Abstract
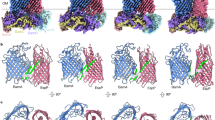
Computational and statistical analysis has formed a large component of the biophysical efforts put forth to understand protein structure and function, due to the diversity and complexity of their structure. Outer membrane proteins form a diverse and complex set of proteins. Of these, porins which allow passage of molecules across the membrane interface have been analyzed here from a biophysical and structural perspective. The objective of this study is to analyze the structural organization of porins using atomic temperature factor as a parameter. Generally atomic temperature factors of molecules from crystal structures indicate the degree of mobility or disorder seen in the crystal structure. As good crystal structures have fewer possibilities of errors so there is less chance that errors are playing roles in temperature factors. Structures of six porins (four 16 stranded beta barrel porins and two 8 stranded beta barrel porins) were taken from the PDB for the analysis based on resolution and R-factor. Programs and scripts were written for extracting the temperature factors for the beta strands, loops and turns so that the analysis could be done for different atom-types and residue-types. The residue distribution and mobility distribution was found to be characteristic of each of the porins. The mobility and residue distribution amongst the secondary structural elements were found to follow the level of homology at the sequence and structural level. The loops that had defined functional roles in structural terms were found to have lower temperature factors than the other loops. The turn regions that are thought to face the periplasmic region in the cell, showed higher temperature factors. For both the 16 stranded and the 8 stranded barrels it was found one part of the barrel (the lower wall or ‘inner’ wall comprising the trimer interface in the case of the 16 stranded barrels) was more rigid and the other half of the barrel (the higher or ‘outer’ wall) showed more mobility as seen from the temperature factors. This seems to be an intrinsic structural component of the beta barrels.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A. Structural Analysis of Outer Membrane Beta-stranded Porins using Temperature Factor. Nat Prec (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2012.7016.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2012.7016.1