Abstract
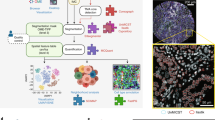
Tissue microarray (TMA) is a well-established technique that connects basic research with clinical applications that allow the validation of many pathobiologic events from gene expression dysregulation to genomic aberrations. However, conventional TMAs have several limitations such as limited representation of tissue heterogeneity, destruction of donor tissue blocks due to coring and usage of particular specimens that have limited evaluable material (tissue from thin specimens or needle biopsies). We have developed a novel method, which we termed "Spiral TMA" that generates TMAs that allow for improved representation of the donor tissue while keeping the architectural details of the donor block intact. This technology is ideal for specimens with limited tissue without the need to punch holes into the original block and therefore preserving the tissue integrity. In this report, we describe the methodology of constructing Spiral TMA and demonstrate the validation of tumor representation and tissue heterogeneity by comparing Spiral TMA to conventional TMA using immunohistochemical staining to EGFR and CK7.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uemura, T., Chirieac, L., Fukuoka, J. et al. Spiral Tissue Microarrays as Next Evolutionary Step in the High-density Tissue Microarray Technology. Nat Prec (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4831.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4831.1