due to IgG4 immune-complex tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with autoimmune pancreatocentric disease. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 31, 1586–1597 (2007).
Alkhasawneh, A. & Allan, R. W. IgG4 inflammatory pseudotumor of the kidney. Case Rep. Urol. 2012, 919087 (2012).
Yoshita, K. et al. Light-microscopic characteristics of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis: distinction from non-IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 27, 2755–2761 (2012).
Kawano, M. et al. Immunohistochemical characteristics of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis: detailed analysis of 20 Japanese cases. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 609795 (2012).
Yamaguchi, Y. et al. Characteristic tubulointerstitial nephritis in IgG4-related disease. Hum. Pathol. 43, 536–549 (2012).
Kawano, M. et al. Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 15, 615–626 (2011).
Beck, L. H. Jr et al. M-type phospholipase A2 receptor as target antigen in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 361, 11–21 (2009).
Alexander, M. P. et al. Membranous glomerulonephritis is a manifestation of IgG4-related disease. Kidney Int. 83, 455–462 (2013).
Ong, A. C. & Fine, L. G. Loss of glomerular function and tubulointerstitial fibrosis: cause or effect? Kidney Int. 45, 345–351 (1994).
Debiec, H. & Ronco, P. PLA2R autoantibodies and PLA2R glomerular deposits in membranous nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 364, 689–690 (2011).
Jennette, J. C., Iskandar, S. S. & Dalldorf, F. G. Pathologic differentiation between lupus and nonlupus membranous glomerulopathy. Kidney Int. 24, 377–385 (1983).
Davenport, A., Maciver, A. G., Hall, C. L. & MacKenzie, J. C. Do mesangial immune complex deposits affect the renal prognosis in membranous glomerulonephritis? Clin. Nephrol. 41, 271–276 (1994).
Vaglio, A., Salvarani, C. & Buzio, C. Retroperitoneal fibrosis. Lancet 367, 241–251 (2006).
van Bommel, E. F., Jansen, I., Hendriksz, T. R. & Aarnoudse, A. L. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: prospective evaluation of incidence and clinicoradiologic presentation. Medicine (Baltimore) 88, 193–201 (2009).
Kermani, T. A., Crowson, C. S., Achenbach, S. J. & Luthra, H. S. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: a retrospective review of clinical presentation, treatment, and outcomes. Mayo Clin. Proc. 86, 297–303 (2011).
Stone, J. R. Aortitis, periaortitis, and retroperitoneal fibrosis, as manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 23, 88–94 (2011).
Khosroshahi, A. et al. Rethinking Ormond's disease: “idiopathic” retroperitoneal fibrosis in the era of IgG4-related disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 92, 82–91 (2013).
Saeki, T. et al. The clinical course of patients with IgG4-related kidney disease. Kidney Int. 84, 826–833 (2013).
Khosroshahi, A. & Stone, J. H. Treatment approaches to IgG4-related systemic disease. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 23, 67–71 (2011).
Ghazale, A. et al. Immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis: clinical profile and response to therapy. Gastroenterology 134, 706–715 (2008).
Wallace, Z. S. et al. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 74, 190–195 (2015).
González, E. et al. Early steroid treatment improves the recovery of renal function in patients with drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 73, 940–946 (2008).
Mizushima, I. et al. Clinical and histological changes associated with corticosteroid therapy in IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 22, 859–870 (2012).
Austin, H. A. 3rd, Illei, G. G., Braun, M. J. & Balow, J. E. Randomized, controlled trial of prednisone, cyclophosphamide, and cyclosporine in lupus membranous nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 20, 901–911 (2009).
Sarafidis, P. A., Khosla, N. & Bakris, G. L. Antihypertensive therapy in the presence of proteinuria. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 49, 12–26 (2007).
Wheeler, D. C. & Bernard, D. B. Lipid abnormalities in the nephrotic syndrome: causes, consequences, and treatment. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 23, 331–346 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors researched data for the article, made substantial contributions to discussions of the content, wrote the article and reviewed and/or edited the manuscript before submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cortazar, F., Stone, J. IgG4-related disease and the kidney. Nat Rev Nephrol 11, 599–609 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2015.95
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2015.95
This article is cited by
-
Clinical phenotypes and prognosis of IgG4-related diseases accompanied by deteriorated kidney function: a retrospective study
Clinical Rheumatology (2024)
-
An overlap of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis and microscopic polyangiitis-associated glomerulonephritis: a case-based review
Clinical Rheumatology (2023)
-
IgG4-assoziierte Nierenerkrankungen
Die Nephrologie (2023)
-
Clinical and pathological predictors of relapse in IgG4-related disease
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2022)
-
IgG4-related diseases of the digestive tract
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2022)