Abstract
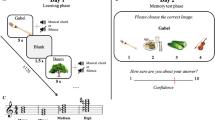
The fundamental cognitive functions of music in the brain have not been known and evolutionary reasons for musical abilities seem mysterious. A recent hypothesis suggested that a fundamental function of music has been to help mitigating cognitive dissonances. A cognitive dissonance is "a discomfort caused by holding conflicting cognitions" simultaneously; it usually leads to devaluation of conflicting knowledge. Since every concept implies some degree of contradictions to other knowledge, unmitigated cognitive dissonances could prevent evolution of cognition. Thus music might be fundamental for the evolution of cognition. Here we provide experimental confirmation of this hypothesis using a classical paradigm known to induce a cognitive dissonance and devaluation of a dissonant object; in presence of music devaluation has not occurred.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masataka, N., Perlovsky, L. Music can reduce cognitive dissonance. Nat Prec (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2012.7080.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2012.7080.1
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Cognitive interference can be mitigated by consonant music and facilitated by dissonant music
Scientific Reports (2013)
-
The Drive for Creativity and the Escape from Creativity: Neurocognitive Mechanisms
Cognitive Computation (2012)